| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1615 |
Weekly Contest 130 Q4 |
|
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid, where 0 represents a sea cell and 1 represents a land cell.
A move consists of walking from one land cell to another adjacent (4-directionally) land cell or walking off the boundary of the grid.
Return the number of land cells in grid for which we cannot walk off the boundary of the grid in any number of moves.
Example 1:
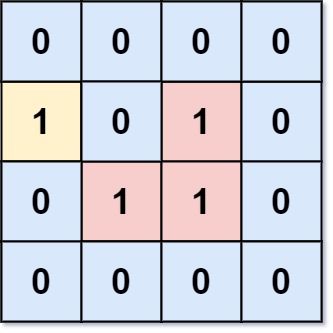
Input: grid = [[0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]] Output: 3 Explanation: There are three 1s that are enclosed by 0s, and one 1 that is not enclosed because its on the boundary.
Example 2:
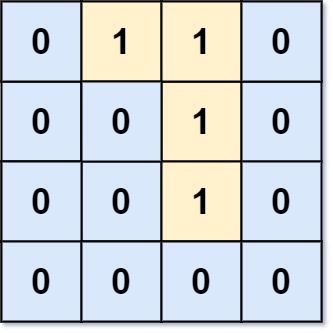
Input: grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: All 1s are either on the boundary or can reach the boundary.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500grid[i][j]is either0or1.
class Solution:
def numEnclaves(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i: int, j: int):
grid[i][j] = 0
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y]:
dfs(x, y)
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
for j in range(n):
if grid[0][j]:
dfs(0, j)
if grid[m - 1][j]:
dfs(m - 1, j)
for i in range(m):
if grid[i][0]:
dfs(i, 0)
if grid[i][n - 1]:
dfs(i, n - 1)
return sum(sum(row) for row in grid)class Solution {
private int[][] grid;
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 1) {
dfs(0, j);
}
if (grid[m - 1][j] == 1) {
dfs(m - 1, j);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) {
dfs(i, 0);
}
if (grid[i][n - 1] == 1) {
dfs(i, n - 1);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (var row : grid) {
for (int x : row) {
ans += x;
}
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i, int j) {
grid[i][j] = 0;
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < grid.length && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].length && grid[x][y] == 1) {
dfs(x, y);
}
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int j) {
grid[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y]) {
dfs(x, y);
}
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] && (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1)) {
dfs(i, j);
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (auto& row : grid) {
for (auto& v : row) {
ans += v;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func numEnclaves(grid [][]int) (ans int) {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
var dfs func(i, j int)
dfs = func(i, j int) {
grid[i][j] = 0
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 {
dfs(x, y)
}
}
}
for i, row := range grid {
for j, v := range row {
if v == 1 && (i == 0 || i == m-1 || j == 0 || j == n-1) {
dfs(i, j)
}
}
}
for _, row := range grid {
for _, v := range row {
ans += v
}
}
return
}function numEnclaves(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const dfs = (i: number, j: number) => {
grid[i][j] = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y <= n && grid[x][y] === 1) {
dfs(x, y);
}
}
};
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] === 1 && (i === 0 || i === m - 1 || j === 0 || j === n - 1)) {
dfs(i, j);
}
}
}
let ans = 0;
for (const row of grid) {
for (const v of row) {
ans += v;
}
}
return ans;
}impl Solution {
fn dfs(grid: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, y: usize, x: usize) {
if y >= grid.len() || x >= grid[0].len() || grid[y][x] == 0 {
return;
}
grid[y][x] = 0;
Solution::dfs(grid, y + 1, x);
Solution::dfs(grid, y, x + 1);
if y != 0 {
Solution::dfs(grid, y - 1, x);
}
if x != 0 {
Solution::dfs(grid, y, x - 1);
}
}
pub fn num_enclaves(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let mut res = 0;
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
for i in 0..m {
Solution::dfs(&mut grid, i, 0);
Solution::dfs(&mut grid, i, n - 1);
}
for i in 0..n {
Solution::dfs(&mut grid, 0, i);
Solution::dfs(&mut grid, m - 1, i);
}
for i in 1..m - 1 {
for j in 1..n - 1 {
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
res += 1;
}
}
}
res
}
}class Solution:
def numEnclaves(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
q = deque()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] and (i == 0 or i == m - 1 or j == 0 or j == n - 1):
q.append((i, j))
grid[i][j] = 0
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if x >= 0 and x < m and y >= 0 and y < n and grid[x][y]:
q.append((x, y))
grid[x][y] = 0
return sum(v for row in grid for v in row)class Solution {
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1)) {
q.offer(new int[] {i, j});
grid[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var p = q.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = p[0] + dirs[k], y = p[1] + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) {
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
grid[x][y] = 0;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (var row : grid) {
for (var v : row) {
ans += v;
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] && (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1)) {
q.emplace(i, j);
grid[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [i, j] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y]) {
q.emplace(x, y);
grid[x][y] = 0;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (auto& row : grid) {
for (auto& v : row) {
ans += v;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func numEnclaves(grid [][]int) (ans int) {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
q := [][2]int{}
for i, row := range grid {
for j, v := range row {
if v == 1 && (i == 0 || i == m-1 || j == 0 || j == n-1) {
q = append(q, [2]int{i, j})
grid[i][j] = 0
}
}
}
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := p[0]+dirs[k], p[1]+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 {
q = append(q, [2]int{x, y})
grid[x][y] = 0
}
}
}
for _, row := range grid {
for _, v := range row {
ans += v
}
}
return
}function numEnclaves(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const q: number[][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] === 1 && (i === 0 || i === m - 1 || j === 0 || j === n - 1)) {
q.push([i, j]);
grid[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
while (q.length) {
const [i, j] = q.shift()!;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y <= n && grid[x][y] === 1) {
q.push([x, y]);
grid[x][y] = 0;
}
}
}
let ans = 0;
for (const row of grid) {
for (const v of row) {
ans += v;
}
}
return ans;
}class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.p = list(range(n))
self.size = [1] * n
def find(self, x):
if self.p[x] != x:
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x])
return self.p[x]
def union(self, a, b):
pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b)
if pa != pb:
if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]:
self.p[pb] = pa
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb]
else:
self.p[pa] = pb
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa]
class Solution:
def numEnclaves(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
uf = UnionFind(m * n + 1)
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, v in enumerate(row):
if v:
if i == 0 or i == m - 1 or j == 0 or j == n - 1:
uf.union(i * n + j, m * n)
else:
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if x >= 0 and x < m and y >= 0 and y < n and grid[x][y]:
uf.union(i * n + j, x * n + y)
return sum(
grid[i][j] == 1 and uf.find(i * n + j) != uf.find(m * n)
for i in range(m)
for j in range(n)
)class UnionFind {
private int[] p;
private int[] size;
public UnionFind(int n) {
p = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
public void union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa != pb) {
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
}
}
}
class Solution {
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m * n + 1);
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) {
uf.union(i * n + j, m * n);
} else {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) {
uf.union(i * n + j, x * n + y);
}
}
}
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && uf.find(i * n + j) != uf.find(m * n)) {
++ans;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
p = vector<int>(n);
size = vector<int>(n, 1);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
}
void unite(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa != pb) {
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
private:
vector<int> p, size;
};
class Solution {
public:
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
UnionFind uf(m * n + 1);
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) {
uf.unite(i * n + j, m * n);
} else {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) {
uf.unite(i * n + j, x * n + y);
}
}
}
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; ++j) {
ans += grid[i][j] == 1 && uf.find(i * n + j) != uf.find(m * n);
}
}
return ans;
}
};type unionFind struct {
p, size []int
}
func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind {
p := make([]int, n)
size := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
return &unionFind{p, size}
}
func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int {
if uf.p[x] != x {
uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x])
}
return uf.p[x]
}
func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) {
pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b)
if pa != pb {
if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] {
uf.p[pb] = pa
uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb]
} else {
uf.p[pa] = pb
uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa]
}
}
}
func numEnclaves(grid [][]int) (ans int) {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
uf := newUnionFind(m*n + 1)
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for i, row := range grid {
for j, v := range row {
if v == 1 {
if i == 0 || i == m-1 || j == 0 || j == n-1 {
uf.union(i*n+j, m*n)
} else {
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 {
uf.union(i*n+j, x*n+y)
}
}
}
}
}
}
for i, row := range grid {
for j, v := range row {
if v == 1 && uf.find(i*n+j) != uf.find(m*n) {
ans++
}
}
}
return
}