| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1341 |
Weekly Contest 406 Q2 |
|
You are given an array of integers nums and the head of a linked list. Return the head of the modified linked list after removing all nodes from the linked list that have a value that exists in nums.
Example 1:
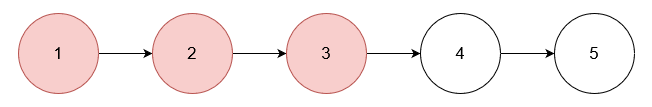
Input: nums = [1,2,3], head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [4,5]
Explanation:
Remove the nodes with values 1, 2, and 3.
Example 2:
Example 3:
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105- All elements in
numsare unique. - The number of nodes in the given list is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- The input is generated such that there is at least one node in the linked list that has a value not present in
nums.
We can use a hash table
Next, we traverse the list starting from the dummy node
Finally, we return the next node of the dummy node
The time complexity is
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def modifiedList(
self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]
) -> Optional[ListNode]:
s = set(nums)
pre = dummy = ListNode(next=head)
while pre.next:
if pre.next.val in s:
pre.next = pre.next.next
else:
pre = pre.next
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
for (int x : nums) {
s.add(x);
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (ListNode pre = dummy; pre.next != null;) {
if (s.contains(pre.next.val)) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
} else {
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {
unordered_set<int> s(nums.begin(), nums.end());
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (ListNode* pre = dummy; pre->next;) {
if (s.count(pre->next->val)) {
pre->next = pre->next->next;
} else {
pre = pre->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func modifiedList(nums []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode {
s := map[int]bool{}
for _, x := range nums {
s[x] = true
}
dummy := &ListNode{Next: head}
for pre := dummy; pre.Next != nil; {
if s[pre.Next.Val] {
pre.Next = pre.Next.Next
} else {
pre = pre.Next
}
}
return dummy.Next
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function modifiedList(nums: number[], head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
const s: Set<number> = new Set(nums);
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (let pre = dummy; pre.next; ) {
if (s.has(pre.next.val)) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
} else {
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}