| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
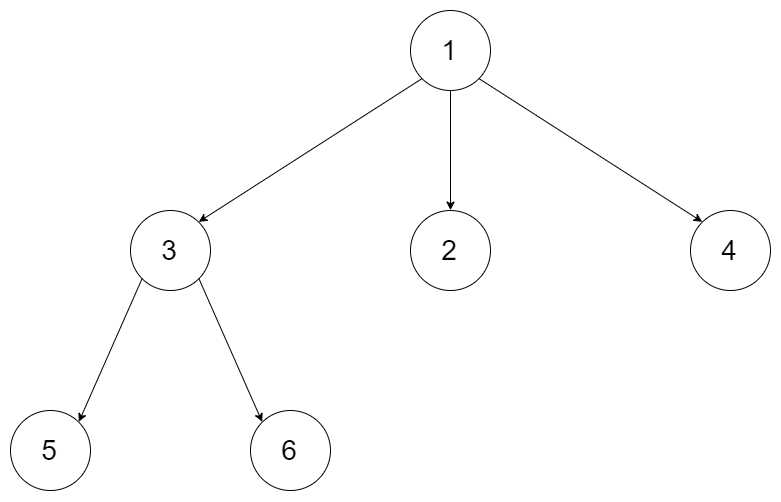
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
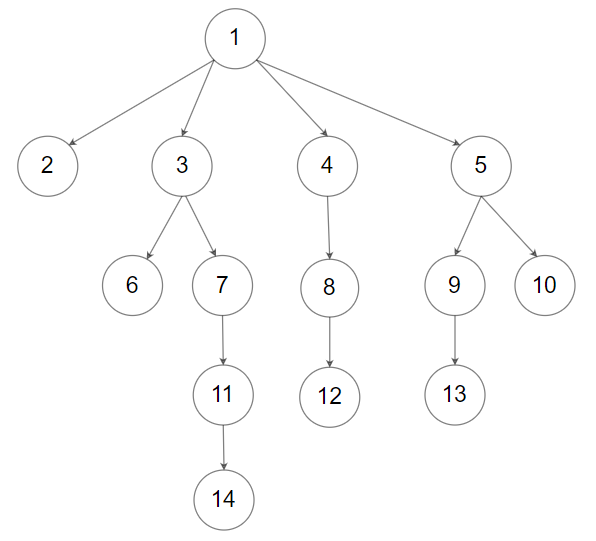
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
Constraints:
- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to
1000 - The total number of nodes is between
[0, 104]
First, we check if the root node is null. If it is, we return an empty list directly.
Otherwise, we create a queue
When the queue is not empty, we loop through the following operations:
- Create an empty list
$t$ to store the values of the current level nodes. - For each node in the queue, add its value to
$t$ and add its child nodes to the queue. - Add
$t$ to the result list$ans$ .
Finally, return the result list
The time complexity is
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]:
ans = []
if root is None:
return ans
q = deque([root])
while q:
t = []
for _ in range(len(q)):
root = q.popleft()
t.append(root.val)
q.extend(root.children)
ans.append(t)
return ans/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<Node> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
root = q.poll();
t.add(root.val);
q.addAll(root.children);
}
ans.add(t);
}
return ans;
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
queue<Node*> q{{root}};
while (!q.empty()) {
vector<int> t;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
t.push_back(root->val);
for (auto& child : root->children) {
q.push(child);
}
}
ans.push_back(t);
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func levelOrder(root *Node) (ans [][]int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
q := []*Node{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
var t []int
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
root = q[0]
q = q[1:]
t = append(t, root.Val)
for _, child := range root.Children {
q = append(q, child)
}
}
ans = append(ans, t)
}
return
}/**
* Definition for node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* children: Node[]
* constructor(val?: number) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.children = []
* }
* }
*/
function levelOrder(root: Node | null): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = [];
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
const q: Node[] = [root];
while (q.length) {
const qq: Node[] = [];
const t: number[] = [];
for (const { val, children } of q) {
qq.push(...children);
t.push(val);
}
ans.push(t);
q.splice(0, q.length, ...qq);
}
return ans;
}We can use the Depth-First Search method to traverse the entire tree.
We define a helper function
In the
Otherwise, we check if the length of
Next, we traverse all child nodes of
In the main function, we call
The time complexity is
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(root, i):
if root is None:
return
if len(ans) <= i:
ans.append([])
ans[i].append(root.val)
for child in root.children:
dfs(child, i + 1)
ans = []
dfs(root, 0)
return ans/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(Node root, int i) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (ans.size() <= i) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
ans.get(i++).add(root.val);
for (Node child : root.children) {
dfs(child, i);
}
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
function<void(Node*, int i)> dfs = [&](Node* root, int i) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (ans.size() <= i) {
ans.push_back({});
}
ans[i++].push_back(root->val);
for (auto& child : root->children) {
dfs(child, i);
}
};
dfs(root, 0);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func levelOrder(root *Node) (ans [][]int) {
var dfs func(root *Node, i int)
dfs = func(root *Node, i int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if len(ans) <= i {
ans = append(ans, []int{})
}
ans[i] = append(ans[i], root.Val)
for _, child := range root.Children {
dfs(child, i+1)
}
}
dfs(root, 0)
return
}/**
* Definition for node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* children: Node[]
* constructor(val?: number) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.children = []
* }
* }
*/
function levelOrder(root: Node | null): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = [];
const dfs = (root: Node | null, i: number) => {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
if (ans.length <= i) {
ans.push([]);
}
const { val, children } = root;
ans[i++].push(val);
children.forEach(node => dfs(node, i));
};
dfs(root, 0);
return ans;
}