| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给你一个整数嵌套列表 nestedList ,每一个元素要么是一个整数,要么是一个列表(这个列表中的每个元素也同样是整数或列表)。
整数的 深度 取决于它位于多少个列表内部。例如,嵌套列表 [1,[2,2],[[3],2],1] 的每个整数的值都等于它的 深度 。令 maxDepth 是任意整数的 最大深度 。
整数的 权重 为 maxDepth - (整数的深度) + 1 。
将 nestedList 列表中每个整数先乘权重再求和,返回该加权和。
示例 1:
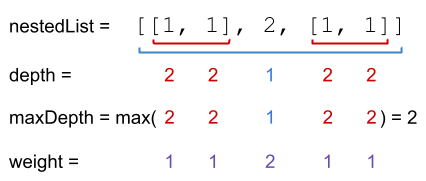
输入:nestedList = [[1,1],2,[1,1]] 输出:8 解释:4 个 1 在深度为 1 的位置, 一个 2 在深度为 2 的位置。 1*1 + 1*1 + 2*2 + 1*1 + 1*1 = 8
示例 2:
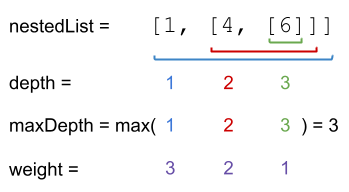
输入:nestedList = [1,[4,[6]]] 输出:17 解释:一个 1 在深度为 3 的位置, 一个 4 在深度为 2 的位置,一个 6 在深度为 1 的位置。 1*3 + 4*2 + 6*1 = 17
提示:
1 <= nestedList.length <= 50- 嵌套列表中整数的值在范围
[-100, 100] - 任意整数的最大 深度 小于等于
50
我们不妨假设整数分别为
即:
如果我们记所有整数的和为
因此,我们设计一个函数
- 我们先更新
$\textit{maxDepth} = \max(\textit{maxDepth}, d)$ ; - 如果
$x$ 是一个整数,那么我们更新$s = s + x$ ,$ws = ws + x \times d$ ; - 否则,我们递归地遍历
$x$ 的每一个元素$y$ ,调用$dfs(y, d + 1)$ 。
我们遍历整个列表,对于每一个元素
时间复杂度
# """
# This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
# You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
# """
# class NestedInteger:
# def __init__(self, value=None):
# """
# If value is not specified, initializes an empty list.
# Otherwise initializes a single integer equal to value.
# """
#
# def isInteger(self):
# """
# @return True if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
# :rtype bool
# """
#
# def add(self, elem):
# """
# Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer elem to it.
# :rtype void
# """
#
# def setInteger(self, value):
# """
# Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer equal to value.
# :rtype void
# """
#
# def getInteger(self):
# """
# @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
# Return None if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
# :rtype int
# """
#
# def getList(self):
# """
# @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
# Return None if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
# :rtype List[NestedInteger]
# """
class Solution:
def depthSumInverse(self, nestedList: List[NestedInteger]) -> int:
def dfs(x, d):
nonlocal maxDepth, s, ws
maxDepth = max(maxDepth, d)
if x.isInteger():
s += x.getInteger()
ws += x.getInteger() * d
else:
for y in x.getList():
dfs(y, d + 1)
maxDepth = s = ws = 0
for x in nestedList:
dfs(x, 1)
return (maxDepth + 1) * s - ws/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* public interface NestedInteger {
* // Constructor initializes an empty nested list.
* public NestedInteger();
*
* // Constructor initializes a single integer.
* public NestedInteger(int value);
*
* // @return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* public boolean isInteger();
*
* // @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* public Integer getInteger();
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer.
* public void setInteger(int value);
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer to it.
* public void add(NestedInteger ni);
*
* // @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // Return empty list if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* public List<NestedInteger> getList();
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int maxDepth;
private int ws;
private int s;
public int depthSumInverse(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) {
for (NestedInteger x : nestedList) {
dfs(x, 1);
}
return (maxDepth + 1) * s - ws;
}
private void dfs(NestedInteger x, int d) {
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, d);
if (x.isInteger()) {
ws += x.getInteger() * d;
s += x.getInteger();
} else {
for (NestedInteger y : x.getList()) {
dfs(y, d + 1);
}
}
}
}/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Constructor initializes an empty nested list.
* NestedInteger();
*
* // Constructor initializes a single integer.
* NestedInteger(int value);
*
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer.
* void setInteger(int value);
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer to it.
* void add(const NestedInteger &ni);
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int depthSumInverse(vector<NestedInteger>& nestedList) {
int maxDepth = 0, ws = 0, s = 0;
function<void(NestedInteger&, int)> dfs = [&](NestedInteger& x, int d) {
maxDepth = max(maxDepth, d);
if (x.isInteger()) {
ws += x.getInteger() * d;
s += x.getInteger();
} else {
for (auto& y : x.getList()) {
dfs(y, d + 1);
}
}
};
for (auto& x : nestedList) {
dfs(x, 1);
}
return (maxDepth + 1) * s - ws;
}
};/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* type NestedInteger struct {
* }
*
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* func (n NestedInteger) IsInteger() bool {}
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* // So before calling this method, you should have a check
* func (n NestedInteger) GetInteger() int {}
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer.
* func (n *NestedInteger) SetInteger(value int) {}
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer to it.
* func (n *NestedInteger) Add(elem NestedInteger) {}
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The list length is zero if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* // You can access NestedInteger's List element directly if you want to modify it
* func (n NestedInteger) GetList() []*NestedInteger {}
*/
func depthSumInverse(nestedList []*NestedInteger) int {
var maxDepth, ws, s int
var dfs func(*NestedInteger, int)
dfs = func(x *NestedInteger, d int) {
maxDepth = max(maxDepth, d)
if x.IsInteger() {
ws += x.GetInteger() * d
s += x.GetInteger()
} else {
for _, y := range x.GetList() {
dfs(y, d+1)
}
}
}
for _, x := range nestedList {
dfs(x, 1)
}
return (maxDepth+1)*s - ws
}/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* If value is provided, then it holds a single integer
* Otherwise it holds an empty nested list
* constructor(value?: number) {
* ...
* };
*
* Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* isInteger(): boolean {
* ...
* };
*
* Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* getInteger(): number | null {
* ...
* };
*
* Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer equal to value.
* setInteger(value: number) {
* ...
* };
*
* Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer elem to it.
* add(elem: NestedInteger) {
* ...
* };
*
* Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds,
* or an empty list if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* getList(): NestedInteger[] {
* ...
* };
* };
*/
function depthSumInverse(nestedList: NestedInteger[]): number {
let [maxDepth, ws, s] = [0, 0, 0];
const dfs = (x: NestedInteger, d: number) => {
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, d);
if (x.isInteger()) {
ws += x.getInteger() * d;
s += x.getInteger();
} else {
for (const y of x.getList()) {
dfs(y, d + 1);
}
}
};
for (const x of nestedList) {
dfs(x, 1);
}
return (maxDepth + 1) * s - ws;
}/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* function NestedInteger() {
*
* Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* @return {boolean}
* this.isInteger = function() {
* ...
* };
*
* Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* @return {integer}
* this.getInteger = function() {
* ...
* };
*
* Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer equal to value.
* @return {void}
* this.setInteger = function(value) {
* ...
* };
*
* Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer elem to it.
* @return {void}
* this.add = function(elem) {
* ...
* };
*
* Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* Return null if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* @return {NestedInteger[]}
* this.getList = function() {
* ...
* };
* };
*/
/**
* @param {NestedInteger[]} nestedList
* @return {number}
*/
var depthSumInverse = function (nestedList) {
let [maxDepth, ws, s] = [0, 0, 0];
const dfs = (x, d) => {
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, d);
if (x.isInteger()) {
ws += x.getInteger() * d;
s += x.getInteger();
} else {
for (const y of x.getList()) {
dfs(y, d + 1);
}
}
};
for (const x of nestedList) {
dfs(x, 1);
}
return (maxDepth + 1) * s - ws;
};