You are given the root of a binary tree where each node has a value in the range [0, 25] representing the letters 'a' to 'z'.
Return the lexicographically smallest string that starts at a leaf of this tree and ends at the root.
As a reminder, any shorter prefix of a string is lexicographically smaller.
- For example,
"ab"is lexicographically smaller than"aba".
A leaf of a node is a node that has no children.
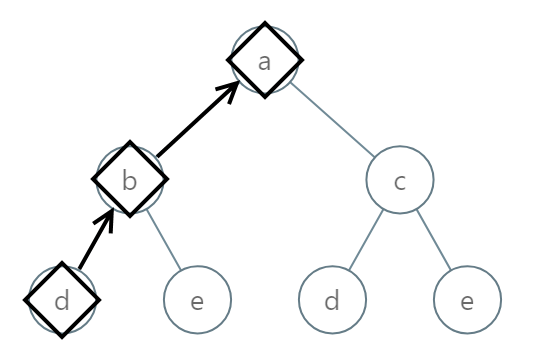
Input: root = [0,1,2,3,4,3,4] Output: "dba"
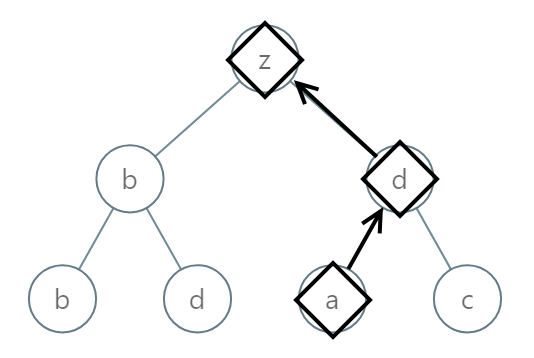
Input: root = [25,1,3,1,3,0,2] Output: "adz"
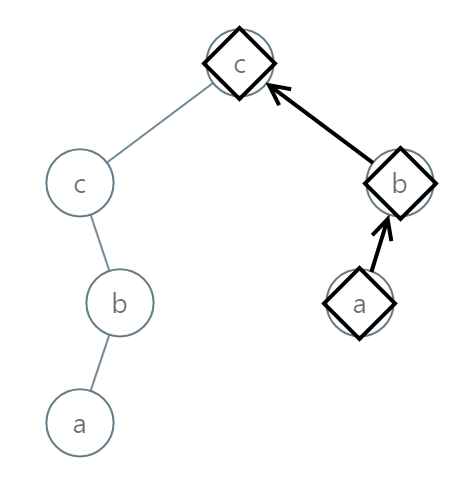
Input: root = [2,2,1,null,1,0,null,0] Output: "abc"
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 8500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 25
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def smallestFromLeaf(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> str:
return self.dfs("", root)
def dfs(self, s: str, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> str:
if root is None:
return s
s = chr(root.val + 97) + s
if root.left is None:
return self.dfs(s, root.right)
elif root.right is None:
return self.dfs(s, root.left)
else:
return min(self.dfs(s, root.left), self.dfs(s, root.right))