| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle. You may return the answer in any order.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
Example 1:
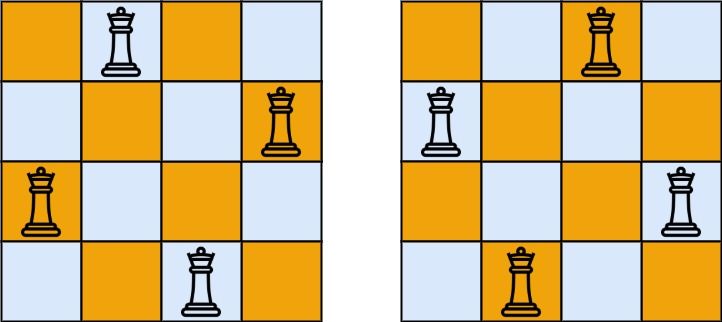
Input: n = 4 Output: [[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]] Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above
Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: [["Q"]]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 9
We define three arrays '.'.
Next, we define a function
In
Otherwise, we enumerate each column 'Q', and set '.' and set
In the main function, we call
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def solveNQueens(self, n: int) -> List[List[str]]:
def dfs(i: int):
if i == n:
ans.append(["".join(row) for row in g])
return
for j in range(n):
if col[j] + dg[i + j] + udg[n - i + j] == 0:
g[i][j] = "Q"
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 1
dfs(i + 1)
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 0
g[i][j] = "."
ans = []
g = [["."] * n for _ in range(n)]
col = [0] * n
dg = [0] * (n << 1)
udg = [0] * (n << 1)
dfs(0)
return ansclass Solution {
private List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private int[] col;
private int[] dg;
private int[] udg;
private String[][] g;
private int n;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
this.n = n;
col = new int[n];
dg = new int[n << 1];
udg = new int[n << 1];
g = new String[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(g[i], ".");
}
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
if (i == n) {
List<String> t = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
t.add(String.join("", g[j]));
}
ans.add(t);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (col[j] + dg[i + j] + udg[n - i + j] == 0) {
g[i][j] = "Q";
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 1;
dfs(i + 1);
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 0;
g[i][j] = ".";
}
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
vector<int> col(n);
vector<int> dg(n << 1);
vector<int> udg(n << 1);
vector<vector<string>> ans;
vector<string> t(n, string(n, '.'));
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) -> void {
if (i == n) {
ans.push_back(t);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (col[j] + dg[i + j] + udg[n - i + j] == 0) {
t[i][j] = 'Q';
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 1;
dfs(i + 1);
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 0;
t[i][j] = '.';
}
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};func solveNQueens(n int) (ans [][]string) {
col := make([]int, n)
dg := make([]int, n<<1)
udg := make([]int, n<<1)
t := make([][]byte, n)
for i := range t {
t[i] = make([]byte, n)
for j := range t[i] {
t[i][j] = '.'
}
}
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(i int) {
if i == n {
tmp := make([]string, n)
for i := range tmp {
tmp[i] = string(t[i])
}
ans = append(ans, tmp)
return
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if col[j]+dg[i+j]+udg[n-i+j] == 0 {
col[j], dg[i+j], udg[n-i+j] = 1, 1, 1
t[i][j] = 'Q'
dfs(i + 1)
t[i][j] = '.'
col[j], dg[i+j], udg[n-i+j] = 0, 0, 0
}
}
}
dfs(0)
return
}function solveNQueens(n: number): string[][] {
const col: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
const dg: number[] = Array(n << 1).fill(0);
const udg: number[] = Array(n << 1).fill(0);
const ans: string[][] = [];
const t: string[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill('.'));
const dfs = (i: number) => {
if (i === n) {
ans.push(t.map(x => x.join('')));
return;
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (col[j] + dg[i + j] + udg[n - i + j] === 0) {
t[i][j] = 'Q';
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 1;
dfs(i + 1);
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 0;
t[i][j] = '.';
}
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}public class Solution {
private int n;
private int[] col;
private int[] dg;
private int[] udg;
private IList<IList<string>> ans = new List<IList<string>>();
private IList<string> t = new List<string>();
public IList<IList<string>> SolveNQueens(int n) {
this.n = n;
col = new int[n];
dg = new int[n << 1];
udg = new int[n << 1];
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
if (i == n) {
ans.Add(new List<string>(t));
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (col[j] + dg[i + j] + udg[n - i + j] == 0) {
char[] row = new char[n];
Array.Fill(row, '.');
row[j] = 'Q';
t.Add(new string(row));
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 1;
dfs(i + 1);
col[j] = dg[i + j] = udg[n - i + j] = 0;
t.RemoveAt(t.Count - 1);
}
}
}
}