| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2195 |
Weekly Contest 323 Q4 |
|
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid and an array queries of size k.
Find an array answer of size k such that for each integer queries[i] you start in the top left cell of the matrix and repeat the following process:
- If
queries[i]is strictly greater than the value of the current cell that you are in, then you get one point if it is your first time visiting this cell, and you can move to any adjacent cell in all4directions: up, down, left, and right. - Otherwise, you do not get any points, and you end this process.
After the process, answer[i] is the maximum number of points you can get. Note that for each query you are allowed to visit the same cell multiple times.
Return the resulting array answer.
Example 1:
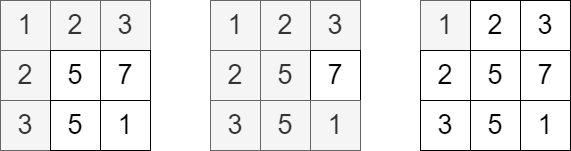
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[2,5,7],[3,5,1]], queries = [5,6,2] Output: [5,8,1] Explanation: The diagrams above show which cells we visit to get points for each query.
Example 2:
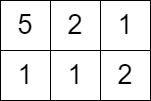
Input: grid = [[5,2,1],[1,1,2]], queries = [3] Output: [0] Explanation: We can not get any points because the value of the top left cell is already greater than or equal to 3.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 105k == queries.length1 <= k <= 1041 <= grid[i][j], queries[i] <= 106
According to the problem description, each query is independent, the order of the queries does not affect the result, and we are required to start from the top left corner each time, counting the number of cells that can be accessed and whose value is less than the current query value.
Therefore, we can first sort the queries array, and then process each query in ascending order.
We use a priority queue (min heap) to maintain the smallest cell value that we have currently accessed, and use an array or hash table vis to record whether the current cell has been visited. Initially, we add the data vis[0][0] to True.
For each query queries[i], we judge whether the minimum value of the current priority queue is less than queries[i]. If it is, we pop the current minimum value, increment the counter cnt, and add the four cells above, below, left, and right of the current cell to the priority queue, noting to check whether they have been visited. Repeat the above operation until the minimum value of the current priority queue is greater than or equal to queries[i], at which point cnt is the answer to the current query.
The time complexity is queries array, which has a time complexity of
class Solution:
def maxPoints(self, grid: List[List[int]], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
qs = sorted((v, i) for i, v in enumerate(queries))
ans = [0] * len(qs)
q = [(grid[0][0], 0, 0)]
cnt = 0
vis = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
vis[0][0] = True
for v, k in qs:
while q and q[0][0] < v:
_, i, j = heappop(q)
cnt += 1
for a, b in pairwise((-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and not vis[x][y]:
heappush(q, (grid[x][y], x, y))
vis[x][y] = True
ans[k] = cnt
return ansclass Solution {
public int[] maxPoints(int[][] grid, int[] queries) {
int k = queries.length;
int[][] qs = new int[k][2];
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
qs[i] = new int[] {queries[i], i};
}
Arrays.sort(qs, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int[] ans = new int[k];
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
vis[0][0] = true;
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
q.offer(new int[] {grid[0][0], 0, 0});
int[] dirs = new int[] {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
int cnt = 0;
for (var e : qs) {
int v = e[0];
k = e[1];
while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek()[0] < v) {
var p = q.poll();
++cnt;
for (int h = 0; h < 4; ++h) {
int x = p[1] + dirs[h], y = p[2] + dirs[h + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y]) {
vis[x][y] = true;
q.offer(new int[] {grid[x][y], x, y});
}
}
}
ans[k] = cnt;
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
const int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
vector<int> maxPoints(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<int>& queries) {
int k = queries.size();
vector<pair<int, int>> qs(k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) qs[i] = {queries[i], i};
sort(qs.begin(), qs.end());
vector<int> ans(k);
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
bool vis[m][n];
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
vis[0][0] = true;
priority_queue<tuple<int, int, int>, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>, greater<tuple<int, int, int>>> q;
q.push({grid[0][0], 0, 0});
int cnt = 0;
for (auto& e : qs) {
int v = e.first;
k = e.second;
while (!q.empty() && get<0>(q.top()) < v) {
auto [_, i, j] = q.top();
q.pop();
++cnt;
for (int h = 0; h < 4; ++h) {
int x = i + dirs[h], y = j + dirs[h + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y]) {
vis[x][y] = true;
q.push({grid[x][y], x, y});
}
}
}
ans[k] = cnt;
}
return ans;
}
};func maxPoints(grid [][]int, queries []int) []int {
k := len(queries)
qs := make([]pair, k)
for i, v := range queries {
qs[i] = pair{v, i}
}
sort.Slice(qs, func(i, j int) bool { return qs[i].v < qs[j].v })
ans := make([]int, k)
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
q := hp{}
heap.Push(&q, tuple{grid[0][0], 0, 0})
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
vis := map[int]bool{0: true}
cnt := 0
for _, e := range qs {
v := e.v
k = e.i
for len(q) > 0 && q[0].v < v {
p := heap.Pop(&q).(tuple)
i, j := p.i, p.j
cnt++
for h := 0; h < 4; h++ {
x, y := i+dirs[h], j+dirs[h+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x*n+y] {
vis[x*n+y] = true
heap.Push(&q, tuple{grid[x][y], x, y})
}
}
}
ans[k] = cnt
}
return ans
}
type pair struct{ v, i int }
type tuple struct{ v, i, j int }
type hp []tuple
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].v < h[j].v }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(tuple)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }