| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
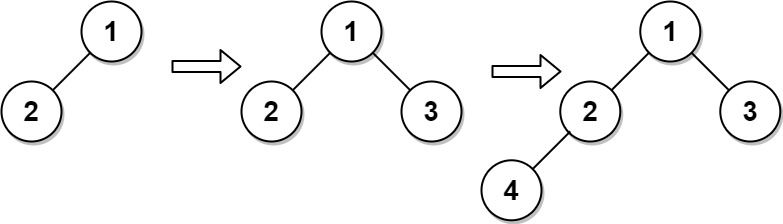
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Design an algorithm to insert a new node to a complete binary tree keeping it complete after the insertion.
Implement the CBTInserter class:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)Initializes the data structure with therootof the complete binary tree.int insert(int v)Inserts aTreeNodeinto the tree with valueNode.val == valso that the tree remains complete, and returns the value of the parent of the insertedTreeNode.TreeNode get_root()Returns the root node of the tree.
Example 1:
Input ["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"] [[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []] Output [null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]]Explanation CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]); cBTInserter.insert(3); // return 1 cBTInserter.insert(4); // return 2 cBTInserter.get_root(); // return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5000rootis a complete binary tree.0 <= val <= 5000- At most
104calls will be made toinsertandget_root.
We can use an array
When inserting a node, we can find the parent node
When getting the root node, we directly return the first element of the array
In terms of time complexity, it takes
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class CBTInserter:
def __init__(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]):
self.tree = []
q = deque([root])
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft()
self.tree.append(node)
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
def insert(self, val: int) -> int:
p = self.tree[(len(self.tree) - 1) // 2]
node = TreeNode(val)
self.tree.append(node)
if p.left is None:
p.left = node
else:
p.right = node
return p.val
def get_root(self) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
return self.tree[0]
# Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = CBTInserter(root)
# param_1 = obj.insert(val)
# param_2 = obj.get_root()/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class CBTInserter {
private List<TreeNode> tree = new ArrayList<>();
public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
tree.add(node);
if (node.left != null) {
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
}
public int insert(int val) {
TreeNode p = tree.get((tree.size() - 1) / 2);
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
tree.add(node);
if (p.left == null) {
p.left = node;
} else {
p.right = node;
}
return p.val;
}
public TreeNode get_root() {
return tree.get(0);
}
}
/**
* Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CBTInserter obj = new CBTInserter(root);
* int param_1 = obj.insert(val);
* TreeNode param_2 = obj.get_root();
*//**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class CBTInserter {
public:
CBTInserter(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
while (q.size()) {
for (int i = q.size(); i; --i) {
auto node = q.front();
q.pop();
tree.push_back(node);
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
}
int insert(int val) {
auto p = tree[(tree.size() - 1) / 2];
auto node = new TreeNode(val);
tree.push_back(node);
if (!p->left) {
p->left = node;
} else {
p->right = node;
}
return p->val;
}
TreeNode* get_root() {
return tree[0];
}
private:
vector<TreeNode*> tree;
};
/**
* Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CBTInserter* obj = new CBTInserter(root);
* int param_1 = obj->insert(val);
* TreeNode* param_2 = obj->get_root();
*//**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
type CBTInserter struct {
tree []*TreeNode
}
func Constructor(root *TreeNode) CBTInserter {
q := []*TreeNode{root}
tree := []*TreeNode{}
for len(q) > 0 {
for i := len(q); i > 0; i-- {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
tree = append(tree, node)
if node.Left != nil {
q = append(q, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q = append(q, node.Right)
}
}
}
return CBTInserter{tree}
}
func (this *CBTInserter) Insert(val int) int {
p := this.tree[(len(this.tree)-1)/2]
node := &TreeNode{val, nil, nil}
this.tree = append(this.tree, node)
if p.Left == nil {
p.Left = node
} else {
p.Right = node
}
return p.Val
}
func (this *CBTInserter) Get_root() *TreeNode {
return this.tree[0]
}
/**
* Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(root);
* param_1 := obj.Insert(val);
* param_2 := obj.Get_root();
*//**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
class CBTInserter {
private tree: TreeNode[] = [];
constructor(root: TreeNode | null) {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
const q: TreeNode[] = [root];
while (q.length) {
const t: TreeNode[] = [];
for (const node of q) {
this.tree.push(node);
node.left !== null && t.push(node.left);
node.right !== null && t.push(node.right);
}
q.splice(0, q.length, ...t);
}
}
insert(val: number): number {
const p = this.tree[(this.tree.length - 1) >> 1];
const node = new TreeNode(val);
this.tree.push(node);
if (p.left === null) {
p.left = node;
} else {
p.right = node;
}
return p.val;
}
get_root(): TreeNode | null {
return this.tree[0];
}
}
/**
* Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new CBTInserter(root)
* var param_1 = obj.insert(val)
* var param_2 = obj.get_root()
*//**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
*/
var CBTInserter = function (root) {
this.tree = [];
if (root === null) {
return;
}
const q = [root];
while (q.length) {
const t = [];
for (const node of q) {
this.tree.push(node);
node.left !== null && t.push(node.left);
node.right !== null && t.push(node.right);
}
q.splice(0, q.length, ...t);
}
};
/**
* @param {number} val
* @return {number}
*/
CBTInserter.prototype.insert = function (val) {
const p = this.tree[(this.tree.length - 1) >> 1];
const node = new TreeNode(val);
this.tree.push(node);
if (p.left === null) {
p.left = node;
} else {
p.right = node;
}
return p.val;
};
/**
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
CBTInserter.prototype.get_root = function () {
return this.tree[0];
};
/**
* Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new CBTInserter(root)
* var param_1 = obj.insert(val)
* var param_2 = obj.get_root()
*/