| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1426 |
Biweekly Contest 17 Q3 |
|
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of values of nodes with an even-valued grandparent. If there are no nodes with an even-valued grandparent, return 0.
A grandparent of a node is the parent of its parent if it exists.
Example 1:
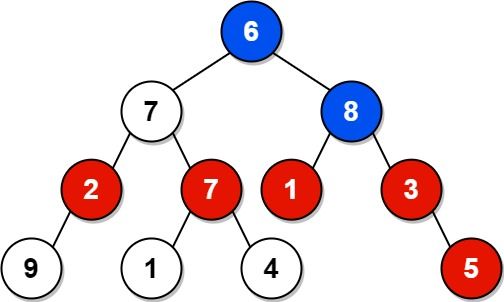
Input: root = [6,7,8,2,7,1,3,9,null,1,4,null,null,null,5] Output: 18 Explanation: The red nodes are the nodes with even-value grandparent while the blue nodes are the even-value grandparents.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
We design a function
The execution process of the function
- If
$root$ is null, return$0$ . - Otherwise, we recursively calculate the answers of the left and right subtrees of
$root$ , that is,$dfs(root.left, root.val)$ and$dfs(root.right, root.val)$ , and add them to the answer. If$x$ is even, we check whether the left and right children of$root$ exist. If they exist, we add their values to the answer. - Finally, return the answer.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumEvenGrandparent(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(root: TreeNode, x: int) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
ans = dfs(root.left, root.val) + dfs(root.right, root.val)
if x % 2 == 0:
if root.left:
ans += root.left.val
if root.right:
ans += root.right.val
return ans
return dfs(root, 1)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumEvenGrandparent(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, 1);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int x) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int ans = dfs(root.left, root.val) + dfs(root.right, root.val);
if (x % 2 == 0) {
if (root.left != null) {
ans += root.left.val;
}
if (root.right != null) {
ans += root.right.val;
}
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumEvenGrandparent(TreeNode* root) {
function<int(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int x) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int ans = dfs(root->left, root->val) + dfs(root->right, root->val);
if (x % 2 == 0) {
if (root->left) {
ans += root->left->val;
}
if (root->right) {
ans += root->right->val;
}
}
return ans;
};
return dfs(root, 1);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sumEvenGrandparent(root *TreeNode) int {
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, x int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
ans := dfs(root.Left, root.Val) + dfs(root.Right, root.Val)
if x%2 == 0 {
if root.Left != nil {
ans += root.Left.Val
}
if root.Right != nil {
ans += root.Right.Val
}
}
return ans
}
return dfs(root, 1)
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function sumEvenGrandparent(root: TreeNode | null): number {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, x: number): number => {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
const { val, left, right } = root;
let ans = dfs(left, val) + dfs(right, val);
if (x % 2 === 0) {
ans += left?.val ?? 0;
ans += right?.val ?? 0;
}
return ans;
};
return dfs(root, 1);
}