| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
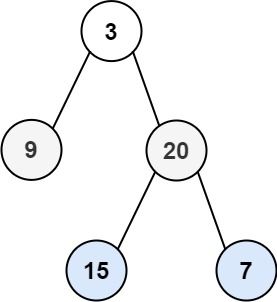
Given the root of a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [[1]]
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
To implement zigzag level order traversal, we need to add a flag left on the basis of level order traversal. This flag is used to mark the order of the node values in the current level. If left is true, the node values of the current level are stored in the result array ans from left to right. If left is false, the node values of the current level are stored in the result array ans from right to left.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def zigzagLevelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = []
if root is None:
return ans
q = deque([root])
ans = []
left = 1
while q:
t = []
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft()
t.append(node.val)
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
ans.append(t if left else t[::-1])
left ^= 1
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
boolean left = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
t.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
if (!left) {
Collections.reverse(t);
}
ans.add(t);
left = !left;
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
int left = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
vector<int> t;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
auto node = q.front();
q.pop();
t.emplace_back(node->val);
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
if (!left) {
reverse(t.begin(), t.end());
}
ans.emplace_back(t);
left ^= 1;
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func zigzagLevelOrder(root *TreeNode) (ans [][]int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
q := []*TreeNode{root}
left := true
for len(q) > 0 {
t := []int{}
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
t = append(t, node.Val)
if node.Left != nil {
q = append(q, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q = append(q, node.Right)
}
}
if !left {
for i, j := 0, len(t)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
t[i], t[j] = t[j], t[i]
}
}
ans = append(ans, t)
left = !left
}
return
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function zigzagLevelOrder(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = [];
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
const q: TreeNode[] = [root];
let left: number = 1;
while (q.length) {
const t: number[] = [];
const qq: TreeNode[] = [];
for (const { val, left, right } of q) {
t.push(val);
left && qq.push(left);
right && qq.push(right);
}
ans.push(left ? t : t.reverse());
q.splice(0, q.length, ...qq);
left ^= 1;
}
return ans;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::VecDeque;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn zigzag_level_order(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut ans = Vec::new();
let mut left = true;
if let Some(root_node) = root {
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back(root_node);
while !q.is_empty() {
let mut t = Vec::new();
for _ in 0..q.len() {
if let Some(node) = q.pop_front() {
let node_ref = node.borrow();
t.push(node_ref.val);
if let Some(ref left) = node_ref.left {
q.push_back(Rc::clone(left));
}
if let Some(ref right) = node_ref.right {
q.push_back(Rc::clone(right));
}
}
}
if !left {
t.reverse();
}
ans.push(t);
left = !left;
}
}
ans
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var zigzagLevelOrder = function (root) {
const ans = [];
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
const q = [root];
let left = 1;
while (q.length) {
const t = [];
const qq = [];
for (const { val, left, right } of q) {
t.push(val);
left && qq.push(left);
right && qq.push(right);
}
ans.push(left ? t : t.reverse());
q.splice(0, q.length, ...qq);
left ^= 1;
}
return ans;
};