| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given a 0-indexed integer 2D array nodes, your task is to determine if the given array represents the preorder traversal of some binary tree.
For each index i, nodes[i] = [id, parentId], where id is the id of the node at the index i and parentId is the id of its parent in the tree (if the node has no parent, then parentId == -1).
Return true if the given array represents the preorder traversal of some tree, and false otherwise.
Note: the preorder traversal of a tree is a recursive way to traverse a tree in which we first visit the current node, then we do the preorder traversal for the left child, and finally, we do it for the right child.
Example 1:
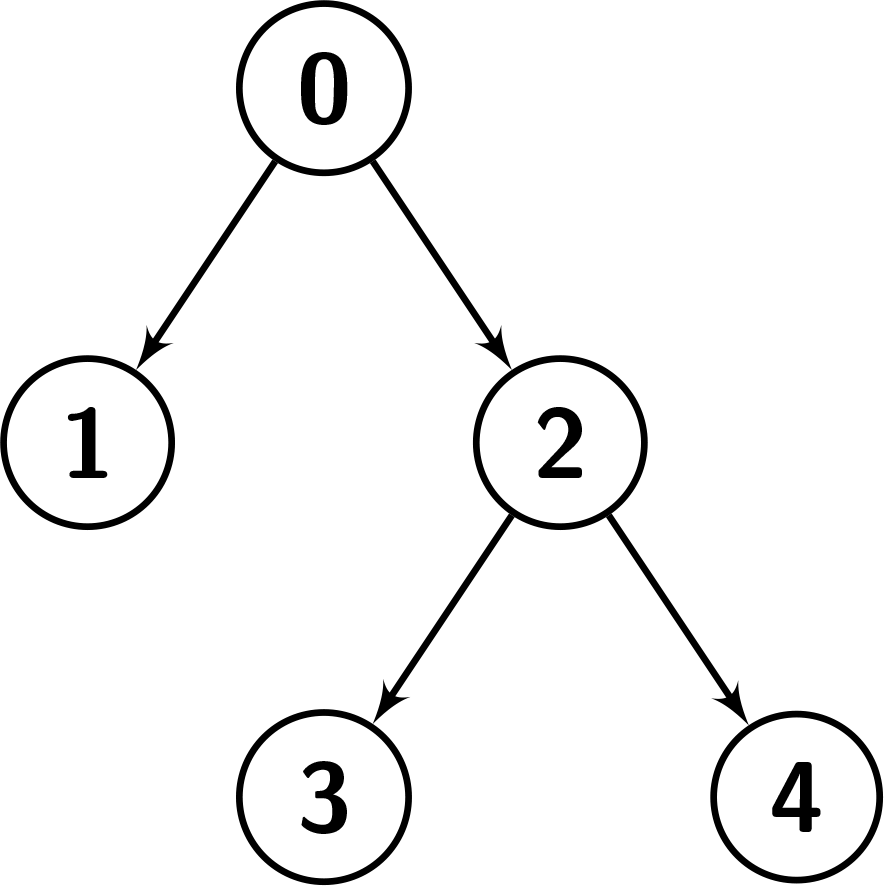
Input: nodes = [[0,-1],[1,0],[2,0],[3,2],[4,2]] Output: true Explanation: The given nodes make the tree in the picture below. We can show that this is the preorder traversal of the tree, first we visit node 0, then we do the preorder traversal of the right child which is [1], then we do the preorder traversal of the left child which is [2,3,4].
Example 2:
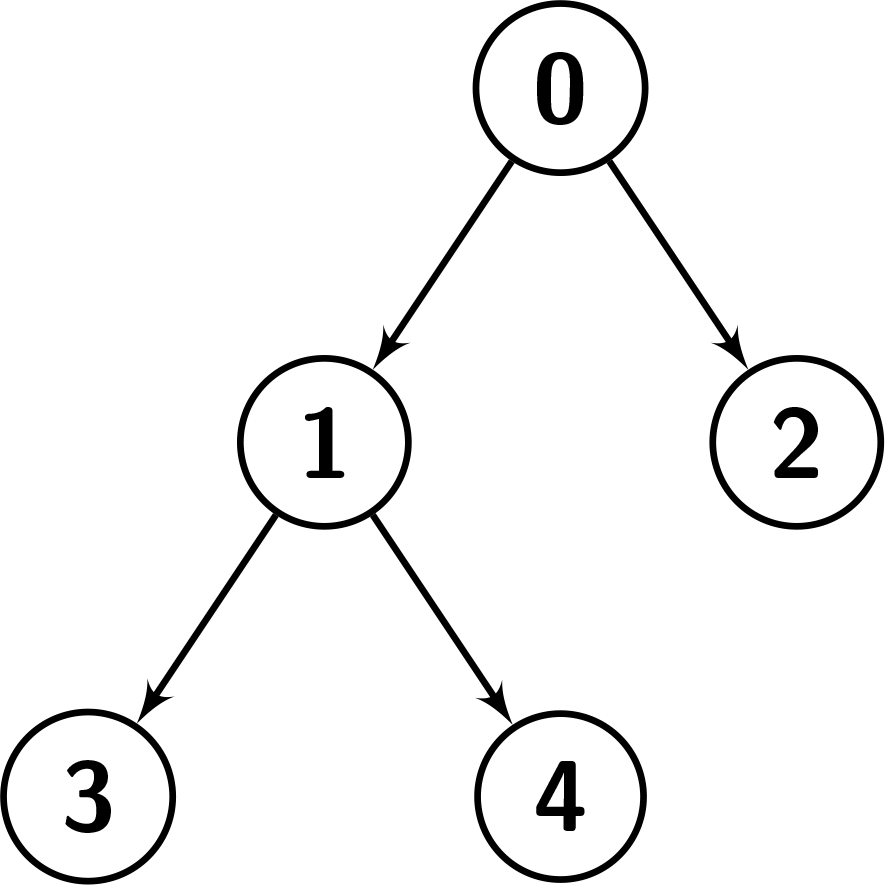
Input: nodes = [[0,-1],[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[4,1]] Output: false Explanation: The given nodes make the tree in the picture below. For the preorder traversal, first we visit node 0, then we do the preorder traversal of the right child which is [1,3,4], but we can see that in the given order, 2 comes between 1 and 3, so, it's not the preorder traversal of the tree.
Constraints:
1 <= nodes.length <= 105nodes[i].length == 20 <= nodes[i][0] <= 105-1 <= nodes[i][1] <= 105- The input is generated such that
nodesmake a binary tree.
class Solution:
def isPreorder(self, nodes: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
def dfs(i: int) -> int:
nonlocal k
if i != nodes[k][0]:
return False
k += 1
return all(dfs(j) for j in g[i])
g = defaultdict(list)
for i, p in nodes:
g[p].append(i)
k = 0
return dfs(nodes[0][0]) and k == len(nodes)class Solution {
private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>();
private List<List<Integer>> nodes;
private int k;
public boolean isPreorder(List<List<Integer>> nodes) {
this.nodes = nodes;
for (var node : nodes) {
g.computeIfAbsent(node.get(1), key -> new ArrayList<>()).add(node.get(0));
}
return dfs(nodes.get(0).get(0)) && k == nodes.size();
}
private boolean dfs(int i) {
if (i != nodes.get(k).get(0)) {
return false;
}
++k;
for (int j : g.getOrDefault(i, List.of())) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool isPreorder(vector<vector<int>>& nodes) {
int k = 0;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> g;
for (auto& node : nodes) {
g[node[1]].push_back(node[0]);
}
function<bool(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i != nodes[k][0]) {
return false;
}
++k;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
return dfs(nodes[0][0]) && k == nodes.size();
}
};func isPreorder(nodes [][]int) bool {
k := 0
g := map[int][]int{}
for _, node := range nodes {
g[node[1]] = append(g[node[1]], node[0])
}
var dfs func(int) bool
dfs = func(i int) bool {
if i != nodes[k][0] {
return false
}
k++
for _, j := range g[i] {
if !dfs(j) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
return dfs(nodes[0][0]) && k == len(nodes)
}function isPreorder(nodes: number[][]): boolean {
let k = 0;
const g: Map<number, number[]> = new Map();
for (const [i, p] of nodes) {
if (!g.has(p)) {
g.set(p, []);
}
g.get(p)!.push(i);
}
const dfs = (i: number): boolean => {
if (i !== nodes[k][0]) {
return false;
}
++k;
for (const j of g.get(i) ?? []) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
return dfs(nodes[0][0]) && k === nodes.length;
}