| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
Example 1:
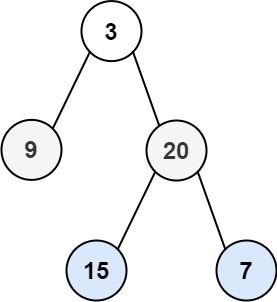
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [[1]]
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
We can use the BFS method to solve this problem. First, enqueue the root node, then continuously perform the following operations until the queue is empty:
- Traverse all nodes in the current queue, store their values in a temporary array
$t$ , and then enqueue their child nodes. - Store the temporary array
$t$ in the answer array.
Finally, return the answer array.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = []
if root is None:
return ans
q = deque([root])
while q:
t = []
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft()
t.append(node.val)
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
ans.append(t)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
t.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
ans.add(t);
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
while (!q.empty()) {
vector<int> t;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
auto node = q.front();
q.pop();
t.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
ans.push_back(t);
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) (ans [][]int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
t := []int{}
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
t = append(t, node.Val)
if node.Left != nil {
q = append(q, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q = append(q, node.Right)
}
}
ans = append(ans, t)
}
return
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function levelOrder(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = [];
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
const q: TreeNode[] = [root];
while (q.length) {
const t: number[] = [];
const qq: TreeNode[] = [];
for (const { val, left, right } of q) {
t.push(val);
left && qq.push(left);
right && qq.push(right);
}
ans.push(t);
q.splice(0, q.length, ...qq);
}
return ans;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::VecDeque;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn level_order(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut ans = Vec::new();
if let Some(root_node) = root {
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back(root_node);
while !q.is_empty() {
let mut t = Vec::new();
for _ in 0..q.len() {
if let Some(node) = q.pop_front() {
let node_ref = node.borrow();
t.push(node_ref.val);
if let Some(ref left) = node_ref.left {
q.push_back(Rc::clone(left));
}
if let Some(ref right) = node_ref.right {
q.push_back(Rc::clone(right));
}
}
}
ans.push(t);
}
}
ans
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function (root) {
const ans = [];
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
const q = [root];
while (q.length) {
const t = [];
const qq = [];
for (const { val, left, right } of q) {
t.push(val);
left && qq.push(left);
right && qq.push(right);
}
ans.push(t);
q.splice(0, q.length, ...qq);
}
return ans;
};