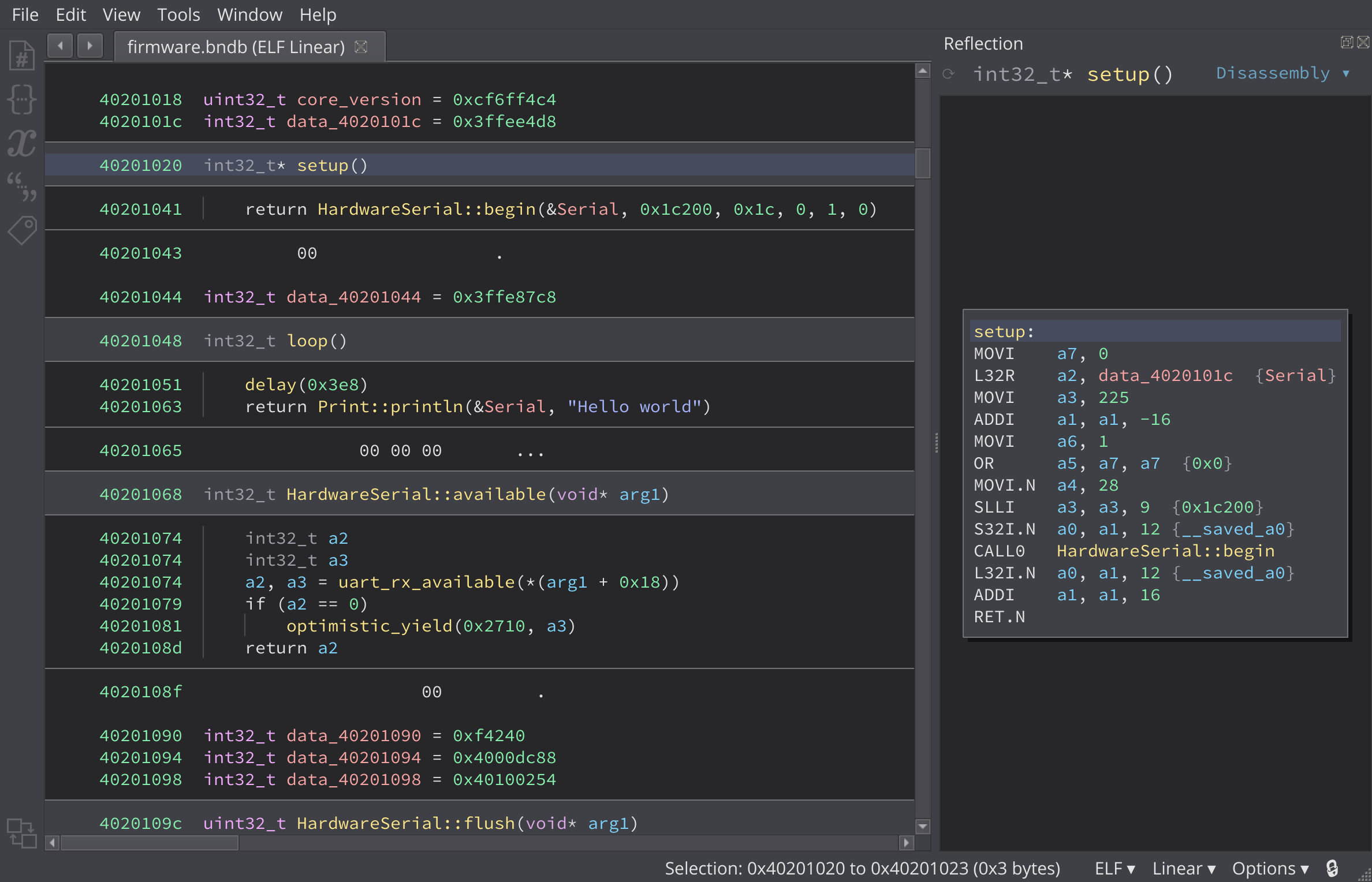
Tensilica Xtensa Architecture Plugin and ESP8266 Firmware Loader for Binary Ninja.
- Disassembly of nearly all Xtensa instructions
- Lifting for most Xtensa instructions you'll see in ESP8266 Firmware
- Support for Xtensa ELF files so they will be automatically recognized
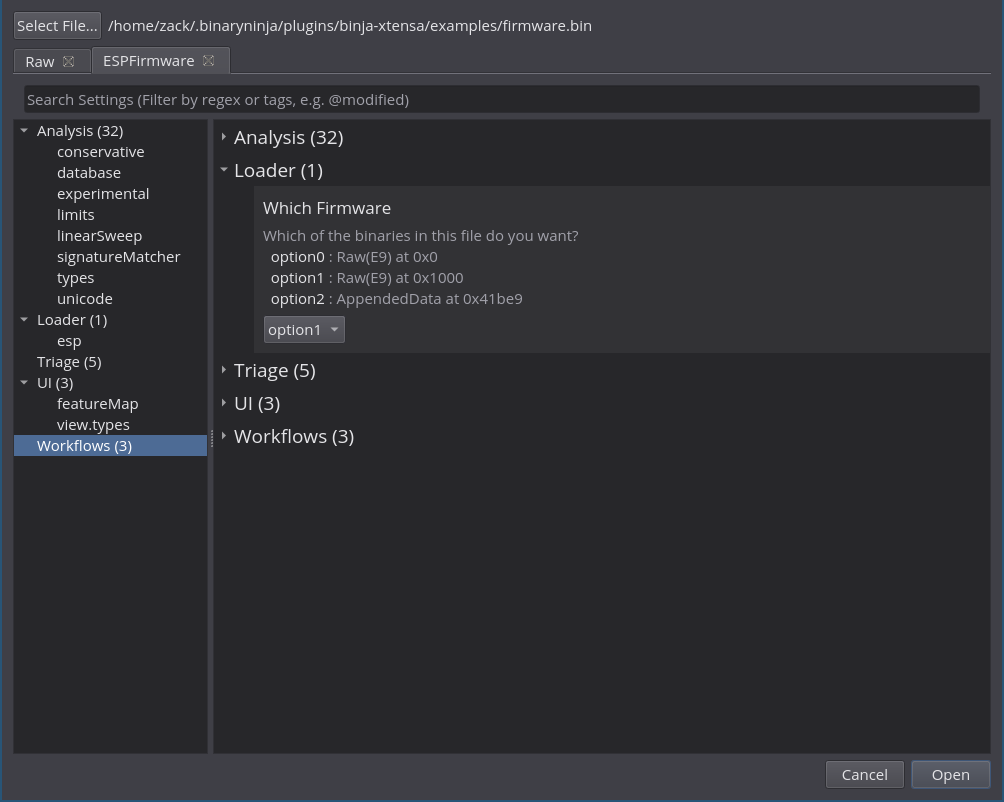
- Loader for ESP8266 raw firmware dumps. This support is a little finicky to
use, as there's multiple partitions in the firmware dumps. By default it uses
the last one with a detected header; you can adjust this via Open With
Options
- At the moment it doesn't completely map the sections properly, but it's a start :)
- It was written mostly as an exercise for the author. It's useful enough to share, but no promises it's useful for your project :)
- Lift register windowing instructions (it disassembles most of them)
- You need this for ESP32 support. It shouldn't be too bad to add, as long as you can figure out how to lift the windowed registers
- Anything with the optional vector unit
- Disassemble and lift most of the boolean instructions
- Lift most floating point instructions
- Deal with special registers (I figure you might as well look at the asm for that anyway)
- Anything quickly. This is Python, and not particularly well optimized Python at that. If you're using this seriously, I recommend rewriting in C++
- Find
mainin a raw binary for you
Install via the Binary Ninja plugin manager. Alternatively, clone this repository into your Binary Ninja plugins directory. See the official Binary Ninja documentation for more details.
The default of picking the last usable partition works decent, but if you want
more control, use Open With Options and change Loader > Which Firmware to the
option corresponding to the address you want to load.
I attempt to load in symbols from the SDK's linker script so some of the
ROM-implemented functions are less mysterious. See
parse_rom_ld.py for the parsing code,
known_symbols.py for the database it'll apply,
and function setup_esp8266_map in
binaryview.py for the code that applies it.
This should probably be a load time option... but it's not at the moment :/
- Support register windowing instructions to support ESP32 firmware
- Improve the raw firmware loader
- Rewrite to be faster
- I was goofing around with ESP8266 and Arduino and was annoyed I didn't have an easy way to disassemble the built binaries
- I hadn't written a full architecture plugin and I thought it'd be a good exercise
- I got bored over COVID-19 lockdown in 2020 and needed something to do
There are some simple tests in
test_instruction.py, which are mostly just
taking uniq'd output from objdump on some binaries I had laying around and
making sure the output matches. They can be run with python -m pytest from the
root of the project.
This project copyright Zack Orndorff (@zackorndorff) and is available under the MIT license. See LICENSE.