| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1685 |
Weekly Contest 267 Q2 |
|
You are given the head of a linked list.
The nodes in the linked list are sequentially assigned to non-empty groups whose lengths form the sequence of the natural numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, ...). The length of a group is the number of nodes assigned to it. In other words,
- The
1stnode is assigned to the first group. - The
2ndand the3rdnodes are assigned to the second group. - The
4th,5th, and6thnodes are assigned to the third group, and so on.
Note that the length of the last group may be less than or equal to 1 + the length of the second to last group.
Reverse the nodes in each group with an even length, and return the head of the modified linked list.
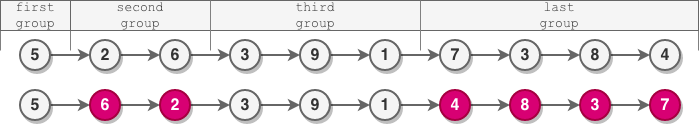
Example 1:
Input: head = [5,2,6,3,9,1,7,3,8,4] Output: [5,6,2,3,9,1,4,8,3,7] Explanation: - The length of the first group is 1, which is odd, hence no reversal occurs. - The length of the second group is 2, which is even, hence the nodes are reversed. - The length of the third group is 3, which is odd, hence no reversal occurs. - The length of the last group is 4, which is even, hence the nodes are reversed.
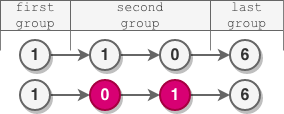
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,1,0,6] Output: [1,0,1,6] Explanation: - The length of the first group is 1. No reversal occurs. - The length of the second group is 2. The nodes are reversed. - The length of the last group is 1. No reversal occurs.
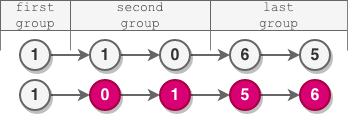
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,1,0,6,5] Output: [1,0,1,5,6] Explanation: - The length of the first group is 1. No reversal occurs. - The length of the second group is 2. The nodes are reversed. - The length of the last group is 2. The nodes are reversed.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 105
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseEvenLengthGroups(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
def reverse(head, l):
prev, cur, tail = None, head, head
i = 0
while cur and i < l:
t = cur.next
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = t
i += 1
tail.next = cur
return prev
n = 0
t = head
while t:
t = t.next
n += 1
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
prev = dummy
l = 1
while (1 + l) * l // 2 <= n and prev:
if l % 2 == 0:
prev.next = reverse(prev.next, l)
i = 0
while i < l and prev:
prev = prev.next
i += 1
l += 1
left = n - l * (l - 1) // 2
if left > 0 and left % 2 == 0:
prev.next = reverse(prev.next, left)
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseEvenLengthGroups(ListNode head) {
int n = 0;
for (ListNode t = head; t != null; t = t.next) {
++n;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode prev = dummy;
int l = 1;
for (; (1 + l) * l / 2 <= n && prev != null; ++l) {
if (l % 2 == 0) {
ListNode node = prev.next;
prev.next = reverse(node, l);
}
for (int i = 0; i < l && prev != null; ++i) {
prev = prev.next;
}
}
int left = n - l * (l - 1) / 2;
if (left > 0 && left % 2 == 0) {
ListNode node = prev.next;
prev.next = reverse(node, left);
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head, int l) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode tail = cur;
int i = 0;
while (cur != null && i < l) {
ListNode t = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = t;
++i;
}
tail.next = cur;
return prev;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function reverseEvenLengthGroups(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let nums = [];
let cur = head;
while (cur) {
nums.push(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
const n = nums.length;
for (let i = 0, k = 1; i < n; i += k, k++) {
// 最后一组, 可能出现不足
k = Math.min(n - i, k);
if (!(k & 1)) {
let tmp = nums.splice(i, k);
tmp.reverse();
nums.splice(i, 0, ...tmp);
}
}
cur = head;
for (let num of nums) {
cur.val = num;
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}