[caption id="attachment_10522" align="alignnone" width="1920"]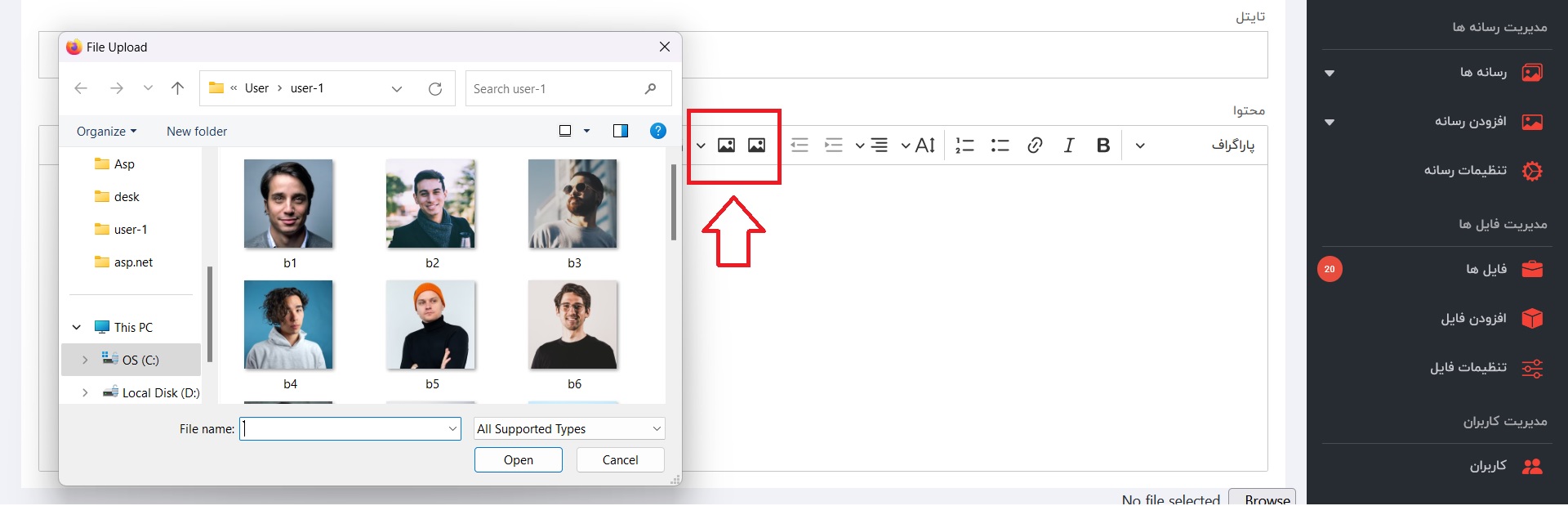
- در قسمتی که کد های Java Script ای خود را وارد میکنید، دقیقا بالای قسمتی که CKeditor خود را توسط دستورات جاوا اسکریپتی لود میکنید، کلاس و دستورات Custom image upload adapter را وارد کنید.
توجه در بخشی که به رنگ قرمز نوشته شده نام کنترلر و اکشنی که قرار است تصاویر را آپلود کند، وارد کنید.
class MyUploadAdapter {
constructor(loader) {
// The file loader instance to use during the upload.
this.loader = loader;
}
// Starts the upload process.
upload() {
return this.loader.file
.then(file => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this._initRequest();
this._initListeners(resolve, reject, file);
this._sendRequest(file);
}));
}
// Aborts the upload process.
abort() {
if (this.xhr) {
this.xhr.abort();
}
}
// Initializes the XMLHttpRequest object using the URL passed to the constructor.
_initRequest() {
const xhr = this.xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// Note that your request may look different. It is up to you and your editor
// integration to choose the right communication channel. This example uses
// a POST request with JSON as a data structure but your configuration
// could be different.
xhr.open('POST', '/Posts/MyUpload', true);
xhr.responseType = 'json';
}
// Initializes XMLHttpRequest listeners.
_initListeners(resolve, reject, file) {
const xhr = this.xhr;
const loader = this.loader;
const genericErrorText = `Couldn't upload file: ${file.name}.`;
xhr.addEventListener('error', () => reject(genericErrorText));
xhr.addEventListener('abort', () => reject());
xhr.addEventListener('load', () => {
const response = xhr.response;
// This example assumes the XHR server's "response" object will come with
// an "error" which has its own "message" that can be passed to reject()
// in the upload promise.
//
// Your integration may handle upload errors in a different way so make sure
// it is done properly. The reject() function must be called when the upload fails.
if (!response || response.error) {
return reject(response && response.error ? response.error.message : genericErrorText);
}
// If the upload is successful, resolve the upload promise with an object containing
// at least the "default" URL, pointing to the image on the server.
// This URL will be used to display the image in the content. Learn more in the
// UploadAdapter#upload documentation.
resolve({
default: response.url
});
});
// Upload progress when it is supported. The file loader has the #uploadTotal and #uploaded
// properties which are used e.g. to display the upload progress bar in the editor
// user interface.
if (xhr.upload) {
xhr.upload.addEventListener('progress', evt => {
if (evt.lengthComputable) {
loader.uploadTotal = evt.total;
loader.uploaded = evt.loaded;
}
});
}
}
// Prepares the data and sends the request.
_sendRequest(file) {
// Prepare the form data.
const data = new FormData();
data.append('upload', file);
// Important note: This is the right place to implement security mechanisms
// like authentication and CSRF protection. For instance, you can use
// XMLHttpRequest.setRequestHeader() to set the request headers containing
// the CSRF token generated earlier by your application.
// Send the request.
this.xhr.send(data);
}
}
function MyCustomUploadAdapterPlugin(editor) {
editor.plugins.get('FileRepository').createUploadAdapter = (loader) => {
// Configure the URL to the upload script in your back-end here!
return new MyUploadAdapter(loader);
};
}
- حال باید آداپتور - Adapter خود را در بحشی که مربوط به وارد کردن کانفیگ های CKeditor است، توسط کد زیر فراخوانی کنید.
extraPlugins: [MyCustomUploadAdapterPlugin],
- در صورتی که با ارور روبرو شدید میتوانید CKeditor را مانند زیر فراخوانی کنید.
window.addEventListener("load", (e) => {
ClassicEditor
.create(document.querySelector('.editor'), {
extraPlugins: [MyCustomUploadAdapterPlugin],
})
.then(editor => {
console.log(editor);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
});
- ابتدا یک کنترلر و یک اکشن ایجاد میکنیم، در مرحله قبل مشخص کردیم اطلاعات به کنترلر Posts و اکشن MyUpload ارسال شود. همچنین توجه داشته باشید که اکشن ما باید دارای اتربیوت HttpPost باشد.
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult MyUpload()
{
}
- برای دسترسی به فایل های ارسال شده میتوان از دستور Request.Files استفاده کرد. پس ابتدا توسط شرطی برسی میکنیم ببینیم فایلی ارسال شده یا خیر. در صورتی که فایلی ارسال نشده باشد به بخش else منتقل میشویم و در انجا توسط یک مقدار Json مقدار error را به سمت کلاینت ارسال میکنیم.
if (Request.Files.Count > 0)
{
}
else
{
return Json(new { uploaded = false, error = "تصویری برای آپلود ارسال نشده است", JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
}
- اگر فایل ارسال شده باشد وارد شرط میشویم. ابتدا باید یک ساختار try catch ایجاد کنیم. تا در صورتی که با ارور روبرو شدیم آن را مدیریت کنیم. در صورتی که Error یا مشکلی پیش اید به بخش catch منتقل میشویم و در انجا توسط یک مقدار Json مقدار error را به سمت کلاینت ارسال میکنیم.
try
{
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return Json(new { uploaded = false, error = "خطایی روی داده است" + ex.Message, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
}
- و در نهایت عکس های ارسال شده را دریافت و توسط یک حلقه یکی یکی در سرور ذحیره میکنیم.
NewName نام جدیدی است که برای تصویر به صورت یکتا ایجاد میشود تا از نان تکراری جلوگیری شود.
extension فرمت فایل یا تصویر را میگیرد مثلا فرمت .jpg
Imagename نام جدید تصویر همراه با قرمت آن میباشد.
ImageUrl آدرس تصویر از مبدا میباشد از این مقدار برای ذخیره در دیتابیس و یا آدرس دهی به تگ Img استفاده میشود.
ImageUrlUpload از این آدرس برای آپلود تصویر استفاده میشود.
HttpFileCollectionBase files = Request.Files;
for (int i = 0; i < files.Count; i++)
{
HttpPostedFileBase file = files[i];
string Loaction = "/Images/upload";
string NewName = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
string extension = Path.GetExtension(file.FileName);
string Imagename = NewName + extension;
string ImageUrl = Loaction + "/" + Imagename;
string ImageUrlUpload = Path.Combine(Server.MapPath(Loaction), Imagename);
file.SaveAs(ImageUrlUpload);
return Json(new { uploaded = true, url = ImageUrl, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
}
return Json(new { uploaded = true, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
- مشاهده کد های اکشن به صورت یکجا
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult MyUpload()
{
if (Request.Files.Count > 0)
{
try
{
HttpFileCollectionBase files = Request.Files;
for (int i = 0; i < files.Count; i++)
{
HttpPostedFileBase file = files[i];
string Loaction = "/Images/upload";
string NewName = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
string extension = Path.GetExtension(file.FileName);
string Imagename = NewName + extension;
string ImageUrl = Loaction + "/" + Imagename;
string ImageUrlUpload = Path.Combine(Server.MapPath(Loaction), Imagename);
file.SaveAs(ImageUrlUpload);
return Json(new { uploaded = true, url = ImageUrl, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
}
return Json(new { uploaded = true, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return Json(new { uploaded = false, error = "خطایی روی داده است" + ex.Message, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
}
}
else
{
return Json(new { uploaded = false, error = "تصویری برای آپلود ارسال نشده است", JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet });
}
}
- درصورتی که به تصویر نیازی نداشته باشیم نمیتوانیم آن را از سرور حذف کنیم و این باعث افزونگی در سرور میشود.
- در صورتی که بخواهیم از یک تصویر در ۲ بهش استفاده کنیم باید آن تصویر را ۲ بار در سرور آپلود کنیم. که این هم باعث افزونگی در سرور میشود.