| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1792 |
Biweekly Contest 12 Q3 |
|
The diameter of a tree is the number of edges in the longest path in that tree.
There is an undirected tree of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given a 2D array edges where edges.length == n - 1 and edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return the diameter of the tree.
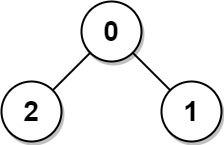
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: The longest path of the tree is the path 1 - 0 - 2.
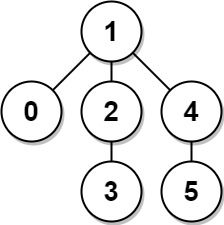
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,4],[4,5]] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest path of the tree is the path 3 - 2 - 1 - 4 - 5.
Constraints:
n == edges.length + 11 <= n <= 1040 <= ai, bi < nai != bi
First, we arbitrarily select a node and start a depth-first search (DFS) from this node to find the farthest node from it, denoted as node
Time complexity is
Similar problems:
class Solution:
def treeDiameter(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i: int, fa: int, t: int):
for j in g[i]:
if j != fa:
dfs(j, i, t + 1)
nonlocal ans, a
if ans < t:
ans = t
a = i
g = defaultdict(list)
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
ans = a = 0
dfs(0, -1, 0)
dfs(a, -1, 0)
return ansclass Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int ans;
private int a;
public int treeDiameter(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length + 1;
g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
dfs(0, -1, 0);
dfs(a, -1, 0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i, int fa, int t) {
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa) {
dfs(j, i, t + 1);
}
}
if (ans < t) {
ans = t;
a = i;
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int treeDiameter(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = edges.size() + 1;
vector<int> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
int ans = 0, a = 0;
auto dfs = [&](auto&& dfs, int i, int fa, int t) -> void {
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa) {
dfs(dfs, j, i, t + 1);
}
}
if (ans < t) {
ans = t;
a = i;
}
};
dfs(dfs, 0, -1, 0);
dfs(dfs, a, -1, 0);
return ans;
}
};func treeDiameter(edges [][]int) (ans int) {
n := len(edges) + 1
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
a := 0
var dfs func(i, fa, t int)
dfs = func(i, fa, t int) {
for _, j := range g[i] {
if j != fa {
dfs(j, i, t+1)
}
}
if ans < t {
ans = t
a = i
}
}
dfs(0, -1, 0)
dfs(a, -1, 0)
return
}function treeDiameter(edges: number[][]): number {
const n = edges.length + 1;
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
g[b].push(a);
}
let [ans, a] = [0, 0];
const dfs = (i: number, fa: number, t: number): void => {
for (const j of g[i]) {
if (j !== fa) {
dfs(j, i, t + 1);
}
}
if (ans < t) {
ans = t;
a = i;
}
};
dfs(0, -1, 0);
dfs(a, -1, 0);
return ans;
}