| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2022 |
Weekly Contest 159 Q4 |
|
We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You're given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
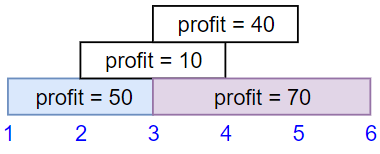
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] Output: 120 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
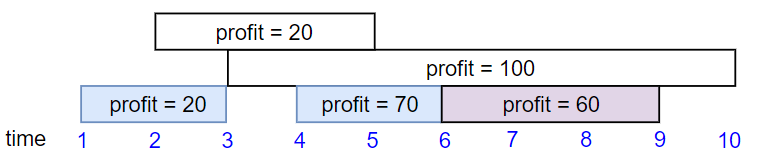
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] Output: 150 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
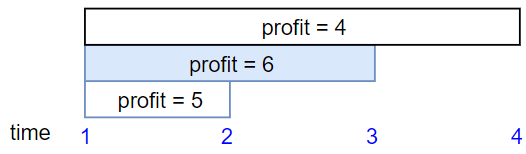
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 1091 <= profit[i] <= 104
First, we sort the jobs by start time in ascending order, then design a function
The calculation process of function
For the
Where
In this process, we can use memoization search to save the answer of each state to avoid repeated calculations.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def jobScheduling(
self, startTime: List[int], endTime: List[int], profit: List[int]
) -> int:
@cache
def dfs(i):
if i >= n:
return 0
_, e, p = jobs[i]
j = bisect_left(jobs, e, lo=i + 1, key=lambda x: x[0])
return max(dfs(i + 1), p + dfs(j))
jobs = sorted(zip(startTime, endTime, profit))
n = len(profit)
return dfs(0)class Solution {
private int[][] jobs;
private int[] f;
private int n;
public int jobScheduling(int[] startTime, int[] endTime, int[] profit) {
n = profit.length;
jobs = new int[n][3];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
jobs[i] = new int[] {startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]};
}
Arrays.sort(jobs, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
f = new int[n];
return dfs(0);
}
private int dfs(int i) {
if (i >= n) {
return 0;
}
if (f[i] != 0) {
return f[i];
}
int e = jobs[i][1], p = jobs[i][2];
int j = search(jobs, e, i + 1);
int ans = Math.max(dfs(i + 1), p + dfs(j));
f[i] = ans;
return ans;
}
private int search(int[][] jobs, int x, int i) {
int left = i, right = n;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (jobs[mid][0] >= x) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
int n = profit.size();
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> jobs(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) jobs[i] = {startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]};
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
vector<int> f(n);
function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int i) -> int {
if (i >= n) return 0;
if (f[i]) return f[i];
auto [_, e, p] = jobs[i];
tuple<int, int, int> t{e, 0, 0};
int j = lower_bound(jobs.begin() + i + 1, jobs.end(), t, [&](auto& l, auto& r) -> bool { return get<0>(l) < get<0>(r); }) - jobs.begin();
int ans = max(dfs(i + 1), p + dfs(j));
f[i] = ans;
return ans;
};
return dfs(0);
}
};func jobScheduling(startTime []int, endTime []int, profit []int) int {
n := len(profit)
type tuple struct{ s, e, p int }
jobs := make([]tuple, n)
for i, p := range profit {
jobs[i] = tuple{startTime[i], endTime[i], p}
}
sort.Slice(jobs, func(i, j int) bool { return jobs[i].s < jobs[j].s })
f := make([]int, n)
var dfs func(int) int
dfs = func(i int) int {
if i >= n {
return 0
}
if f[i] != 0 {
return f[i]
}
j := sort.Search(n, func(j int) bool { return jobs[j].s >= jobs[i].e })
ans := max(dfs(i+1), jobs[i].p+dfs(j))
f[i] = ans
return ans
}
return dfs(0)
}function jobScheduling(startTime: number[], endTime: number[], profit: number[]): number {
const n = startTime.length;
const f = new Array(n).fill(0);
const idx = new Array(n).fill(0).map((_, i) => i);
idx.sort((i, j) => startTime[i] - startTime[j]);
const search = (x: number) => {
let l = 0;
let r = n;
while (l < r) {
const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (startTime[idx[mid]] >= x) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
};
const dfs = (i: number): number => {
if (i >= n) {
return 0;
}
if (f[i] !== 0) {
return f[i];
}
const j = search(endTime[idx[i]]);
return (f[i] = Math.max(dfs(i + 1), dfs(j) + profit[idx[i]]));
};
return dfs(0);
}We can also change the memoization search in Solution 1 to dynamic programming.
First, sort the jobs, this time we sort by end time in ascending order, then define
For the
Where
The time complexity is
Similar problems:
class Solution:
def jobScheduling(
self, startTime: List[int], endTime: List[int], profit: List[int]
) -> int:
jobs = sorted(zip(endTime, startTime, profit))
n = len(profit)
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
for i, (_, s, p) in enumerate(jobs):
j = bisect_right(jobs, s, hi=i, key=lambda x: x[0])
dp[i + 1] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + p)
return dp[n]class Solution {
public int jobScheduling(int[] startTime, int[] endTime, int[] profit) {
int n = profit.length;
int[][] jobs = new int[n][3];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
jobs[i] = new int[] {startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]};
}
Arrays.sort(jobs, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int j = search(jobs, jobs[i][0], i);
dp[i + 1] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + jobs[i][2]);
}
return dp[n];
}
private int search(int[][] jobs, int x, int n) {
int left = 0, right = n;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (jobs[mid][1] > x) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
int n = profit.size();
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> jobs(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) jobs[i] = {endTime[i], startTime[i], profit[i]};
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
vector<int> dp(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
auto [_, s, p] = jobs[i];
int j = upper_bound(jobs.begin(), jobs.begin() + i, s, [&](int x, auto& job) -> bool { return x < get<0>(job); }) - jobs.begin();
dp[i + 1] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + p);
}
return dp[n];
}
};func jobScheduling(startTime []int, endTime []int, profit []int) int {
n := len(profit)
type tuple struct{ s, e, p int }
jobs := make([]tuple, n)
for i, p := range profit {
jobs[i] = tuple{startTime[i], endTime[i], p}
}
sort.Slice(jobs, func(i, j int) bool { return jobs[i].e < jobs[j].e })
dp := make([]int, n+1)
for i, job := range jobs {
j := sort.Search(i, func(k int) bool { return jobs[k].e > job.s })
dp[i+1] = max(dp[i], dp[j]+job.p)
}
return dp[n]
}function jobScheduling(startTime: number[], endTime: number[], profit: number[]): number {
const n = profit.length;
const jobs: [number, number, number][] = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => [
startTime[i],
endTime[i],
profit[i],
]);
jobs.sort((a, b) => a[1] - b[1]);
const dp: number[] = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => 0);
const search = (x: number, right: number): number => {
let left = 0;
while (left < right) {
const mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (jobs[mid][1] > x) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
};
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
const j = search(jobs[i][0], i);
dp[i + 1] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + jobs[i][2]);
}
return dp[n];
}class Solution {
func binarySearch<T: Comparable>(inputArr: [T], searchItem: T) -> Int? {
var lowerIndex = 0
var upperIndex = inputArr.count - 1
while lowerIndex < upperIndex {
let currentIndex = (lowerIndex + upperIndex) / 2
if inputArr[currentIndex] <= searchItem {
lowerIndex = currentIndex + 1
} else {
upperIndex = currentIndex
}
}
if inputArr[upperIndex] <= searchItem {
return upperIndex + 1
}
return lowerIndex
}
func jobScheduling(_ startTime: [Int], _ endTime: [Int], _ profit: [Int]) -> Int {
let zipList = zip(zip(startTime, endTime), profit)
var table: [(startTime: Int, endTime: Int, profit: Int, cumsum: Int)] = []
for ((x, y), z) in zipList {
table.append((x, y, z, 0))
}
table.sort(by: { $0.endTime < $1.endTime })
let sortedEndTime = endTime.sorted()
var profits: [Int] = [0]
for iJob in table {
let index: Int! = binarySearch(inputArr: sortedEndTime, searchItem: iJob.startTime)
if profits.last! < profits[index] + iJob.profit {
profits.append(profits[index] + iJob.profit)
} else {
profits.append(profits.last!)
}
}
return profits.last!
}
}