| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
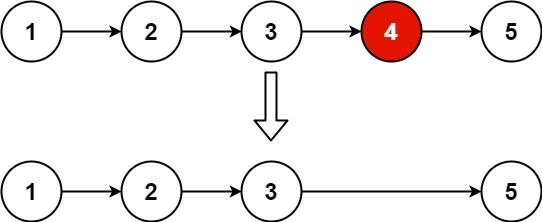
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
我们定义两个指针 fast 和 slow,初始时都指向链表的虚拟头结点 dummy。
接着 fast 指针先向前移动 fast 和 slow 指针同时向前移动,直到 fast 指针到达链表的末尾。此时 slow.next 指针指向的结点就是倒数第 n 个结点的前驱结点,将其删除即可。
时间复杂度
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(next=head)
fast = slow = dummy
for _ in range(n):
fast = fast.next
while fast.next:
slow, fast = slow.next, fast.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode fast = dummy, slow = dummy;
while (n-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* fast = dummy;
ListNode* slow = dummy;
while (n--) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{0, head}
fast, slow := dummy, dummy
for ; n > 0; n-- {
fast = fast.Next
}
for fast.Next != nil {
slow, fast = slow.Next, fast.Next
}
slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
return dummy.Next
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode | null, n: number): ListNode | null {
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let fast = dummy;
let slow = dummy;
while (n--) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, n: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy = Some(Box::new(ListNode { val: 0, next: head }));
let mut slow = &mut dummy;
let mut fast = &slow.clone();
for _ in 0..=n {
fast = &fast.as_ref().unwrap().next;
}
while fast.is_some() {
fast = &fast.as_ref().unwrap().next;
slow = &mut slow.as_mut().unwrap().next;
}
slow.as_mut().unwrap().next = slow.as_mut().unwrap().next.as_mut().unwrap().next.take();
dummy.unwrap().next
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let fast = dummy,
slow = dummy;
while (n--) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
};# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
# @param {ListNode} head
# @param {Integer} n
# @return {ListNode}
def remove_nth_from_end(head, n)
dummy = ListNode.new(0, head)
fast = slow = dummy
while n > 0
fast = fast.next
n -= 1
end
while fast.next
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
end
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
end# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode {
# public $val;
# public $next;
# public function __construct($val = 0, $next = null)
# {
# $this->val = $val;
# $this->next = $next;
# }
# }
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @param int $n
* @return ListNode
*/
function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
$dummy = new ListNode(0);
$dummy->next = $head;
$first = $dummy;
$second = $dummy;
for ($i = 0; $i <= $n; $i++) {
$second = $second->next;
}
while ($second != null) {
$first = $first->next;
$second = $second->next;
}
$first->next = $first->next->next;
return $dummy->next;
}
}