| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
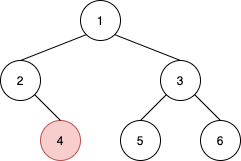
Given the root of a binary tree and a node u in the tree, return the nearest node on the same level that is to the right of u, or return null if u is the rightmost node in its level.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4,5,6], u = 4 Output: 5 Explanation: The nearest node on the same level to the right of node 4 is node 5.
Example 2:
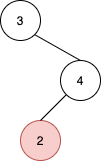
Input: root = [3,null,4,2], u = 2 Output: null Explanation: There are no nodes to the right of 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- All values in the tree are distinct.
uis a node in the binary tree rooted atroot.
We can use Breadth-First Search, starting from the root node. When we reach node
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findNearestRightNode(self, root: TreeNode, u: TreeNode) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
q = deque([root])
while q:
for i in range(len(q) - 1, -1, -1):
root = q.popleft()
if root == u:
return q[0] if i else None
if root.left:
q.append(root.left)
if root.right:
q.append(root.right)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode findNearestRightNode(TreeNode root, TreeNode u) {
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) {
root = q.pollFirst();
if (root == u) {
return i > 1 ? q.peekFirst() : null;
}
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(root.right);
}
}
}
return null;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* findNearestRightNode(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* u) {
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
while (q.size()) {
for (int i = q.size(); i; --i) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
if (root == u) {
return i > 1 ? q.front() : nullptr;
}
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func findNearestRightNode(root *TreeNode, u *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
for i := len(q); i > 0; i-- {
root = q[0]
q = q[1:]
if root == u {
if i > 1 {
return q[0]
}
return nil
}
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, root.Right)
}
}
}
return nil
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} u
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var findNearestRightNode = function (root, u) {
const q = [root];
while (q.length) {
for (let i = q.length; i; --i) {
root = q.shift();
if (root == u) {
return i > 1 ? q[0] : null;
}
if (root.left) {
q.push(root.left);
}
if (root.right) {
q.push(root.right);
}
}
}
return null;
};DFS performs a pre-order traversal of the binary tree. The first time we search to node
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findNearestRightNode(self, root: TreeNode, u: TreeNode) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
def dfs(root, i):
nonlocal d, ans
if root is None or ans:
return
if d == i:
ans = root
return
if root == u:
d = i
return
dfs(root.left, i + 1)
dfs(root.right, i + 1)
d = 0
ans = None
dfs(root, 1)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode u;
private TreeNode ans;
private int d;
public TreeNode findNearestRightNode(TreeNode root, TreeNode u) {
this.u = u;
dfs(root, 1);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int i) {
if (root == null || ans != null) {
return;
}
if (d == i) {
ans = root;
return;
}
if (root == u) {
d = i;
return;
}
dfs(root.left, i + 1);
dfs(root.right, i + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* findNearestRightNode(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* u) {
TreeNode* ans;
int d = 0;
function<void(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int i) {
if (!root || ans) {
return;
}
if (d == i) {
ans = root;
return;
}
if (root == u) {
d = i;
return;
}
dfs(root->left, i + 1);
dfs(root->right, i + 1);
};
dfs(root, 1);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func findNearestRightNode(root *TreeNode, u *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
d := 0
var ans *TreeNode
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, i int) {
if root == nil || ans != nil {
return
}
if d == i {
ans = root
return
}
if root == u {
d = i
return
}
dfs(root.Left, i+1)
dfs(root.Right, i+1)
}
dfs(root, 1)
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} u
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var findNearestRightNode = function (root, u) {
let d = 0;
let ans = null;
function dfs(root, i) {
if (!root || ans) {
return;
}
if (d == i) {
ans = root;
return;
}
if (root == u) {
d = i;
return;
}
dfs(root.left, i + 1);
dfs(root.right, i + 1);
}
dfs(root, 1);
return ans;
};