| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1517 |
Biweekly Contest 131 Q3 |
|
You are given an integer limit and a 2D array queries of size n x 2.
There are limit + 1 balls with distinct labels in the range [0, limit]. Initially, all balls are uncolored. For every query in queries that is of the form [x, y], you mark ball x with the color y. After each query, you need to find the number of distinct colors among the balls.
Return an array result of length n, where result[i] denotes the number of distinct colors after ith query.
Note that when answering a query, lack of a color will not be considered as a color.
Example 1:
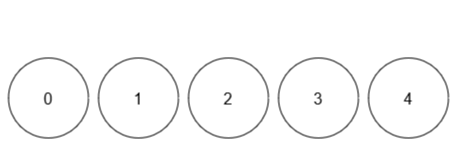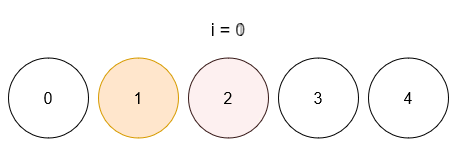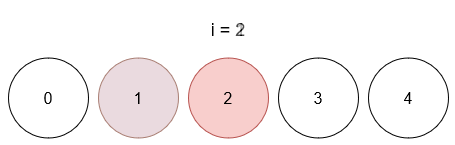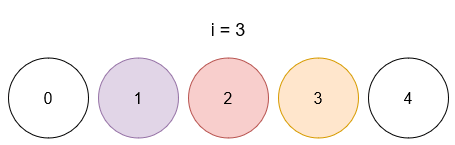
Input: limit = 4, queries = [[1,4],[2,5],[1,3],[3,4]]
Output: [1,2,2,3]
Explanation:
- After query 0, ball 1 has color 4.
- After query 1, ball 1 has color 4, and ball 2 has color 5.
- After query 2, ball 1 has color 3, and ball 2 has color 5.
- After query 3, ball 1 has color 3, ball 2 has color 5, and ball 3 has color 4.
Example 2:
Input: limit = 4, queries = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5]]
Output: [1,2,2,3,4]
Explanation:
- After query 0, ball 0 has color 1.
- After query 1, ball 0 has color 1, and ball 1 has color 2.
- After query 2, ball 0 has color 1, and balls 1 and 2 have color 2.
- After query 3, ball 0 has color 1, balls 1 and 2 have color 2, and ball 3 has color 4.
- After query 4, ball 0 has color 1, balls 1 and 2 have color 2, ball 3 has color 4, and ball 4 has color 5.
Constraints:
1 <= limit <= 1091 <= n == queries.length <= 105queries[i].length == 20 <= queries[i][0] <= limit1 <= queries[i][1] <= 109
We use a hash table g to record the color of each ball, and another hash table cnt to record the count of each color.
Next, we traverse the array queries. For each query cnt. Then, we update the color of ball cnt to the answer array.
After the traversal, we return the answer array.
The time complexity is queries.
class Solution:
def queryResults(self, limit: int, queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
g = {}
cnt = Counter()
ans = []
for x, y in queries:
cnt[y] += 1
if x in g:
cnt[g[x]] -= 1
if cnt[g[x]] == 0:
cnt.pop(g[x])
g[x] = y
ans.append(len(cnt))
return ansclass Solution {
public int[] queryResults(int limit, int[][] queries) {
Map<Integer, Integer> g = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
int m = queries.length;
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int x = queries[i][0], y = queries[i][1];
cnt.merge(y, 1, Integer::sum);
if (g.containsKey(x) && cnt.merge(g.get(x), -1, Integer::sum) == 0) {
cnt.remove(g.get(x));
}
g.put(x, y);
ans[i] = cnt.size();
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> queryResults(int limit, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
unordered_map<int, int> g;
unordered_map<int, int> cnt;
vector<int> ans;
for (auto& q : queries) {
int x = q[0], y = q[1];
cnt[y]++;
if (g.contains(x) && --cnt[g[x]] == 0) {
cnt.erase(g[x]);
}
g[x] = y;
ans.push_back(cnt.size());
}
return ans;
}
};func queryResults(limit int, queries [][]int) (ans []int) {
g := map[int]int{}
cnt := map[int]int{}
for _, q := range queries {
x, y := q[0], q[1]
cnt[y]++
if v, ok := g[x]; ok {
cnt[v]--
if cnt[v] == 0 {
delete(cnt, v)
}
}
g[x] = y
ans = append(ans, len(cnt))
}
return
}function queryResults(limit: number, queries: number[][]): number[] {
const g = new Map<number, number>();
const cnt = new Map<number, number>();
const ans: number[] = [];
for (const [x, y] of queries) {
cnt.set(y, (cnt.get(y) ?? 0) + 1);
if (g.has(x)) {
const v = g.get(x)!;
cnt.set(v, cnt.get(v)! - 1);
if (cnt.get(v) === 0) {
cnt.delete(v);
}
}
g.set(x, y);
ans.push(cnt.size);
}
return ans;
}