| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes in a connected undirected graph containing exactly one cycle. The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive).
You are also given a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [node1i, node2i] denotes that there is a bidirectional edge connecting node1i and node2i in the graph.
The distance between two nodes a and b is defined to be the minimum number of edges that are needed to go from a to b.
Return an integer array answer of size n, where answer[i] is the minimum distance between the ith node and any node in the cycle.
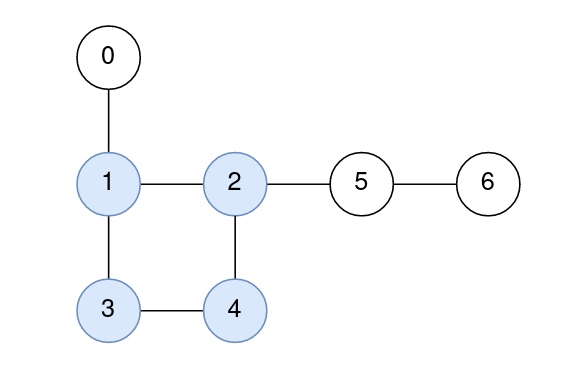
Example 1:
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,2],[2,4],[4,3],[3,1],[0,1],[5,2],[6,5]] Output: [1,0,0,0,0,1,2] Explanation: The nodes 1, 2, 3, and 4 form the cycle. The distance from 0 to 1 is 1. The distance from 1 to 1 is 0. The distance from 2 to 2 is 0. The distance from 3 to 3 is 0. The distance from 4 to 4 is 0. The distance from 5 to 2 is 1. The distance from 6 to 2 is 2.
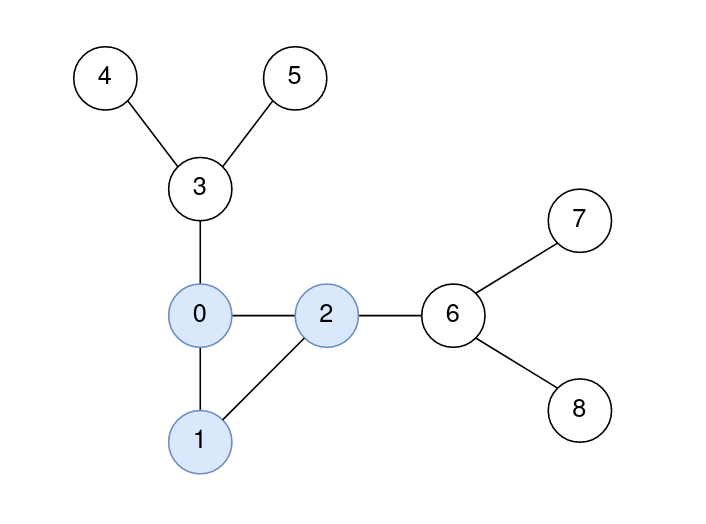
Example 2:
Input: n = 9, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2],[2,6],[6,7],[6,8],[0,3],[3,4],[3,5]] Output: [0,0,0,1,2,2,1,2,2] Explanation: The nodes 0, 1, and 2 form the cycle. The distance from 0 to 0 is 0. The distance from 1 to 1 is 0. The distance from 2 to 2 is 0. The distance from 3 to 1 is 1. The distance from 4 to 1 is 2. The distance from 5 to 1 is 2. The distance from 6 to 2 is 1. The distance from 7 to 2 is 2. The distance from 8 to 2 is 2.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 105edges.length == nedges[i].length == 20 <= node1i, node2i <= n - 1node1i != node2i- The graph is connected.
- The graph has exactly one cycle.
- There is at most one edge between any pair of vertices.
We can first convert the edges in
Next, we delete nodes layer by layer from the outside to the inside until only a cycle remains. The specific method is as follows:
We first find all nodes with a degree of
Finally, we initialize an answer array
After the traversal, return the answer array
The time complexity is
Similar problems:
class Solution:
def distanceToCycle(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
g = defaultdict(set)
for a, b in edges:
g[a].add(b)
g[b].add(a)
q = deque(i for i in range(n) if len(g[i]) == 1)
f = [0] * n
seq = []
while q:
i = q.popleft()
seq.append(i)
for j in g[i]:
g[j].remove(i)
f[i] = j
if len(g[j]) == 1:
q.append(j)
g[i].clear()
ans = [0] * n
for i in seq[::-1]:
ans[i] = ans[f[i]] + 1
return ansclass Solution {
public int[] distanceToCycle(int n, int[][] edges) {
Set<Integer>[] g = new Set[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new HashSet<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (g[i].size() == 1) {
q.offer(i);
}
}
int[] f = new int[n];
Deque<Integer> seq = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int i = q.poll();
seq.push(i);
for (int j : g[i]) {
g[j].remove(i);
f[i] = j;
if (g[j].size() == 1) {
q.offer(j);
}
}
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
while (!seq.isEmpty()) {
int i = seq.pop();
ans[i] = ans[f[i]] + 1;
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> distanceToCycle(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
unordered_set<int> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].insert(b);
g[b].insert(a);
}
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (g[i].size() == 1) {
q.push(i);
}
}
int f[n];
int seq[n];
int k = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int i = q.front();
q.pop();
seq[k++] = i;
for (int j : g[i]) {
g[j].erase(i);
f[i] = j;
if (g[j].size() == 1) {
q.push(j);
}
}
g[i].clear();
}
vector<int> ans(n);
for (; k; --k) {
int i = seq[k - 1];
ans[i] = ans[f[i]] + 1;
}
return ans;
}
};func distanceToCycle(n int, edges [][]int) []int {
g := make([]map[int]bool, n)
for i := range g {
g[i] = map[int]bool{}
}
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a][b] = true
g[b][a] = true
}
q := []int{}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if len(g[i]) == 1 {
q = append(q, i)
}
}
f := make([]int, n)
seq := []int{}
for len(q) > 0 {
i := q[0]
q = q[1:]
seq = append(seq, i)
for j := range g[i] {
delete(g[j], i)
f[i] = j
if len(g[j]) == 1 {
q = append(q, j)
}
}
g[i] = map[int]bool{}
}
ans := make([]int, n)
for k := len(seq) - 1; k >= 0; k-- {
i := seq[k]
ans[i] = ans[f[i]] + 1
}
return ans
}function distanceToCycle(n: number, edges: number[][]): number[] {
const g: Set<number>[] = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Set<number>());
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
const q: number[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (g[i].size === 1) {
q.push(i);
}
}
const f: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
const seq: number[] = [];
while (q.length) {
const i = q.pop()!;
seq.push(i);
for (const j of g[i]) {
g[j].delete(i);
f[i] = j;
if (g[j].size === 1) {
q.push(j);
}
}
g[i].clear();
}
const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
while (seq.length) {
const i = seq.pop()!;
ans[i] = ans[f[i]] + 1;
}
return ans;
}