| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2093 |
Weekly Contest 394 Q4 |
|
You are given an undirected weighted graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The graph consists of m edges represented by a 2D array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi with weight wi.
Consider all the shortest paths from node 0 to node n - 1 in the graph. You need to find a boolean array answer where answer[i] is true if the edge edges[i] is part of at least one shortest path. Otherwise, answer[i] is false.
Return the array answer.
Note that the graph may not be connected.
Example 1:
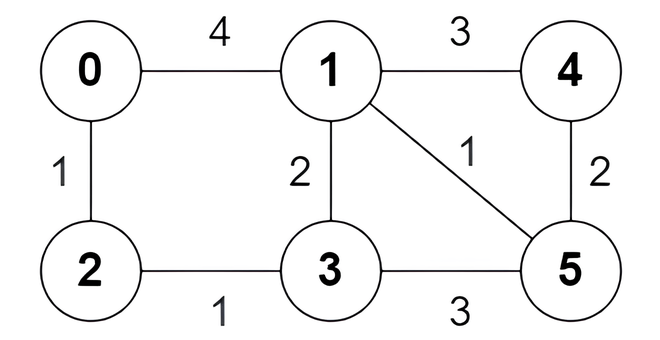
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1,4],[0,2,1],[1,3,2],[1,4,3],[1,5,1],[2,3,1],[3,5,3],[4,5,2]]
Output: [true,true,true,false,true,true,true,false]
Explanation:
The following are all the shortest paths between nodes 0 and 5:
- The path
0 -> 1 -> 5: The sum of weights is4 + 1 = 5. - The path
0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5: The sum of weights is1 + 1 + 3 = 5. - The path
0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1 -> 5: The sum of weights is1 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 5.
Example 2:
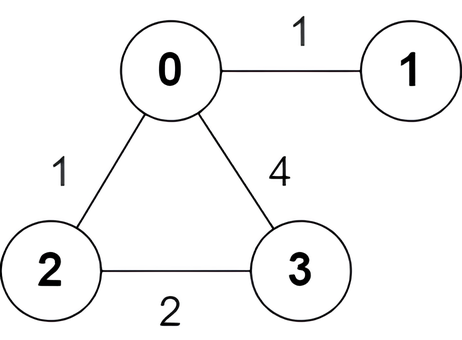
Input: n = 4, edges = [[2,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,3,4],[3,2,2]]
Output: [true,false,false,true]
Explanation:
There is one shortest path between nodes 0 and 3, which is the path 0 -> 2 -> 3 with the sum of weights 1 + 2 = 3.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 104m == edges.length1 <= m <= min(5 * 104, n * (n - 1) / 2)0 <= ai, bi < nai != bi1 <= wi <= 105- There are no repeated edges.
First, we create an adjacency list
Then, we use the Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the shortest distance from node
- Create a priority queue
$q$ to store the distance and node number of the nodes. Initially, add node$0$ to the queue with a distance of$0$ . - Take a node
$a$ from the queue. If the distance$da$ of$a$ is greater than$dist[a]$ , it means that$a$ has been updated, so skip it directly. - Traverse all neighbor nodes
$b$ of node$a$ . If$dist[b] > dist[a] + w$ , update$dist[b] = dist[a] + w$ , and add node$b$ to the queue. - Repeat steps 2 and 3 until the queue is empty.
Next, we create an answer array
Finally, return the answer.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def findAnswer(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[bool]:
g = defaultdict(list)
for i, (a, b, w) in enumerate(edges):
g[a].append((b, w, i))
g[b].append((a, w, i))
dist = [inf] * n
dist[0] = 0
q = [(0, 0)]
while q:
da, a = heappop(q)
if da > dist[a]:
continue
for b, w, _ in g[a]:
if dist[b] > dist[a] + w:
dist[b] = dist[a] + w
heappush(q, (dist[b], b))
m = len(edges)
ans = [False] * m
if dist[n - 1] == inf:
return ans
q = deque([n - 1])
while q:
a = q.popleft()
for b, w, i in g[a]:
if dist[a] == dist[b] + w:
ans[i] = True
q.append(b)
return ansclass Solution {
public boolean[] findAnswer(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<int[]>[] g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
int m = edges.length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int a = edges[i][0], b = edges[i][1], w = edges[i][2];
g[a].add(new int[] {b, w, i});
g[b].add(new int[] {a, w, i});
}
int[] dist = new int[n];
final int inf = 1 << 30;
Arrays.fill(dist, inf);
dist[0] = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
pq.offer(new int[] {0, 0});
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
var p = pq.poll();
int da = p[0], a = p[1];
if (da > dist[a]) {
continue;
}
for (var e : g[a]) {
int b = e[0], w = e[1];
if (dist[b] > dist[a] + w) {
dist[b] = dist[a] + w;
pq.offer(new int[] {dist[b], b});
}
}
}
boolean[] ans = new boolean[m];
if (dist[n - 1] == inf) {
return ans;
}
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(n - 1);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int a = q.poll();
for (var e : g[a]) {
int b = e[0], w = e[1], i = e[2];
if (dist[a] == dist[b] + w) {
ans[i] = true;
q.offer(b);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<bool> findAnswer(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<array<int, 3>>> g(n);
int m = edges.size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
auto e = edges[i];
int a = e[0], b = e[1], w = e[2];
g[a].push_back({b, w, i});
g[b].push_back({a, w, i});
}
const int inf = 1 << 30;
vector<int> dist(n, inf);
dist[0] = 0;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii>> pq;
pq.push({0, 0});
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [da, a] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (da > dist[a]) {
continue;
}
for (auto [b, w, _] : g[a]) {
if (dist[b] > dist[a] + w) {
dist[b] = dist[a] + w;
pq.push({dist[b], b});
}
}
}
vector<bool> ans(m);
if (dist[n - 1] == inf) {
return ans;
}
queue<int> q{{n - 1}};
while (!q.empty()) {
int a = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto [b, w, i] : g[a]) {
if (dist[a] == dist[b] + w) {
ans[i] = true;
q.push(b);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func findAnswer(n int, edges [][]int) []bool {
g := make([][][3]int, n)
for i, e := range edges {
a, b, w := e[0], e[1], e[2]
g[a] = append(g[a], [3]int{b, w, i})
g[b] = append(g[b], [3]int{a, w, i})
}
dist := make([]int, n)
const inf int = 1 << 30
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = inf
}
dist[0] = 0
pq := hp{{0, 0}}
for len(pq) > 0 {
p := heap.Pop(&pq).(pair)
da, a := p.dis, p.u
if da > dist[a] {
continue
}
for _, e := range g[a] {
b, w := e[0], e[1]
if dist[b] > dist[a]+w {
dist[b] = dist[a] + w
heap.Push(&pq, pair{dist[b], b})
}
}
}
ans := make([]bool, len(edges))
if dist[n-1] == inf {
return ans
}
q := []int{n - 1}
for len(q) > 0 {
a := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for _, e := range g[a] {
b, w, i := e[0], e[1], e[2]
if dist[a] == dist[b]+w {
ans[i] = true
q = append(q, b)
}
}
}
return ans
}
type pair struct{ dis, u int }
type hp []pair
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].dis < h[j].dis }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(pair)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }