| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
You are given an array points where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents a point on an X-Y plane.
Straight lines are going to be added to the X-Y plane, such that every point is covered by at least one line.
Return the minimum number of straight lines needed to cover all the points.
Example 1:
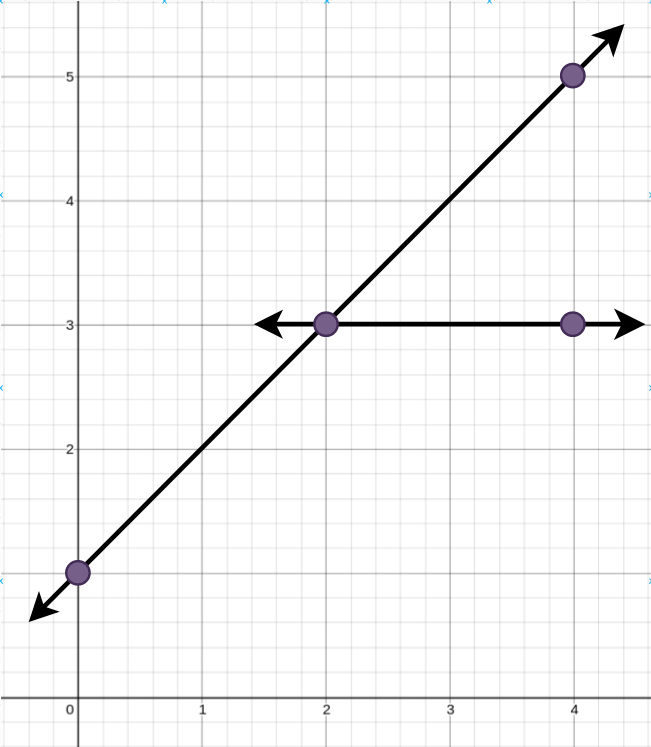
Input: points = [[0,1],[2,3],[4,5],[4,3]] Output: 2 Explanation: The minimum number of straight lines needed is two. One possible solution is to add: - One line connecting the point at (0, 1) to the point at (4, 5). - Another line connecting the point at (2, 3) to the point at (4, 3).
Example 2:
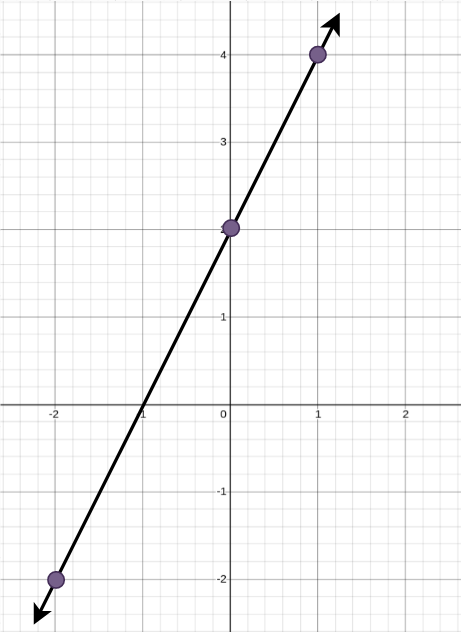
Input: points = [[0,2],[-2,-2],[1,4]] Output: 1 Explanation: The minimum number of straight lines needed is one. The only solution is to add: - One line connecting the point at (-2, -2) to the point at (1, 4).
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 10points[i].length == 2-100 <= xi, yi <= 100- All the
pointsare unique.
class Solution:
def minimumLines(self, points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def check(i, j, k):
x1, y1 = points[i]
x2, y2 = points[j]
x3, y3 = points[k]
return (x2 - x1) * (y3 - y1) == (x3 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
@cache
def dfs(state):
if state == (1 << n) - 1:
return 0
ans = inf
for i in range(n):
if not (state >> i & 1):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
nxt = state | 1 << i | 1 << j
for k in range(j + 1, n):
if not (nxt >> k & 1) and check(i, j, k):
nxt |= 1 << k
ans = min(ans, dfs(nxt) + 1)
if i == n - 1:
ans = min(ans, dfs(state | 1 << i) + 1)
return ans
n = len(points)
return dfs(0)class Solution {
private int[] f;
private int[][] points;
private int n;
public int minimumLines(int[][] points) {
n = points.length;
this.points = points;
f = new int[1 << n];
return dfs(0);
}
private int dfs(int state) {
if (state == (1 << n) - 1) {
return 0;
}
if (f[state] != 0) {
return f[state];
}
int ans = 1 << 30;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (((state >> i) & 1) == 0) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
int nxt = state | 1 << i | 1 << j;
for (int k = j + 1; k < n; ++k) {
if (((state >> k) & 1) == 0 && check(i, j, k)) {
nxt |= 1 << k;
}
}
ans = Math.min(ans, dfs(nxt) + 1);
}
if (i == n - 1) {
ans = Math.min(ans, dfs(state | 1 << i) + 1);
}
}
}
return f[state] = ans;
}
private boolean check(int i, int j, int k) {
int x1 = points[i][0], y1 = points[i][1];
int x2 = points[j][0], y2 = points[j][1];
int x3 = points[k][0], y3 = points[k][1];
return (x2 - x1) * (y3 - y1) == (x3 - x1) * (y2 - y1);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minimumLines(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
auto check = [&](int i, int j, int k) {
int x1 = points[i][0], y1 = points[i][1];
int x2 = points[j][0], y2 = points[j][1];
int x3 = points[k][0], y3 = points[k][1];
return (x2 - x1) * (y3 - y1) == (x3 - x1) * (y2 - y1);
};
int n = points.size();
int f[1 << n];
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int state) -> int {
if (state == (1 << n) - 1) return 0;
if (f[state]) return f[state];
int ans = 1 << 30;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!(state >> i & 1)) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
int nxt = state | 1 << i | 1 << j;
for (int k = j + 1; k < n; ++k) {
if (!(nxt >> k & 1) && check(i, j, k)) {
nxt |= 1 << k;
}
}
ans = min(ans, dfs(nxt) + 1);
}
if (i == n - 1) {
ans = min(ans, dfs(state | 1 << i) + 1);
}
}
}
return f[state] = ans;
};
return dfs(0);
}
};func minimumLines(points [][]int) int {
check := func(i, j, k int) bool {
x1, y1 := points[i][0], points[i][1]
x2, y2 := points[j][0], points[j][1]
x3, y3 := points[k][0], points[k][1]
return (x2-x1)*(y3-y1) == (x3-x1)*(y2-y1)
}
n := len(points)
f := make([]int, 1<<n)
var dfs func(int) int
dfs = func(state int) int {
if state == (1<<n)-1 {
return 0
}
if f[state] > 0 {
return f[state]
}
ans := 1 << 30
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if (state >> i & 1) == 0 {
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
nxt := state | 1<<i | 1<<j
for k := j + 1; k < n; k++ {
if (nxt>>k&1) == 0 && check(i, j, k) {
nxt |= 1 << k
}
}
ans = min(ans, dfs(nxt)+1)
}
if i == n-1 {
ans = min(ans, dfs(state|1<<i)+1)
}
}
}
f[state] = ans
return ans
}
return dfs(0)
}