Link to demo video on Youtube (https://youtu.be/sGAkDtLbkbw)
- 1. Introduction and motivation
- 2. Repository structure
- 3. Data set
- 4. Methodologies
- 5. Evaluation metrics
- 6. Recommendation system
- 7. Resutls
Lately, it has shown the great explosion of entertainment market, especially in music. There are over 60,000 tracks are now uploaded to Spotify every day. It means Spotify is seeing a new track uploaded to its platform every 1.4 seconds [1]. Moreover, previous research [2] has figured out the users preferred listening to music to doing any of other activities as watching television, reading books, and watching movies. This leads to a need of developing a convenient, efficient and user-personalized recommendation system.
DS300.M11 - Recommender system
│ LICENSE
| main.py
│ readme.md
│
└───data/
│ │ content_based/
│ | model_based/
| | private_features/
| | common_fields.txt
| | full_data.csv
| | ...
└───images/
| | ...
| |
└───reports/
│ │ ...
│ |
└───scr/
| |
| └── notebook/ - source code here
│ │ ...
The data set can be found in folder data. There are 2 type of data for content-based method and model-based method.
We employ the Web API provided by Spotify for collecting the track information from this music platform.
With the API, we collect a set of 1781 Vietnamese tracks as the database for our proposed recommendation system.
For the experiments, we continue to collect tracks from 3 Spotify users.
The attributes of a track are classified into 2 types: basis information and acoustic features.
Editorial features: date_added, artists, track_name, id, uri, track_href, analysis_url.
Acoustic features: popularity, danceability, energy, key, loudness, mode, speechiness, acousticness, instrumentalness, liveness, valence, tempo, duration_ms, time_signature.
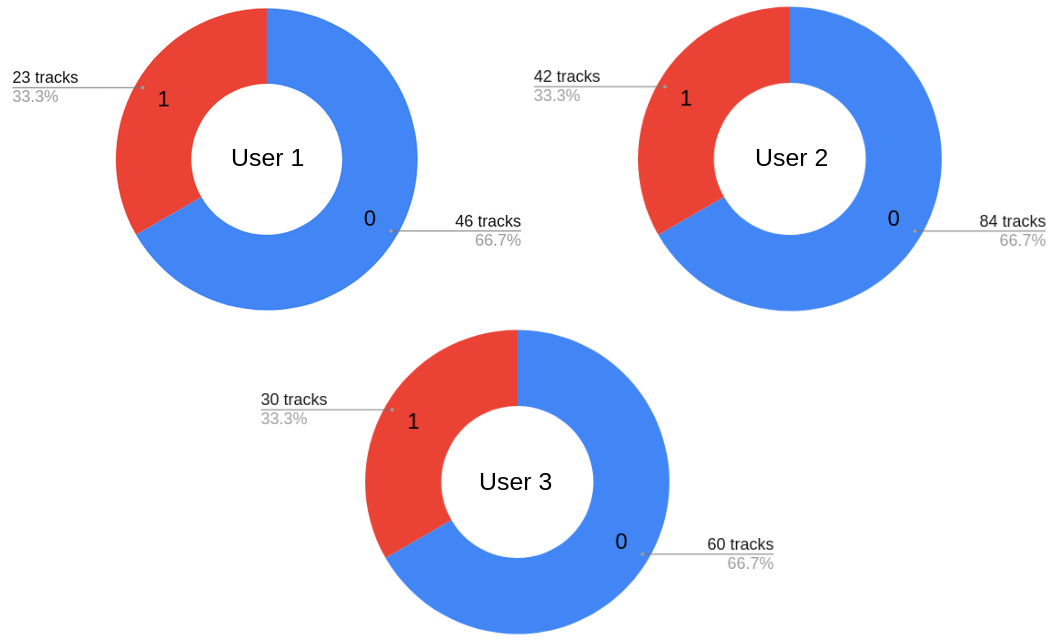
Some statistics of the data:
Content-based method:
User 1: 13 tracks.
User 2: 32 tracks.
User 3: 20 tracks.
Model-based method:
Fig. 1. Label distribution of each users' data.
Content-base method: We experiment on the track_name feature collected from the users' frequently listened track names and acoustic features separately for computing the similarity.
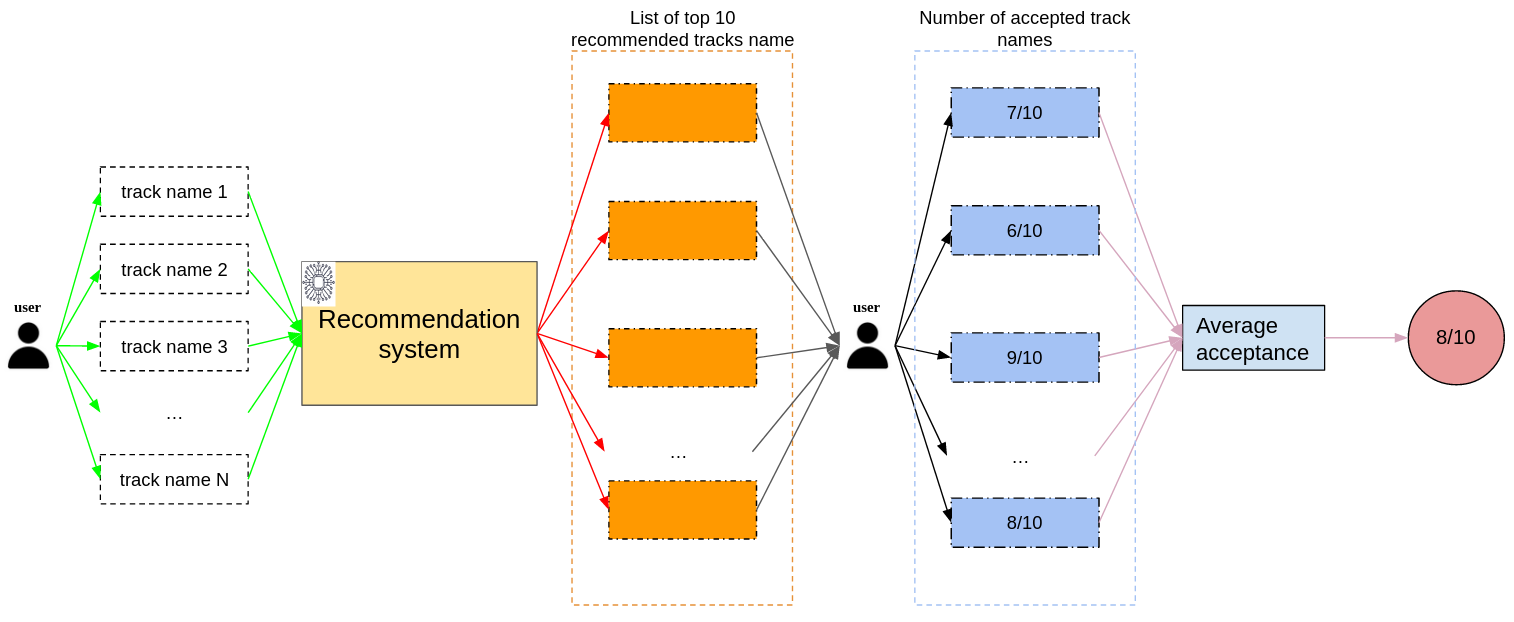
Human evaluation: The list of top 10 recommended track names is given to the user in order to get the feedback. Then,
number of accepted track names are aggregated to have the final evaluation score. The metric pipeline are visualized in
Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Human evaluation pipeline.
k-fold Cross-validation: As the data sets for training machine learning models are small in size. We take advantage of
k-fold Cross-validation in order to train machine learning model.
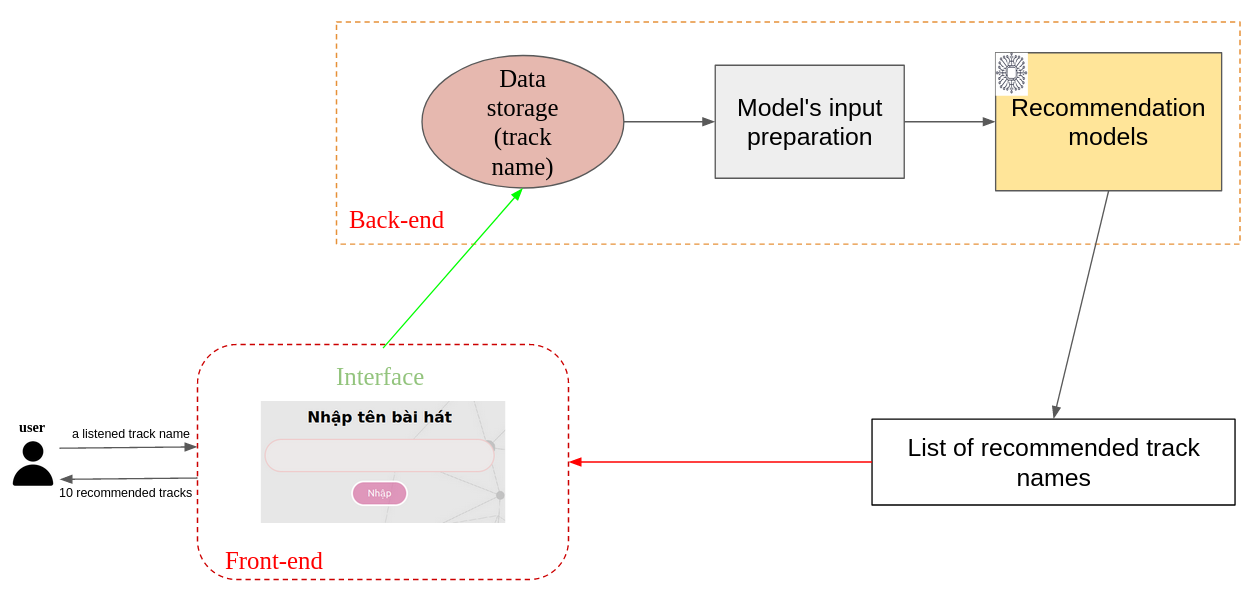
Fig. 3. Web API recommendation system.
Content-based method
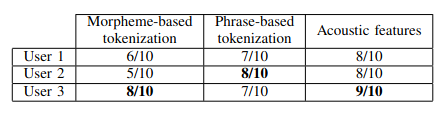
Fig. 4. Human evaluation on 3 types of feature selection.
Model-based method
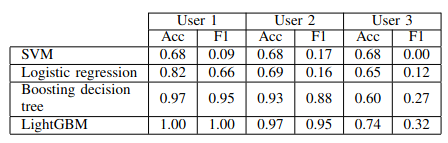
Fig. 5. Accuracy and F1-score after 10-folds Cross-validation.
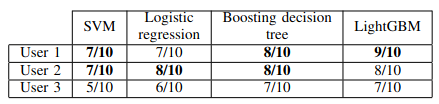
Fig. 6. Human evaluation on 4 models.