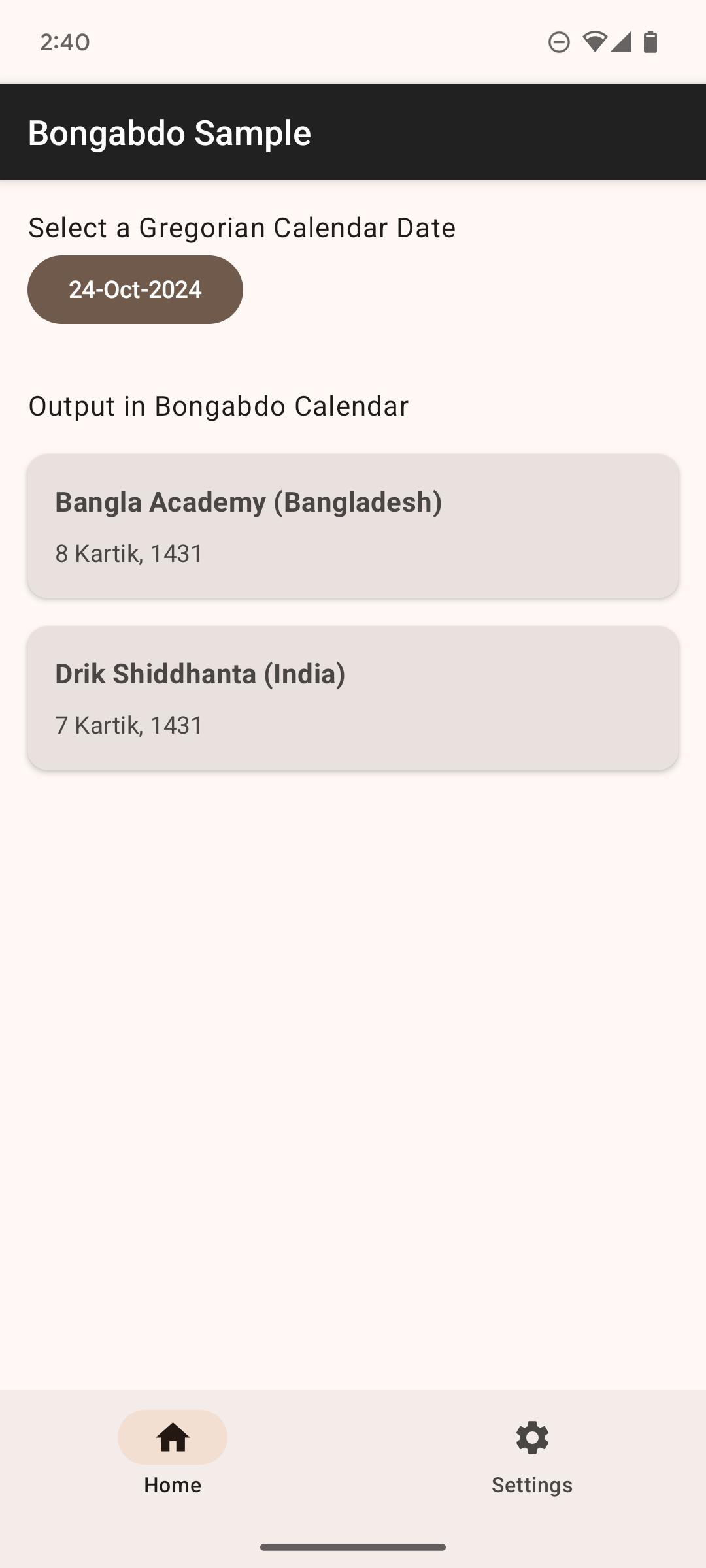
Bongabdo is a powerful Kotlin library that simplifies converting Gregorian dates to Bengali calendar dates (Bongabdo) for your Android or Java/Kotlin projects. It provides flexibility for regional variations and offers customization options.
- Android (Clone this repo to check the sample app)
- Spring Boot (Kotlin)
- Spring Boot (Java)
- Easy Conversions: Convert any Gregorian date to its corresponding Bengali date using two popular calculation methods:
- Bangla Academy: Used in Bangladesh
- Drik Shiddhanta: Used in India
- Extendable: Easily implement additional calculation methods like Surjo Shiddhanta for further customization.
- Multilingual Support: Currently offers English and Bengali localization, with options for extending to other languages.
For Gradle version 7.0 and above (settings.gradle.kts):
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
google()
maven { url = uri("https://jitpack.io") }
}
}For Gradle version below 7.0 (root level build.gradle)
allprojects {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
google()
maven { url = uri("https://jitpack.io") }
}
}Add the following dependency to your module's build.gradle.kts:
dependencies {
implementation("com.github.hasancse91:bongabdo:<latest-version>")
}Latest version:
To convert a Gregorian date to a Bengali date, initialize the Bongabdo class and call the appropriate conversion method.
Example: Convert a Gregorian Date to a Bengali Date (Bangla Academy Method)
Kotlin
fun main() {
val bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.BANGLA_ACADEMY)
val result = bongabdo.getBongabdoData(year = 2014, month = 3, day = 14) // 14 Apr 2024
println("Bongabdo Date: ${result.getFullDate()}") // 1 Baishakh, 1431
}Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.BANGLA_ACADEMY);
var result = bongabdo.getBongabdoData(2014, 3, 14); // 14 Apr 2024
System.out.println("Bongabdo Date: " + result.getFullDate()); // 1 Baishakh, 1431
}
}Bongabdo supports both English and Bengali locales. English is our default locale. You can set the desired locale using the configuration settings.
Bengali Localization
Kotlin
bongabdo.localizationConfig = BengaliLocalizationConfig()Java
bongabdo.setLocalizationConfig(new BengaliLocalizationConfig());You can extend the BongabdoLocalizationConfig class to add your own localization support.
Kotlin
class HindiLocalisationConfig : BongabdoLocalizationConfig() {
override val digitMap: Map<Int, String>
get() = TODO("Not yet implemented")
override val monthNameList: List<String>
get() = TODO("Not yet implemented")
override val seasonNameList: List<String>
get() = TODO("Not yet implemented")
}
fun main() {
val bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.BANGLA_ACADEMY)
bongabdo.localizationConfig = HindiLocalisationConfig()
val bongabdoData = bongabdo.getBongabdoData(2014, 3, 14)
println(bongabdoData.getFullDate())
}Java
class HindiLocalizationConfig extends BongabdoLocalizationConfig {
@Override
public Map<Integer, String> getDigitMap() {
// TODO: Implement this method
}
@Override
public List<String> getMonthNameList() {
// TODO: Implement this method
}
@Override
public List<String> getSeasonNameList() {
// TODO: Implement this method
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.BANGLA_ACADEMY);
bongabdo.setLocalizationConfig(new HindiLocalizationConfig());
var bongabdoData = bongabdo.getBongabdoData(2014, 3, 14);
System.out.println(bongabdoData.getFullDate());
}
}Bongabdo currently supports two calculation methods:
- Bangla Academy (used in Bangladesh)
- Drik Shiddhanta (used in India)
Specify the calculation method during initialization:
Kotlin
val bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.BANGLA_ACADEMY)
// or
val bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.INDIAN_DRIK_SIDDHANTA)Java
var bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.BANGLA_ACADEMY);
// or
var bongabdo = Bongabdo.getInstance(BongabdoMethod.INDIAN_DRIK_SIDDHANTA);Custom Calculation Methods
To add a custom calculation method (e.g., Surya Shiddhanta), extend the Bongabdo class and implement the required logic.
Extend your own class from Bongabdo abstract class:
Kotlin
class SurjaShiddhantaBongabdo : Bongabdo() {
override fun getBongabdoData(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int): BongabdoData {
TODO("Implement your logic here")
}
}
fun main() {
val bongabdo = SurjaShiddhantaBongabdo() // your implemented class
bongabdo.localizationConfig = HindiLocalisationConfig() // you can use your own localization class
val bongabdoData = bongabdo.getBongabdoData(2014, 3, 14)
println(bongabdoData.getFullDate())
}Java
class SurjaShiddhantaBongabdo extends Bongabdo {
@Override
public BongabdoData getBongabdoData(int year, int month, int day) {
// TODO: Implement your logic here
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var bongabdo = new SurjaShiddhantaBongabdo(); // your implemented class
bongabdo.setLocalizationConfig(new HindiLocalizationConfig()); // you can use your own localization class
var bongabdoData = bongabdo.getBongabdoData(2014, 3, 14);
System.out.println(bongabdoData.getFullDate());
}
}In this way you can extend this library for localization and calculation method variation.
Want to contribute? Here’s how you can help:
- Fork the repository.
- Contribute your feature or improvement.
- Ensure that unit tests are updated or created for your changes.
- Submit a pull request.
We appreciate your contributions and will review your pull requests as soon as possible!
A special thanks to Shafayat Hossain Khan for his significant contributions to this project.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.