This repository is for learning Spring
-
Go to https://start.spring.io/
-
Configure your project, for example add Spring MVC package
-
Download zip file and extract
-
Open project with Intellij
Downgrade gradle version from 5 to 4 to solve gradel build failure
In gradle-wrapper.properties
distributionUrl=https\://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-4.4-all.zip
go to https://spring.io/guides/gs/spring-boot/
https://www.baeldung.com/intro-to-servlets
Simply put, a Servlet is a class that handles requests, processes them and reply back with a response.
Servlets are under the control of another Java application called a Servlet Container. When an application running in a web server receives a request, the Server hands the request to the Servlet Container – which in turn passes it to the target Servlet.
Servlet Lifecycle
-
init() The init method is designed to be called only once. If an instance of the servlet does not exist, the web container:
Loads the servlet class Creates an instance of the servlet class Initializes it by calling the init method
-
service()
This method is only called after the servlet’s init() method has completed successfully.
The Container calls the service() method to handle requests coming from the client, interprets the HTTP request type (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) and calls doGet, doPost, doPut, doDelete, etc. methods as appropriate
- destroy() Called by the Servlet Container to take the Servlet out of service.
Example Servlet Code
https://github.com/eugenp/tutorials/tree/master/javax-servlets/src/main/java/com/baeldung
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-xml-vs-java-config (https://github.com/eugenp/tutorials/tree/master/spring-mvc-java)
https://www.baeldung.com/register-servlet
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/4.3.12.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#spring-web
DispatcherServlet (get Bean and init all resolver and handler with bean)
extend FrameworkServlet (Set WebApplicationContext and set context attribute)
extend HttpServletBean
extend HttpServlet
If run in intellij, it will default start a embbed tomcat. And if spring boot found mvc in dependency then it will load dispatcherServelt.
Embeded Spring dispatherServlet was lazy initialized. Only when call the url, then it will initialized it.
Why WebapplicationInitializer can not be loaded -> must use local tomcat server spring-projects/spring-boot#522
Set local tomcat server https://www.mkyong.com/intellij/intellij-idea-run-debug-web-application-on-tomcat/ https://tomcat.apache.org/download-80.cgi (download tomcat) https://www.baeldung.com/register-servlet (Register Servlet by WebApplicationInitializer)
Use ServletContextInitializer as configuration component to add custom Servlet (Work with JSP Web) https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15385596/how-are-servlet-url-mappings-in-web-xml-used https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20915528/how-can-i-register-a-secondary-servlet-with-spring-boot
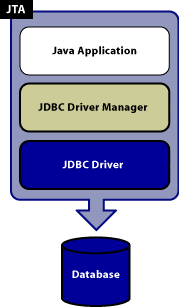
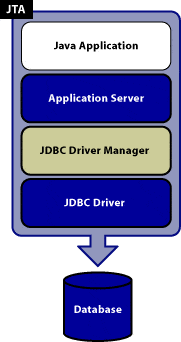
Reference: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/jdbc/basics/transactions.html
The Java Transaction API allows applications to perform distributed transactions, that is, transactions that access and update data on two or more networked computer resources.
A transaction defines a logical unit of work that either completely succeeds or produces no result at all.
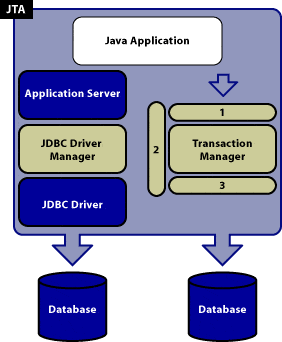
Reference: https://www.progress.com/tutorials/jdbc/understanding-jta
1 - UserTransaction, 2 - Transaction Manager, 3 - XAResource
Two-Phase Commit Protocol.
In the first phase, the transaction manager polls all of the resource managers (RDBMSs) involved in the distributed transaction to see if each one is ready to commit. If a resource manager cannot commit, it responds negatively and rolls back its particular part of the transaction so that data is not altered.
In the second phase, the transaction manager determines if any of the resource managers have responded negatively, and, if so, rolls back the whole transaction. If there are no negative responses, the translation manager commits the whole transaction, and returns the results to the application.
Related technologies - JDBC, Hibernate
Wiki: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_Persistence_API
In 2019 renamed to Jakarta Persistence, is a Java application programming interface specification that describes the management of relational data in applications using Java Platform, Standard Edition and Java Platform, Enterprise Edition/Jakarta EE.
Entities - A persistence entity is a lightweight Java class whose state is typically persisted to a table in a relational database.
Related technologies - Enterprise JavaBeans(EJB), Java Data Objects(JDO), Hibernate, Spring Data JPA
Reference
Back ground https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37934748/article/details/82774230
Basic Concept: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/spring/spring_transaction_management.htm
Official wiki: https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/4.2.x/spring-framework-reference/html/transaction.html
transaction propagation: https://blog.csdn.net/dream_broken/article/details/72845928
Spring Transaction API
Problems
- context.xml dependency
Add in dependency in gradle file
compile 'org.springframework:spring-tx:5.0.2.RELEASE'
compile 'org.springframework.data:spring-data-jpa:1.11.1.RELEASE'
-
Set ClassPathXmlApplicationContext Why use /transaction/context.xml: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12893760/spring-cannot-find-bean-xml-configuration-file-when-it-does-exist
-
Set h2 database https://www.baeldung.com/spring-testing-separate-data-source https://www.baeldung.com/spring-jpa-test-in-memory-database
-
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
compile 'org.aspectj:aspectjweaver:1.7.4'
org.aspectj.weaver.reflect.ReflectionWorld$ReflectionWorldException https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20226558/spring-transaction-management-cannot-resolve-reference-to-bean-transactionmana