In this module, you will:
- Explore common cloud computing services
- Explore the benefits of cloud computing
- Decide which cloud deployment model is best for you
The cloud provider is responsible for the physical hardware required to execute your work, and for keeping it up-to-date. The computing services offered tend to vary by cloud provider. However, typically they include:
- Compute power - such as Linux servers or web applications
- Storage - such as files and databases
- Networking - such as secure connections between the cloud provider and your company
- Analytics - such as visualizing telemetry and performance data
- It's cost-effective: Pay-as-you-go or consumption-based pricing model)
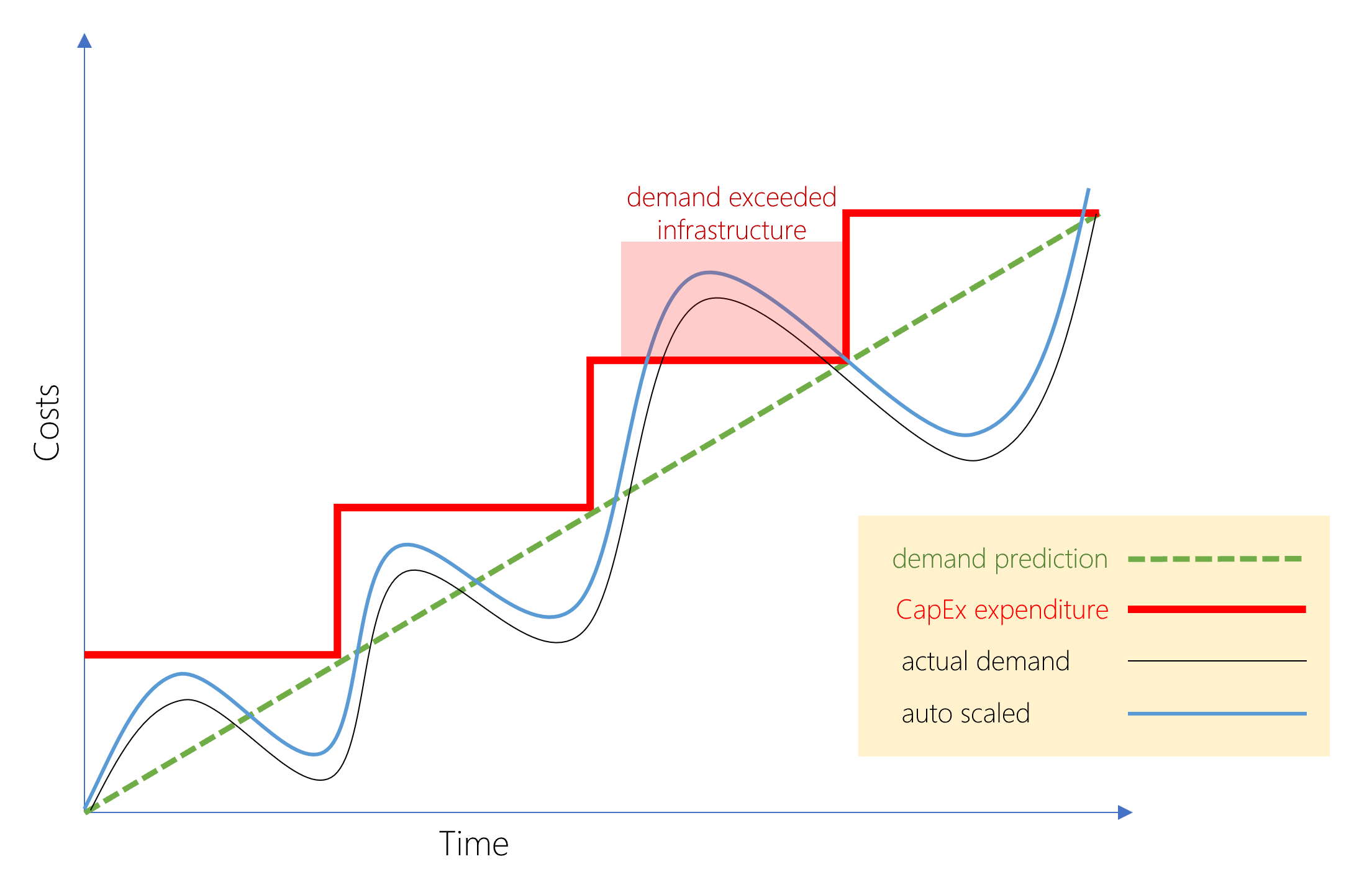
- It's scalable
- Vertical scaling, also known as "scaling up", is the process of adding resources to increase the power of an existing server.
- Horizontal scaling, also known as "scaling out", is the process of adding more servers that function together as one unit.
- It's elastic: Dynamic scaling
- It's current: Maintained and upgraded by the cloud provider
- It's reliable: Fault tolerance
- It's global: Fully redundant datacenters located in various regions all over the globe
- It's secure: Broad set of policies, technologies, controls, and expert technical skills
Compliance Offerings
- Criminal Justice Information Services (CJIS)
- Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) STAR Certification
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) EU Model Clauses
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- Multi-Tier Cloud Security (MTCS) Singapore
- Service Organization Controls (SOC) 1, 2, and 3
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
- UK Government G-Cloud
Economies of scale is the ability to do things more efficiently or at a lower-cost per unit when operating at a larger scale. This cost advantage is an important benefit in cloud computing.
- Server costs
- Storage costs
- Backup and archive costs
- Organization continuity and disaster recovery costs
- Datacenter infrastructure costs
- Technical personnel
- Leasing software and customized features
- Scaling charges based on usage/demand instead of fixed hardware or capacity
- Billing at the user or organization level
- Public cloud: You have no local hardware to manage or keep up-to-date everything runs on your cloud provider's hardware.
- Private cloud: You create a cloud environment in your own datacenter and provide self-service access to compute resources to users in your organization.
- Hybrid cloud: You combine public and private clouds, allowing you to run your applications in the most appropriate location.
Infrastructure as a Service is the most flexible category of cloud services. It aims to give you the most control over the provided hardware that runs your application (IT infrastructure servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, and operating systems). Instead of buying hardware, with IaaS, you rent it.
When using IaaS, ensuring that a service is up and running is a shared responsibility: the cloud provider is responsible for ensuring the cloud infrastructure is functioning correctly; the cloud customer is responsible for ensuring the service they are using is configured correctly, is up to date, and is available to their customers. This is referred to as the shared responsibility model.
PaaS provides an environment for building, testing, and deploying software applications. The goal of PaaS is to help you create an application quickly without managing the underlying infrastructure. For example, when deploying a web application using PaaS, you don't have to install an operating system, web server, or even system updates.
SaaS is software that is centrally hosted and managed for the end customer. It is usually based on an architecture where one version of the application is used for all customers, and licensed through a monthly or annual subscription. Office 365, Skype, and Dynamics CRM Online are perfect examples of SaaS software.
-
Which term from the list below would be viewed as benefits of using cloud services?
- Unpredictable costs
- Elasticity
- Local reach only
-
Suppose you have two types of applications: legacy applications that require specialized mainframe hardware and newer applications that can run on commodity hardware. Which cloud deployment model would be best for you?
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
-
You're developing an application and want to focus on building, testing, and deploying. You don't want to worry about managing the underlying hardware or software. Which cloud service type is best for you?
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Different types of cloud models that are available and the considerations of using those different models.
- Some of the key terms and concepts such as high availability, agility, elasticity, fault tolerance, and CapEx vs. OpEx.
- The different cloud services available, the benefits of using the different types, and the management responsibilities under each service type.
- Cloud models such as public, private and hybrid, and what the key characteristics of each model are.
- The different types of cloud service available: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS; what the key characteristics of each service are and when you would choose one over the other.