| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
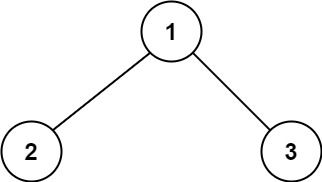
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: 6 Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
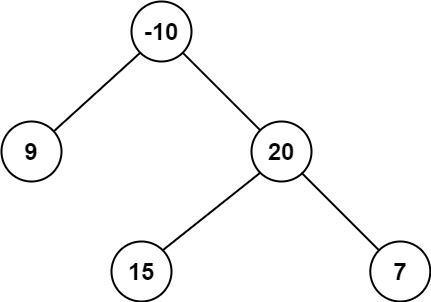
Example 2:
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 42 Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
When thinking about the classic routine of recursion problems in binary trees, we consider:
- Termination condition (when to terminate recursion)
- Recursively process the left and right subtrees
- Merge the calculation results of the left and right subtrees
For this problem, we design a function
The execution logic of the function
If
Otherwise, we recursively calculate the maximum path sum of the left and right subtrees of
Then, we update the answer with
In the main function, we call
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
left = max(0, dfs(root.left))
right = max(0, dfs(root.right))
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans, root.val + left + right)
return root.val + max(left, right)
ans = -inf
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans = -1001;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = Math.max(0, dfs(root.left));
int right = Math.max(0, dfs(root.right));
ans = Math.max(ans, root.val + left + right);
return root.val + Math.max(left, right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = -1001;
function<int(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int left = max(0, dfs(root->left));
int right = max(0, dfs(root->right));
ans = max(ans, left + right + root->val);
return root->val + max(left, right);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := -1001
var dfs func(*TreeNode) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
left := max(0, dfs(root.Left))
right := max(0, dfs(root.Right))
ans = max(ans, left+right+root.Val)
return max(left, right) + root.Val
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function maxPathSum(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let ans = -1001;
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): number => {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
const left = Math.max(0, dfs(root.left));
const right = Math.max(0, dfs(root.right));
ans = Math.max(ans, left + right + root.val);
return Math.max(left, right) + root.val;
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, res: &mut i32) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
let left = (0).max(Self::dfs(&node.left, res));
let right = (0).max(Self::dfs(&node.right, res));
*res = (node.val + left + right).max(*res);
node.val + left.max(right)
}
pub fn max_path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut res = -1000;
Self::dfs(&root, &mut res);
res
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxPathSum = function (root) {
let ans = -1001;
const dfs = root => {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
const left = Math.max(0, dfs(root.left));
const right = Math.max(0, dfs(root.right));
ans = Math.max(ans, left + right + root.val);
return Math.max(left, right) + root.val;
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private int ans = -1001;
public int MaxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = Math.Max(0, dfs(root.left));
int right = Math.Max(0, dfs(root.right));
ans = Math.Max(ans, left + right + root.val);
return root.val + Math.Max(left, right);
}
}