| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
A valid BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
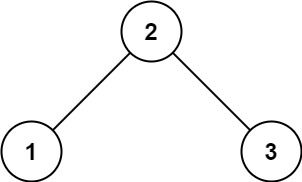
Example 1:
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: true
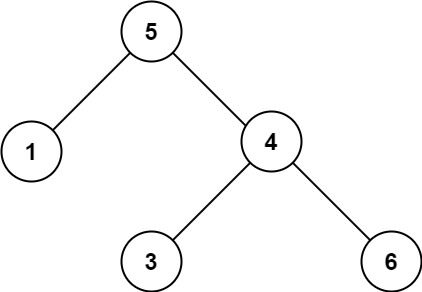
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] Output: false Explanation: The root node's value is 5 but its right child's value is 4.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
We can perform a recursive in-order traversal on the binary tree. If the result of the traversal is strictly ascending, then this tree is a binary search tree.
Therefore, we use a variable prev to save the last node we traversed. Initially, prev = -∞. Then we recursively traverse the left subtree. If the left subtree is not a binary search tree, we directly return False. Otherwise, we check whether the value of the current node is greater than prev. If not, we return False. Otherwise, we update prev to the value of the current node, and then recursively traverse the right subtree.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if root is None:
return True
if not dfs(root.left):
return False
nonlocal prev
if prev >= root.val:
return False
prev = root.val
return dfs(root.right)
prev = -inf
return dfs(root)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode prev;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root);
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (!dfs(root.left)) {
return false;
}
if (prev != null && prev.val >= root.val) {
return false;
}
prev = root;
return dfs(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
function<bool(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
if (!dfs(root->left)) {
return false;
}
if (prev && prev->val >= root->val) {
return false;
}
prev = root;
return dfs(root->right);
};
return dfs(root);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isValidBST(root *TreeNode) bool {
var prev *TreeNode
var dfs func(*TreeNode) bool
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
if !dfs(root.Left) {
return false
}
if prev != nil && prev.Val >= root.Val {
return false
}
prev = root
return dfs(root.Right)
}
return dfs(root)
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function isValidBST(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
let prev: TreeNode | null = null;
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): boolean => {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
if (!dfs(root.left)) {
return false;
}
if (prev && prev.val >= root.val) {
return false;
}
prev = root;
return dfs(root.right);
};
return dfs(root);
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, prev: &mut Option<i32>) -> bool {
if root.is_none() {
return true;
}
let root = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
if !Self::dfs(&root.left, prev) {
return false;
}
if prev.is_some() && prev.unwrap() >= root.val {
return false;
}
*prev = Some(root.val);
Self::dfs(&root.right, prev)
}
pub fn is_valid_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
Self::dfs(&root, &mut None)
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValidBST = function (root) {
let prev = null;
const dfs = root => {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
if (!dfs(root.left)) {
return false;
}
if (prev && prev.val >= root.val) {
return false;
}
prev = root;
return dfs(root.right);
};
return dfs(root);
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private TreeNode prev;
public bool IsValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root);
}
private bool dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (!dfs(root.left)) {
return false;
}
if (prev != null && prev.val >= root.val) {
return false;
}
prev = root;
return dfs(root.right);
}
}