This is a simple Bash script "app" that will run Speedtest and upload the measurements into an Elasticsearch instance.
The script is an all-in-one package that will take care of creating the Elasticsearch resources, run the speedtest app and upload its results, as well as install/uninstall itself.
The Speedtest CLI measurements are spooled locally until they can be updated into Elasticsearch. Note that the spool file is stored by default under system's temporary directory, so it's lost on a reboot. If a measurement is rejected by Elasticsearch due to ingesting errors, the measurements are logged into a dedicated file.
The failures are also sent to local logging system.
Elasticsearch is setup to rotate out the old data, so that the destination indices won't grow forever. It will also drop some of Speedtest CLI redundant JSON fields and consolidate the geographical data into appropriate Elasticsearch data types.
There are a few dependencies, besides speedtest that need to be available on
the system before running this script:
- curl
- cron
- jq
- bc
These are checked on installation only and expected to be available otherwise.
The Elasticsearch server needs to support index lifecycle management.
-
Edit the config file,
esst.confand change the defines between the<change me>tags in both "Elasticsearch" and "Local" sections. -
Create the Elasticsearch resources
This step needs to be done only once, even if probing with Speedtest on multiple hosts. Run:
./esst.sh initThis will create the index template, the pipeline that alters the JSON that Speedtest produces, as well as an index lifecycle managment policy to manage the data rotation.
The opposite of
initisdrop, which will delete all resources created initially. -
Install the "app"
./esst.sh installThis will install the needed files under
/opt/esstdirectory (by default), as well as register a cron entry in the crontab of executing user. This won't make it available in thePATH. To later uninstall it, list the cron entries (crontab -l) to find its location and rununinstall; below is an example that works with the default configuration:/opt/esst/bin/esst uninstall -
Make a test run
To produce one measurement, invoke it with the
probeargument:/opt/esst/bin/esst probe
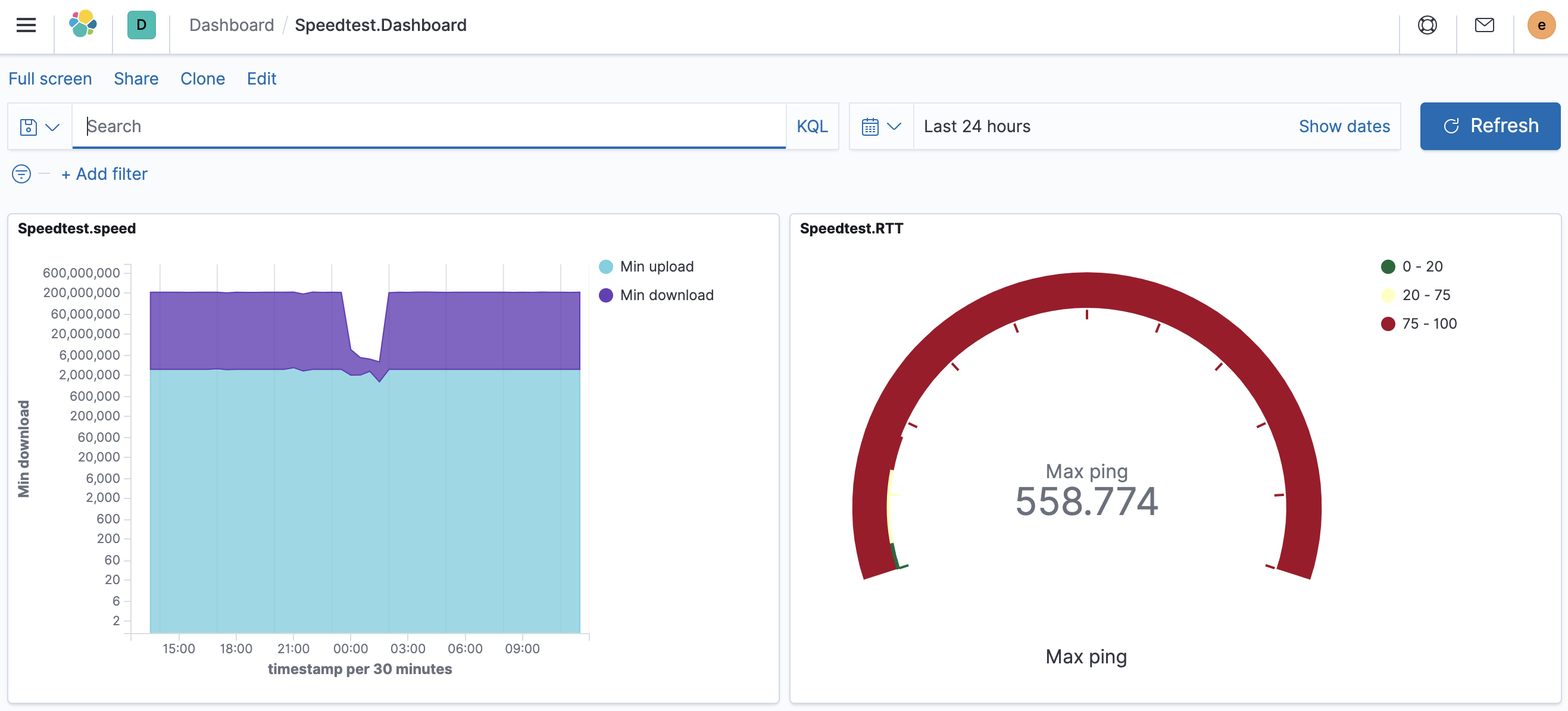
There is one simple dashboard configuration file that can be uploaded into
Kibana, dashboard.ndjson. This will install a graph of upload and download
measurements, as well as a gauge with the max RTT to the speedtest server, over
the data from all probes: