| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
困难 |
2178 |
第 266 场周赛 Q4 |
|
给你一张 无向 图,图中有 n 个节点,节点编号从 0 到 n - 1 (都包括)。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 values ,其中 values[i] 是第 i 个节点的 价值 。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[j] = [uj, vj, timej] 表示节点 uj 和 vj 之间有一条需要 timej 秒才能通过的无向边。最后,给你一个整数 maxTime 。
合法路径 指的是图中任意一条从节点 0 开始,最终回到节点 0 ,且花费的总时间 不超过 maxTime 秒的一条路径。你可以访问一个节点任意次。一条合法路径的 价值 定义为路径中 不同节点 的价值 之和 (每个节点的价值 至多 算入价值总和中一次)。
请你返回一条合法路径的 最大 价值。
注意:每个节点 至多 有 四条 边与之相连。
示例 1:
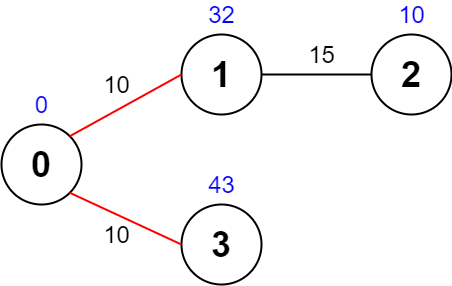
输入:values = [0,32,10,43], edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,15],[0,3,10]], maxTime = 49 输出:75 解释: 一条可能的路径为:0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 3 -> 0 。总花费时间为 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 = 40 <= 49 。 访问过的节点为 0 ,1 和 3 ,最大路径价值为 0 + 32 + 43 = 75 。
示例 2:
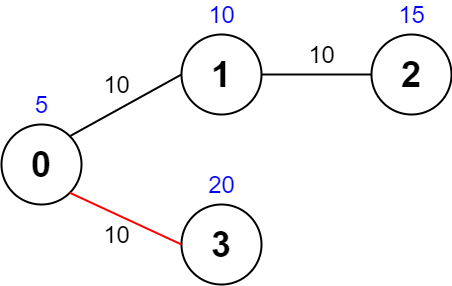
输入:values = [5,10,15,20], edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,10],[0,3,10]], maxTime = 30 输出:25 解释: 一条可能的路径为:0 -> 3 -> 0 。总花费时间为 10 + 10 = 20 <= 30 。 访问过的节点为 0 和 3 ,最大路径价值为 5 + 20 = 25 。
示例 3:
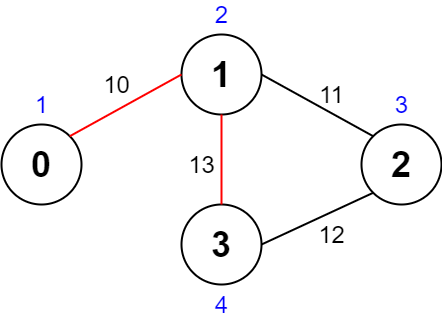
输入:values = [1,2,3,4], edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,11],[2,3,12],[1,3,13]], maxTime = 50 输出:7 解释: 一条可能的路径为:0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 1 -> 0 。总花费时间为 10 + 13 + 13 + 10 = 46 <= 50 。 访问过的节点为 0 ,1 和 3 ,最大路径价值为 1 + 2 + 4 = 7 。
示例 4:
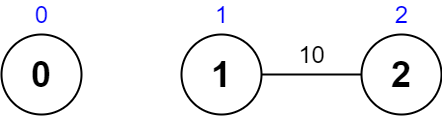
输入:values = [0,1,2], edges = [[1,2,10]], maxTime = 10 输出:0 解释: 唯一一条路径为 0 。总花费时间为 0 。 唯一访问过的节点为 0 ,最大路径价值为 0 。
提示:
n == values.length1 <= n <= 10000 <= values[i] <= 1080 <= edges.length <= 2000edges[j].length == 30 <= uj < vj <= n - 110 <= timej, maxTime <= 100[uj, vj]所有节点对 互不相同 。- 每个节点 至多有四条 边。
- 图可能不连通。
我们观察题目的数据范围,可以发现从
我们先将图的边存储在邻接表表
函数
- 如果当前节点编号
$u$ 等于$0$ ,表示我们已经回到了起点,那么我们更新答案为$\max(\textit{ans}, \textit{value})$ ; - 遍历当前节点
$u$ 的所有邻居节点$v$ ,如果当前路径的花费时间加上边$(u, v)$ 的时间$t$ 不超过$\textit{maxTime}$ ,那么我们可以选择继续访问节点$v$ ;- 如果节点
$v$ 已经被访问过,那么我们直接递归调用$\textit{dfs}(v, \textit{cost} + t, \textit{value})$ ; - 如果节点
$v$ 没有被访问过,我们标记节点$v$ 为已访问,然后递归调用$\textit{dfs}(v, \textit{cost} + t, \textit{value} + \textit{values}[v])$ ,最后恢复节点$v$ 的访问状态。
- 如果节点
在主函数中,我们调用
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def maximalPathQuality(
self, values: List[int], edges: List[List[int]], maxTime: int
) -> int:
def dfs(u: int, cost: int, value: int):
if u == 0:
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans, value)
for v, t in g[u]:
if cost + t <= maxTime:
if vis[v]:
dfs(v, cost + t, value)
else:
vis[v] = True
dfs(v, cost + t, value + values[v])
vis[v] = False
n = len(values)
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, t in edges:
g[u].append((v, t))
g[v].append((u, t))
vis = [False] * n
vis[0] = True
ans = 0
dfs(0, 0, values[0])
return ansclass Solution {
private List<int[]>[] g;
private boolean[] vis;
private int[] values;
private int maxTime;
private int ans;
public int maximalPathQuality(int[] values, int[][] edges, int maxTime) {
int n = values.length;
g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], t = e[2];
g[u].add(new int[] {v, t});
g[v].add(new int[] {u, t});
}
vis = new boolean[n];
vis[0] = true;
this.values = values;
this.maxTime = maxTime;
dfs(0, 0, values[0]);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int u, int cost, int value) {
if (u == 0) {
ans = Math.max(ans, value);
}
for (var e : g[u]) {
int v = e[0], t = e[1];
if (cost + t <= maxTime) {
if (vis[v]) {
dfs(v, cost + t, value);
} else {
vis[v] = true;
dfs(v, cost + t, value + values[v]);
vis[v] = false;
}
}
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maximalPathQuality(vector<int>& values, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int maxTime) {
int n = values.size();
vector<pair<int, int>> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], t = e[2];
g[u].emplace_back(v, t);
g[v].emplace_back(u, t);
}
bool vis[n];
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
vis[0] = true;
int ans = 0;
auto dfs = [&](auto&& dfs, int u, int cost, int value) -> void {
if (u == 0) {
ans = max(ans, value);
}
for (auto& [v, t] : g[u]) {
if (cost + t <= maxTime) {
if (vis[v]) {
dfs(dfs, v, cost + t, value);
} else {
vis[v] = true;
dfs(dfs, v, cost + t, value + values[v]);
vis[v] = false;
}
}
}
};
dfs(dfs, 0, 0, values[0]);
return ans;
}
};func maximalPathQuality(values []int, edges [][]int, maxTime int) (ans int) {
n := len(values)
g := make([][][2]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
u, v, t := e[0], e[1], e[2]
g[u] = append(g[u], [2]int{v, t})
g[v] = append(g[v], [2]int{u, t})
}
vis := make([]bool, n)
vis[0] = true
var dfs func(u, cost, value int)
dfs = func(u, cost, value int) {
if u == 0 {
ans = max(ans, value)
}
for _, e := range g[u] {
v, t := e[0], e[1]
if cost+t <= maxTime {
if vis[v] {
dfs(v, cost+t, value)
} else {
vis[v] = true
dfs(v, cost+t, value+values[v])
vis[v] = false
}
}
}
}
dfs(0, 0, values[0])
return
}function maximalPathQuality(values: number[], edges: number[][], maxTime: number): number {
const n = values.length;
const g: [number, number][][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [u, v, t] of edges) {
g[u].push([v, t]);
g[v].push([u, t]);
}
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
vis[0] = true;
let ans = 0;
const dfs = (u: number, cost: number, value: number) => {
if (u === 0) {
ans = Math.max(ans, value);
}
for (const [v, t] of g[u]) {
if (cost + t <= maxTime) {
if (vis[v]) {
dfs(v, cost + t, value);
} else {
vis[v] = true;
dfs(v, cost + t, value + values[v]);
vis[v] = false;
}
}
}
};
dfs(0, 0, values[0]);
return ans;
}