| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
2368 |
Biweekly Contest 97 Q4 |
|
You are given a 0-indexed m x n binary matrix grid. You can move from a cell (row, col) to any of the cells (row + 1, col) or (row, col + 1) that has the value 1. The matrix is disconnected if there is no path from (0, 0) to (m - 1, n - 1).
You can flip the value of at most one (possibly none) cell. You cannot flip the cells (0, 0) and (m - 1, n - 1).
Return true if it is possible to make the matrix disconnect or false otherwise.
Note that flipping a cell changes its value from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0.
Example 1:
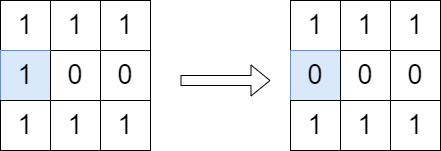
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[1,0,0],[1,1,1]] Output: true Explanation: We can change the cell shown in the diagram above. There is no path from (0, 0) to (2, 2) in the resulting grid.
Example 2:
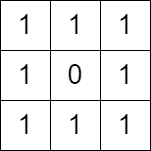
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] Output: false Explanation: It is not possible to change at most one cell such that there is not path from (0, 0) to (2, 2).
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10001 <= m * n <= 105grid[i][j]is either0or1.grid[0][0] == grid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1
First, we perform a DFS traversal to determine whether there is a path from
Next, we set the values of
Finally, if both true, we return false, otherwise, we return true.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def isPossibleToCutPath(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
def dfs(i, j):
if i >= m or j >= n or grid[i][j] == 0:
return False
grid[i][j] = 0
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return True
return dfs(i + 1, j) or dfs(i, j + 1)
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
a = dfs(0, 0)
grid[0][0] = grid[-1][-1] = 1
b = dfs(0, 0)
return not (a and b)class Solution {
private int[][] grid;
private int m;
private int n;
public boolean isPossibleToCutPath(int[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
boolean a = dfs(0, 0);
grid[0][0] = 1;
grid[m - 1][n - 1] = 1;
boolean b = dfs(0, 0);
return !(a && b);
}
private boolean dfs(int i, int j) {
if (i >= m || j >= n || grid[i][j] == 0) {
return false;
}
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return true;
}
grid[i][j] = 0;
return dfs(i + 1, j) || dfs(i, j + 1);
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool isPossibleToCutPath(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
function<bool(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int j) -> bool {
if (i >= m || j >= n || grid[i][j] == 0) {
return false;
}
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return true;
}
grid[i][j] = 0;
return dfs(i + 1, j) || dfs(i, j + 1);
};
bool a = dfs(0, 0);
grid[0][0] = grid[m - 1][n - 1] = 1;
bool b = dfs(0, 0);
return !(a && b);
}
};func isPossibleToCutPath(grid [][]int) bool {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
var dfs func(i, j int) bool
dfs = func(i, j int) bool {
if i >= m || j >= n || grid[i][j] == 0 {
return false
}
if i == m-1 && j == n-1 {
return true
}
grid[i][j] = 0
return dfs(i+1, j) || dfs(i, j+1)
}
a := dfs(0, 0)
grid[0][0], grid[m-1][n-1] = 1, 1
b := dfs(0, 0)
return !(a && b)
}function isPossibleToCutPath(grid: number[][]): boolean {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
const dfs = (i: number, j: number): boolean => {
if (i >= m || j >= n || grid[i][j] !== 1) {
return false;
}
grid[i][j] = 0;
if (i === m - 1 && j === n - 1) {
return true;
}
return dfs(i + 1, j) || dfs(i, j + 1);
};
const a = dfs(0, 0);
grid[0][0] = 1;
grid[m - 1][n - 1] = 1;
const b = dfs(0, 0);
return !(a && b);
}