| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
|
Given the root of a binary search tree and a target value, return the value in the BST that is closest to the target. If there are multiple answers, print the smallest.
Example 1:
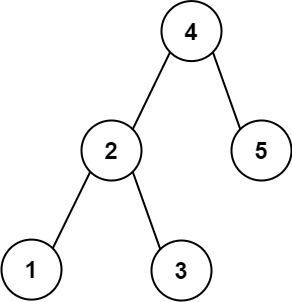
Input: root = [4,2,5,1,3], target = 3.714286 Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 4.428571 Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 109-109 <= target <= 109
We define a recursive function dfs(node), which starts from the current node node and finds the node closest to the target value target. We can update the answer by comparing the absolute difference between the current node's value and the target value. If the target value is less than the current node's value, we recursively search the left subtree; otherwise, we recursively search the right subtree.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def closestValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], target: float) -> int:
def dfs(node: Optional[TreeNode]):
if node is None:
return
nxt = abs(target - node.val)
nonlocal ans, diff
if nxt < diff or (nxt == diff and node.val < ans):
diff = nxt
ans = node.val
node = node.left if target < node.val else node.right
dfs(node)
ans = 0
diff = inf
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans;
private double target;
private double diff = Double.MAX_VALUE;
public int closestValue(TreeNode root, double target) {
this.target = target;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
double nxt = Math.abs(node.val - target);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt == diff && node.val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = node.val;
}
node = target < node.val ? node.left : node.right;
dfs(node);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int closestValue(TreeNode* root, double target) {
int ans = root->val;
double diff = INT_MAX;
function<void(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
double nxt = abs(node->val - target);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt == diff && node->val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = node->val;
}
node = target < node->val ? node->left : node->right;
dfs(node);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func closestValue(root *TreeNode, target float64) int {
ans := root.Val
diff := math.MaxFloat64
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
nxt := math.Abs(float64(node.Val) - target)
if nxt < diff || (nxt == diff && node.Val < ans) {
diff = nxt
ans = node.Val
}
if target < float64(node.Val) {
dfs(node.Left)
} else {
dfs(node.Right)
}
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function closestValue(root: TreeNode | null, target: number): number {
let ans = 0;
let diff = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
const dfs = (node: TreeNode | null): void => {
if (!node) {
return;
}
const nxt = Math.abs(target - node.val);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt === diff && node.val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = node.val;
}
node = target < node.val ? node.left : node.right;
dfs(node);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} target
* @return {number}
*/
var closestValue = function (root, target) {
let ans = 0;
let diff = Infinity;
const dfs = node => {
if (!node) {
return;
}
const nxt = Math.abs(target - node.val);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt === diff && node.val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = node.val;
}
node = target < node.val ? node.left : node.right;
dfs(node);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
};We can rewrite the recursive function in an iterative form, using a loop to simulate the recursive process. We start from the root node and check whether the absolute difference between the current node's value and the target value is less than the current minimum difference. If it is, we update the answer. Then, based on the size relationship between the target value and the current node's value, we decide to move to the left subtree or the right subtree. The loop ends when we traverse to a null node.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def closestValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], target: float) -> int:
ans, diff = root.val, inf
while root:
nxt = abs(root.val - target)
if nxt < diff or (nxt == diff and root.val < ans):
diff = nxt
ans = root.val
root = root.left if target < root.val else root.right
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int closestValue(TreeNode root, double target) {
int ans = root.val;
double diff = Double.MAX_VALUE;
while (root != null) {
double nxt = Math.abs(root.val - target);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt == diff && root.val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = root.val;
}
root = target < root.val ? root.left : root.right;
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int closestValue(TreeNode* root, double target) {
int ans = root->val;
double diff = INT_MAX;
while (root) {
double nxt = abs(root->val - target);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt == diff && root->val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = root->val;
}
root = target < root->val ? root->left : root->right;
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func closestValue(root *TreeNode, target float64) int {
ans := root.Val
diff := math.MaxFloat64
for root != nil {
nxt := math.Abs(float64(root.Val) - target)
if nxt < diff || (nxt == diff && root.Val < ans) {
diff = nxt
ans = root.Val
}
if float64(root.Val) > target {
root = root.Left
} else {
root = root.Right
}
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function closestValue(root: TreeNode | null, target: number): number {
let ans = 0;
let diff = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
while (root) {
const nxt = Math.abs(root.val - target);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt === diff && root.val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = root.val;
}
root = target < root.val ? root.left : root.right;
}
return ans;
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} target
* @return {number}
*/
var closestValue = function (root, target) {
let ans = root.val;
let diff = Infinity;
while (root) {
const nxt = Math.abs(root.val - target);
if (nxt < diff || (nxt === diff && root.val < ans)) {
diff = nxt;
ans = root.val;
}
root = target < root.val ? root.left : root.right;
}
return ans;
};