| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
|
You are given the root of a binary tree and an integer k. Besides the left and right children, every node of this tree has two other properties, a string node.val containing only lowercase English letters (possibly empty) and a non-negative integer node.len. There are two types of nodes in this tree:
- Leaf: These nodes have no children,
node.len = 0, andnode.valis some non-empty string. - Internal: These nodes have at least one child (also at most two children),
node.len > 0, andnode.valis an empty string.
The tree described above is called a Rope binary tree. Now we define S[node] recursively as follows:
- If
nodeis some leaf node,S[node] = node.val, - Otherwise if
nodeis some internal node,S[node] = concat(S[node.left], S[node.right])andS[node].length = node.len.
Return k-th character of the string S[root].
Note: If s and p are two strings, concat(s, p) is a string obtained by concatenating p to s. For example, concat("ab", "zz") = "abzz".
Example 1:
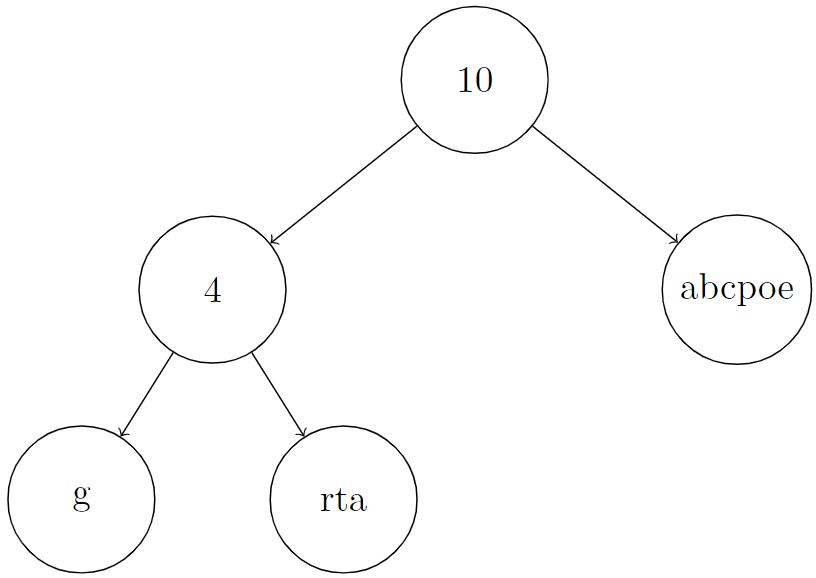
Input: root = [10,4,"abcpoe","g","rta"], k = 6
Output: "b"
Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val.
You can see that S[root] = concat(concat("g", "rta"), "abcpoe") = "grtaabcpoe". So S[root][5], which represents 6th character of it, is equal to "b".
Example 2:
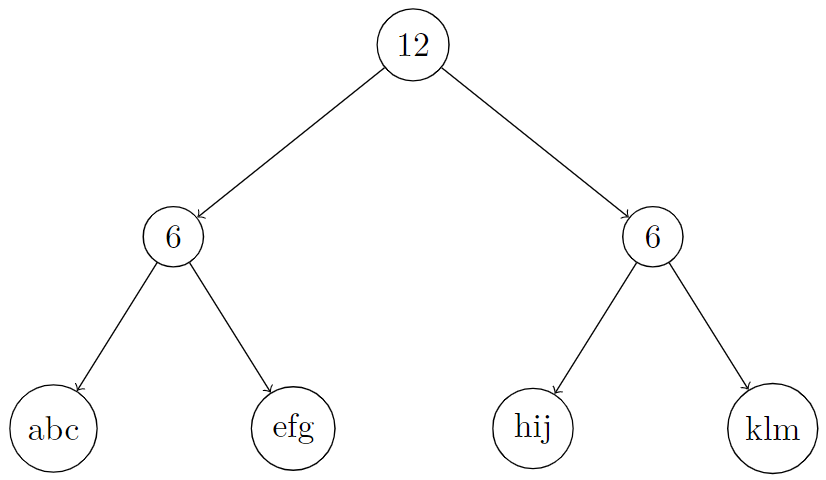
Input: root = [12,6,6,"abc","efg","hij","klm"], k = 3
Output: "c"
Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val.
You can see that S[root] = concat(concat("abc", "efg"), concat("hij", "klm")) = "abcefghijklm". So S[root][2], which represents the 3rd character of it, is equal to "c".
Example 3:
Input: root = ["ropetree"], k = 8 Output: "e" Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val. You can see that S[root] = "ropetree". So S[root][7], which represents 8th character of it, is equal to "e".
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 103] node.valcontains only lowercase English letters0 <= node.val.length <= 500 <= node.len <= 104- for leaf nodes,
node.len = 0andnode.valis non-empty - for internal nodes,
node.len > 0andnode.valis empty 1 <= k <= S[root].length
# Definition for a rope tree node.
# class RopeTreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, len=0, val="", left=None, right=None):
# self.len = len
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getKthCharacter(self, root: Optional[object], k: int) -> str:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return ""
if root.len == 0:
return root.val
return dfs(root.left) + dfs(root.right)
return dfs(root)[k - 1]/**
* Definition for a rope tree node.
* class RopeTreeNode {
* int len;
* String val;
* RopeTreeNode left;
* RopeTreeNode right;
* RopeTreeNode() {}
* RopeTreeNode(String val) {
* this.len = 0;
* this.val = val;
* }
* RopeTreeNode(int len) {
* this.len = len;
* this.val = "";
* }
* RopeTreeNode(int len, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.len = len;
* this.val = "";
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public char getKthCharacter(RopeTreeNode root, int k) {
return dfs(root).charAt(k - 1);
}
private String dfs(RopeTreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "";
}
if (root.val.length() > 0) {
return root.val;
}
String left = dfs(root.left);
String right = dfs(root.right);
return left + right;
}
}/**
* Definition for a rope tree node.
* struct RopeTreeNode {
* int len;
* string val;
* RopeTreeNode *left;
* RopeTreeNode *right;
* RopeTreeNode() : len(0), val(""), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* RopeTreeNode(string s) : len(0), val(std::move(s)), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* RopeTreeNode(int x) : len(x), val(""), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* RopeTreeNode(int x, RopeTreeNode *left, RopeTreeNode *right) : len(x), val(""), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
char getKthCharacter(RopeTreeNode* root, int k) {
function<string(RopeTreeNode * root)> dfs = [&](RopeTreeNode* root) -> string {
if (root == nullptr) {
return "";
}
if (root->len == 0) {
return root->val;
}
string left = dfs(root->left);
string right = dfs(root->right);
return left + right;
};
return dfs(root)[k - 1];
}
};/**
* Definition for a rope tree node.
* type RopeTreeNode struct {
* len int
* val string
* left *RopeTreeNode
* right *RopeTreeNode
* }
*/
func getKthCharacter(root *RopeTreeNode, k int) byte {
var dfs func(root *RopeTreeNode) string
dfs = func(root *RopeTreeNode) string {
if root == nil {
return ""
}
if root.len == 0 {
return root.val
}
left, right := dfs(root.left), dfs(root.right)
return left + right
}
return dfs(root)[k-1]
}