| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2486 |
Weekly Contest 247 Q4 |
|
You are an ant tasked with adding n new rooms numbered 0 to n-1 to your colony. You are given the expansion plan as a 0-indexed integer array of length n, prevRoom, where prevRoom[i] indicates that you must build room prevRoom[i] before building room i, and these two rooms must be connected directly. Room 0 is already built, so prevRoom[0] = -1. The expansion plan is given such that once all the rooms are built, every room will be reachable from room 0.
You can only build one room at a time, and you can travel freely between rooms you have already built only if they are connected. You can choose to build any room as long as its previous room is already built.
Return the number of different orders you can build all the rooms in. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
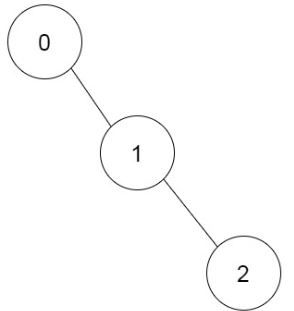
Example 1:
Input: prevRoom = [-1,0,1] Output: 1 Explanation: There is only one way to build the additional rooms: 0 → 1 → 2
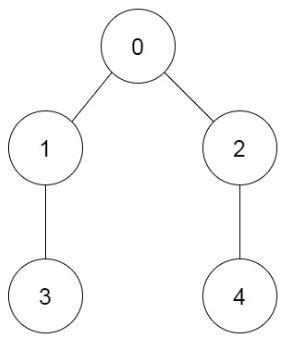
Example 2:
Input: prevRoom = [-1,0,0,1,2] Output: 6 Explanation: The 6 ways are: 0 → 1 → 3 → 2 → 4 0 → 2 → 4 → 1 → 3 0 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 0 → 1 → 2 → 4 → 3 0 → 2 → 1 → 3 → 4 0 → 2 → 1 → 4 → 3
Constraints:
<li><code>n == prevRoom.length</code></li>
<li><code>2 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
<li><code>prevRoom[0] == -1</code></li>
<li><code>0 <= prevRoom[i] < n</code> for all <code>1 <= i < n</code></li>
<li>Every room is reachable from room <code>0</code> once all the rooms are built.</li>
class Solution:
def waysToBuildRooms(self, prevRoom: List[int]) -> int:
modulo = 10**9 + 7
ingoing = defaultdict(set)
outgoing = defaultdict(set)
for i in range(1, len(prevRoom)):
ingoing[i].add(prevRoom[i])
outgoing[prevRoom[i]].add(i)
ans = [1]
def recurse(i):
if len(outgoing[i]) == 0:
return 1
nodes_in_tree = 0
for v in outgoing[i]:
cn = recurse(v)
if nodes_in_tree != 0:
ans[0] *= comb(nodes_in_tree + cn, cn)
ans[0] %= modulo
nodes_in_tree += cn
return nodes_in_tree + 1
recurse(0)
return ans[0] % modulo