| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
You are starving and you want to eat food as quickly as possible. You want to find the shortest path to arrive at any food cell.
You are given an m x n character matrix, grid, of these different types of cells:
'*'is your location. There is exactly one'*'cell.'#'is a food cell. There may be multiple food cells.'O'is free space, and you can travel through these cells.'X'is an obstacle, and you cannot travel through these cells.
You can travel to any adjacent cell north, east, south, or west of your current location if there is not an obstacle.
Return the length of the shortest path for you to reach any food cell. If there is no path for you to reach food, return -1.
Example 1:
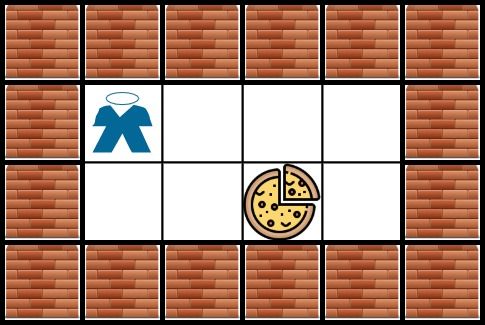
Input: grid = [["X","X","X","X","X","X"],["X","*","O","O","O","X"],["X","O","O","#","O","X"],["X","X","X","X","X","X"]] Output: 3 Explanation: It takes 3 steps to reach the food.
Example 2:
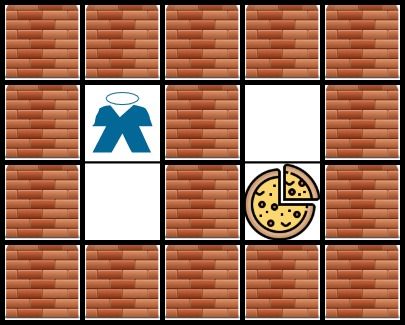
Input: grid = [["X","X","X","X","X"],["X","*","X","O","X"],["X","O","X","#","X"],["X","X","X","X","X"]] Output: -1 Explanation: It is not possible to reach the food.
Example 3:
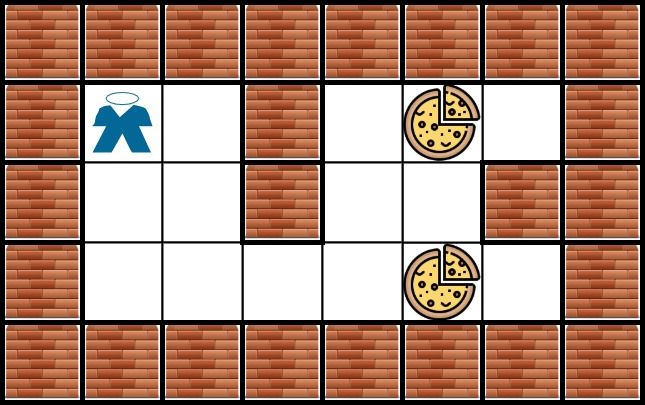
Input: grid = [["X","X","X","X","X","X","X","X"],["X","*","O","X","O","#","O","X"],["X","O","O","X","O","O","X","X"],["X","O","O","O","O","#","O","X"],["X","X","X","X","X","X","X","X"]] Output: 6 Explanation: There can be multiple food cells. It only takes 6 steps to reach the bottom food.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 200grid[row][col]is'*','X','O', or'#'.- The
gridcontains exactly one'*'.
According to the problem, we need to start from *, find the nearest #, and return the shortest path length.
First, we traverse the entire two-dimensional array to find the position of *, which will be the starting point for BFS, and put it into the queue.
Then, we start BFS, traversing the elements in the queue. Each time we traverse an element, we add the elements in the four directions (up, down, left, and right) of it into the queue, until we encounter #, and return the current layer number.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def getFood(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
i, j = next((i, j) for i in range(m) for j in range(n) if grid[i][j] == '*')
q = deque([(i, j)])
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
ans = 0
while q:
ans += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n:
if grid[x][y] == '#':
return ans
if grid[x][y] == 'O':
grid[x][y] = 'X'
q.append((x, y))
return -1class Solution {
private int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
public int getFood(char[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0, x = 1; i < m && x == 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == '*') {
q.offer(new int[] {i, j});
x = 0;
break;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
++ans;
for (int t = q.size(); t > 0; --t) {
var p = q.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = p[0] + dirs[k];
int y = p[1] + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
if (grid[x][y] == '#') {
return ans;
}
if (grid[x][y] == 'O') {
grid[x][y] = 'X';
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}class Solution {
public:
const static inline vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
int getFood(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int i = 0, x = 1; i < m && x == 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == '*') {
q.emplace(i, j);
x = 0;
break;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
++ans;
for (int t = q.size(); t; --t) {
auto [i, j] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
if (grid[x][y] == '#') return ans;
if (grid[x][y] == 'O') {
grid[x][y] = 'X';
q.emplace(x, y);
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};func getFood(grid [][]byte) (ans int) {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
type pair struct{ i, j int }
q := []pair{}
for i, x := 0, 1; i < m && x == 1; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == '*' {
q = append(q, pair{i, j})
x = 0
break
}
}
}
for len(q) > 0 {
ans++
for t := len(q); t > 0; t-- {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := p.i+dirs[k], p.j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n {
if grid[x][y] == '#' {
return ans
}
if grid[x][y] == 'O' {
grid[x][y] = 'X'
q = append(q, pair{x, y})
}
}
}
}
}
return -1
}/**
* @param {character[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
var getFood = function (grid) {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const q = [];
for (let i = 0, x = 1; i < m && x == 1; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == '*') {
q.push([i, j]);
x = 0;
break;
}
}
}
let ans = 0;
while (q.length) {
++ans;
for (let t = q.length; t > 0; --t) {
const [i, j] = q.shift();
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
if (grid[x][y] == '#') {
return ans;
}
if (grid[x][y] == 'O') {
grid[x][y] = 'X';
q.push([x, y]);
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
};