- Operating environment
- Things you may need to buy
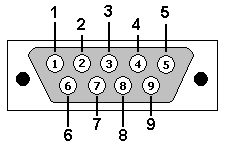
- GlobalSat MR-350PS4 PS/2 pin-out
- DB9 RS232 serial port pin-out
- DB9 D-SUB RS232 Adapter (Female with Screw) screw pins
- NTP time with GPSD and PPS-enabled GPS Garmin 18x LVC GPS
- Package installation
- Package versions
- Assumptions
- Configure GPSD
- Enable kernel PPS
- Configure serial port
- Testing
- Links
- Contents of files
ToC created by gh-md-toc
- Ubuntu Bionic 18.04.3
- Linux kernel 5.4.3 (Vanilla kernel from kernel.org - no patches requried or used)
- Buy GlobalSat MR-350P-S4 on Amazon.com (US)
- Buy DB9 D-SUB RS232 Adapter (Female with Screw) on Amazon.com (US)
- Buy PS/2 Mini-DIN Male-to-Female cable on Amazon.com (US)
- Amazon search for DB9 D-SUB RS232 Adapter (Female with Screw)
- Amazon search for PS/2 Mini-DIN Male-to-Female cable
- Amazon search for GlobalSat MR-350P-S4
- Buy Garmin 18x LVC GPS on Amazon.com (US) - not required if you are using / buying the GlobalSat MR-350P-S4
The diagram above is from GlobalSat MR-350PS4 Technical Specifications
Note that this is NOT the standard PS/2 pin-out.
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | GND |
| 2 | VCC |
| 3 | PPS |
| 4 | RX |
| 5 | TX |
| 6 | NC |
| Pin | Function | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DCD | Into computer from GPS |
| 2 | RX | Into computer from GPS |
| 3 | TX | To GPS from computer |
| 4 | DTR | To GPS from computer (unused here) |
| 5 | GND | - |
Check the pin numbering at the screw terminals - may be different from this image !
| MR-350P-S4 PS/2 PIN | Function | DB9 PIN | USB cable wire |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | 5 | Black |
| 2 | VCC | - | Red |
| 3 | PPS | 1 | - |
| 4 | RX | 2 | - |
| 5 | TX | 3 | - |
| 6 | NC | - | - |
Notes:
- PS/2 Pin 2 (VCC) goes ONLY to USB cable
- PS/2 Pin 1 (GND) goes to DB9 Pin 5 AND to USB cable
NOTE: I have not personally tried the Garmin 18x LVC. I am only including this section in the hope that the wiring tips may help others who have or buy the Garmin 18x LVC
Note that you MUST buy the LVC version, and not the USB version(s).
| Garmin 18x LVC | GlobalSat MR-250P-S4 |
|---|---|
| More expensive | Less expensive |
| Reviews say it will not work indoors (1) | Reviews say it works indoors in wood buildings (1) |
| 1 microsecond PPS accuracy - worse (1) | 50 ns PPS accuracy - better (1) |
| Do not need PS/2 Male-Female cable | Recommend PS/2 Male-Female cable |
| Casing is flat at the botton with a magnetic base | No magnetic base, more clumsy to mount |
The diagram above is from Garmin 18x Technical Specifications
Note: the diagram above does not show PIN 1 (Yellow) (PPS) wire connected anywhere, but it SHOULD be connected to DB9 Pin 1 (DCD). Without that PPS will NOT work !
| Garmin 18x LVC PIN (Color) | Function | DB9 PIN | USB cable wire |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Yellow) | PPS | 1 | - |
| 2 (Red) | VCC | - | Red |
| 3 (Black) | GND | 5 | Black |
| 4 (White) | TX | 3 | - |
| 5 (Black) | GND | - | - |
| 6 (Green) | RX | 2 | - |
apt install gpsd chrony setserial gpsd-clients pps-tools
| Package | Version |
|---|---|
| gpsd | 3.17-5 |
| setserial | 2.17-50 |
| pps-tools | 1.0.2-1 |
| chrony | 3.2-4ubuntu4.2 |
| gpsd-clients | 3.17-5 |
This guide assumes GPS device is connected on SECOND serial port - ttyS1
If this is not the case substitute /dev/ttyABC for /dev/ttyS1 in following files
var/lib/setserial/autoserial.confetc/default/gpsd
Do this before proceeding further
- Make sure you have modified
etc/default/gpsdto reflect serial port being used (if modification is required) - Copy
etc/default/gpsdto/etc/default/gpsd
grep '^CONFIG_PPS' /boot/config-$(uname -r)
Output should contain:
CONFIG_PPS=m
CONFIG_PPS_CLIENT_LDISC=m
- Copy
etc/systemd/system/pps_ldisc.serviceto/etc/systemd/system - Run
systemctl enable pps_ldisc.service - Run
systemctl start pps_ldisc.service - Technically this is not REQUIRED just to test GPSD, but if not using this service you need to do the following:
modprobe pps_ldiscbefore starting gpsd or restart gpsd after the modprobe- Do this after every reboot
- Without module pps_ldisc, PPS capabilities will not be available
- Strictly NOT REQUIRED just for testing PPS with gpsd. All setserial is used for is setting the serial port into low_latency mode - may improve PPS latency / accuracy
- Make sure you have modified
var/lib/setserial/autoserial.confto reflect serial port being used (if modification is required) - Run
dpkg-reconfigure setserialand set configuration mode to MANUAL - Copy
/lib/setserial/autoserial.confto /var/lib/setserial/autoserial.conf for op in stop start; do systemctl $op setserial.service; done
- systemd-timesyncd.service conflicts with chrony and if systemd-timesyncd.service is enabled, chrony will not autostart
for op in stop disable mask; do systemctl $op systemd-timesyncd.service ; done
- copy
etc/chrony/chrony.conftoetc/chrony/
systemctl stop gpsd.socket gpsd.service
for op in stop start; do systemctl $op gpsd.socket gpsd.service
- Stop gpsd
gpsd -b -n -N -D3 /dev/ttyS1 /dev/pps0(IMPORTANT: replace/dev/ttyS1with path to serial port you are using)
ppsfind --help
pps0: name=serial1 path=/dev/ttyS1
sudo ppswatch /dev/pps0
trying PPS source "/dev/pps0"
found PPS source "/dev/pps0"
timestamp: 1577777203, sequence: 83886, offset: 1984
timestamp: 1577777204, sequence: 83887, offset: -31306
timestamp: 1577777205, sequence: 83888, offset: 5836
timestamp: 1577777206, sequence: 83889, offset: 3027
timestamp: 1577777207, sequence: 83890, offset: -24220
timestamp: 1577777208, sequence: 83891, offset: 2041
ntpshmmon -n 5
ntpshmmon version 1
# Name Seen@ Clock Real L Prec
sample NTP2 1577776857.467580012 1577776856.999992825 1577776857.000000000 0 -30
sample NTP2 1577776858.000449336 1577776857.999980312 1577776858.000000000 0 -30
sample NTP2 1577776859.000728372 1577776858.999985236 1577776859.000000000 0 -30
sample NTP2 1577776860.000141189 1577776859.999987295 1577776860.000000000 0 -30
sample NTP2 1577776861.000665371 1577776861.000004892 1577776861.000000000 0 -30
cgpsgpsmon
chronyc -m 'sources -v' tracking 'sourcestats -v'
PPS details highlighted in BOLD
chronyc -m 'sources -v' tracking 'sourcestats -v'
210 Number of sources = 7
.-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock.
/ .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined,
| / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable.
|| .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz
|| Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset,
|| Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset,
|| \ | | zzzz = estimated error.
|| | | \
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
#* PPS 0 4 377 18 +1318ns[+2225ns] +/- 502us
^- 162.159.200.1 3 10 377 56 +8603us[+8606us] +/- 46ms
^- time4.google.com 1 10 377 983 +1242us[+1189us] +/- 24ms
^- time-a-b.nist.gov 1 10 377 128 -2043us[-2039us] +/- 22ms
^- gpstime.la-archdiocese.n> 2 10 377 32m +848us[ +667us] +/- 41ms
^- clock.fmt.he.net 1 10 377 209 -1836us[-1831us] +/- 4597us
^- clock.sjc.he.net 1 10 377 39 -507us[ -507us] +/- 3927us
210 Number of sources = 7
.- Number of sample points in measurement set.
/ .- Number of residual runs with same sign.
| / .- Length of measurement set (time).
| | / .- Est. clock freq error (ppm).
| | | / .- Est. error in freq.
| | | | / .- Est. offset.
| | | | | | On the -.
| | | | | | samples. \
| | | | | | |
Name/IP Address NP NR Span Frequency Freq Skew Offset Std Dev
==============================================================================
PPS 13 8 194 +0.001 0.062 +13ns 2834ns
162.159.200.1 10 8 155m -0.431 0.820 +6442us 1354us
time4.google.com 14 7 223m -0.400 0.509 -1817us 1802us
time-a-b.nist.gov 34 14 568m -0.328 0.070 -1429us 1134us
gpstime.la-archdiocese.n> 20 12 327m -0.342 0.123 -691us 799us
clock.fmt.he.net 17 10 276m -0.429 0.198 -507us 1020us
clock.sjc.he.net 13 5 224m -0.407 0.115 -933us 419us
Reference ID : 50505300 (PPS)
Stratum : 1
Ref time (UTC) : Tue Dec 31 01:59:17 2019
System time : 0.000000606 seconds fast of NTP time
Last offset : +0.000000953 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000001683 seconds
Frequency : 25.250 ppm slow
Residual freq : +0.001 ppm
Skew : 0.068 ppm
Root delay : 0.001000000 seconds
Root dispersion : 0.000021925 seconds
Update interval : 16.0 seconds
Leap status : Normal
- GPSD Time Service HOWTO by author of GPSD
- GPSD Compatible Hardware
- Troubleshooting by author of GPSD
- chrony with GPS for Time Synchronization
- Not quite 5 minute guide to making an NTP Server
- Chrony and GPSD (Archlinux)
- Synchronizing ntpd to a Garmin GPS 18 LVC via gpsd
- GlobalSat MR-350PS4 Technical Specifications
- RS232 Serial Cable Wiring
- Crossover or "Null Modem" vs. Straight Through Serial Cable
- Garmin 18x Technical Specifications
- The Raspberry Pi as a Stratum-1 NTP Server - Uses a Raspberry Pi "hat" module, but otherwise contains a wealth of information
.
├── etc
│ ├── chrony
│ │ └── chrony.conf
│ ├── default
│ │ └── gpsd
│ └── systemd
│ └── system
│ └── pps_ldisc.service
└── var
└── lib
└── setserial
└── autoserial.conf
IMPORTANT Change /dev/ttyS1 to path for serial port you are using
# Default settings for gpsd.
# Please do not edit this file directly - use `dpkg-reconfigure gpsd' to
# change the options.
START_DAEMON="true"
GPSD_OPTIONS="-b -n -D1"
DEVICES="/dev/ttyS1 /dev/pps0"
USBAUTO="false"
GPSD_SOCKET="/var/run/gpsd.sock"
[Unit]
Description=Modprobe pps_ldisc
After=setserial.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/sbin/modprobe pps_core
ExecStart=/sbin/modprobe pps_ldisc
[Install]
WantedBy=gpsd.service
IMPORTANT Change /dev/ttyS1 to path for serial port you are using
#
###AUTOSAVE-ONCE###
###AUTOSAVE-ONCE###
###AUTOSAVE###
#
# If you want to configure this file by hand, use
# dpkg-reconfigure setserial
# and change the configuration mode of the file to MANUAL. If you do not do this, this file may be overwritten automatically the next time you upgrade the
# package.
#
# dpkg-reconfigure setserial ... set configuration mode to MANUAL
# Added next line for ttyS1 for Garmin 18 LVC GPS
# From: http://www.rjsystems.nl/en/2100-ntpd-garmin-gps-18-lvc-gpsd.php
# Only needed to add 'low_latency' to default port configuration
# Print out current port configuration:
# setserial -G /dev/ttyS1
/dev/ttyS1 uart 16550A port 0x02f8 irq 3 baud_base 115200 spd_normal skip_test low_latency
The extra server lines in chrony.conf are totally irrelevant to using PPS
For PPS, only the line reading refclock SHM 1 offset 0 delay 0.001 refid PPS is important.
# This the default chrony.conf file for the Debian chrony package. After
# editing this file use the command 'invoke-rc.d chrony restart' to make
# your changes take effect. John Hasler <jhasler@debian.org> 1998-2008
# See www.pool.ntp.org for an explanation of these servers. Please
# consider joining the project if possible. If you can't or don't want to
# use these servers I suggest that you try your ISP's nameservers. We mark
# the servers 'offline' so that chronyd won't try to connect when the link
# is down. Scripts in /etc/ppp/ip-up.d and /etc/ppp/ip-down.d use chronyc
# commands to switch it on when a dialup link comes up and off when it goes
# down. Code in /etc/init.d/chrony attempts to determine whether or not
# the link is up at boot time and set the online status accordingly. If
# you have an always-on connection such as cable omit the 'offline'
# directive and chronyd will default to online.
#
# Note that if Chrony tries to go "online" and dns lookup of the servers
# fails they will be discarded. Thus under some circumstances it is
# better to use IP numbers than host names.
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Use a local GPS device and gpsd as Staratum 0 GPS source
#
# Disable systemd-timesyncd.service - conflicts with chrony autostart !
# for op in stop disable mask; do systemctl $op systemd-timesyncd.service ; done
#
#
# For Globalsat MR-350PS4 PPS GPS on SERIAL port
# From https://wiki.alpinelinux.org/wiki/Chrony_and_GPSD
# Commenting out NEMA and SOCK -:
# - NEMA is too inaccurate and chrony will not use anyway!
# - SOCK - does not seem to get any values !
#
#refclock SHM 0 delay 0.5 refid NEMA
refclock SHM 1 offset 0 delay 0.001 refid PPS
#refclock SOCK /var/run/chrony.ttyS1.sock delay 0.0 refid SOCK
# C(20180207) Setings for using USB non-PPS GPS device and GPSD
# NEMA is too inaccurate and chrony will not use anyway!
# Need to fiddle with offset (seconds) to make sure refclock is considered
# watch the output of 'chronyc sources' to see 'Last Sample'
#
# refclock SHM 0 offset 0.05 refid NMEA
server clock.fmt.he.net iburst
server clock.sjc.he.net iburst
server time.cloudflare.com iburst
server time.google.com iburst
server time.nist.gov
server gpstime.la-archdiocese.net
#server time1.google.com iburst
#server time2.google.com iburst
#server time3.google.com iburst
#server time4.google.com iburst
#pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
#pool 2.debian.pool.ntp.org offline iburst
# Specify IP address (interface) that chronyd CLIENT will bind to
# The bindacqaddress directive sets the network interface to which
# chronyd will bind its NTP client sockets
# bindacqaddress 0.0.0.0
# Allow other NTP clients in our zone to query time
# allow 10.3/16
# allow 10.30.0/24
# (CHANGED): chronyd version 3.2 commandkey directive is no longer supported
# This directive sets the key ID used for authenticating user commands via the
# 'chronyc' program at run time.
# commandkey 1
# End of customized settings - EXCEPT lines labeled with (CHANGED)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Look here for the admin password needed for chronyc. The initial
# password is generated by a random process at install time. You may
# change it if you wish.
keyfile /etc/chrony/chrony.keys
# I moved the driftfile to /var/lib/chrony to comply with the Debian
# filesystem standard.
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/chrony.drift
# Comment this line out to turn off logging.
log tracking measurements statistics
logdir /var/log/chrony
# Stop bad estimates upsetting machine clock.
maxupdateskew 100.0
# Dump measurements when daemon exits.
dumponexit
# Specify directory for dumping measurements.
dumpdir /var/lib/chrony
# This directive lets 'chronyd' to serve time even if unsynchronised to any
# NTP server.
#local stratum 10
# This directive designates subnets (or nodes) from which NTP clients are allowed
# to access to 'chronyd'.
#allow foo.example.net
#allow 10/8
#allow 0/0 (allow access by any IPv4 node)
#allow ::/0 (allow access by any IPv6 node)
# This directive forces `chronyd' to send a message to syslog if it
# makes a system clock adjustment larger than a threshold value in seconds.
logchange 0.5
# This directive defines an email address to which mail should be sent
# if chronyd applies a correction exceeding a particular threshold to the
# system clock.
# mailonchange root@localhost 0.5
# This directive tells 'chronyd' to parse the 'adjtime' file to find out if the
# real-time clock keeps local time or UTC. It overrides the 'rtconutc' directive.
hwclockfile /etc/adjtime
# This directive enables kernel synchronisation (every 11 minutes) of the
# real-time clock. Note that it can’t be used along with the 'rtcfile' directive.
rtcsync