Casting light on shadow cloud deployments. Detect exposure of resources deployed in AWS.
Luminaut is a utility to scope cloud environment exposure for triage. The goal is to quickly identify exposed resources and collect information to start an investigation.
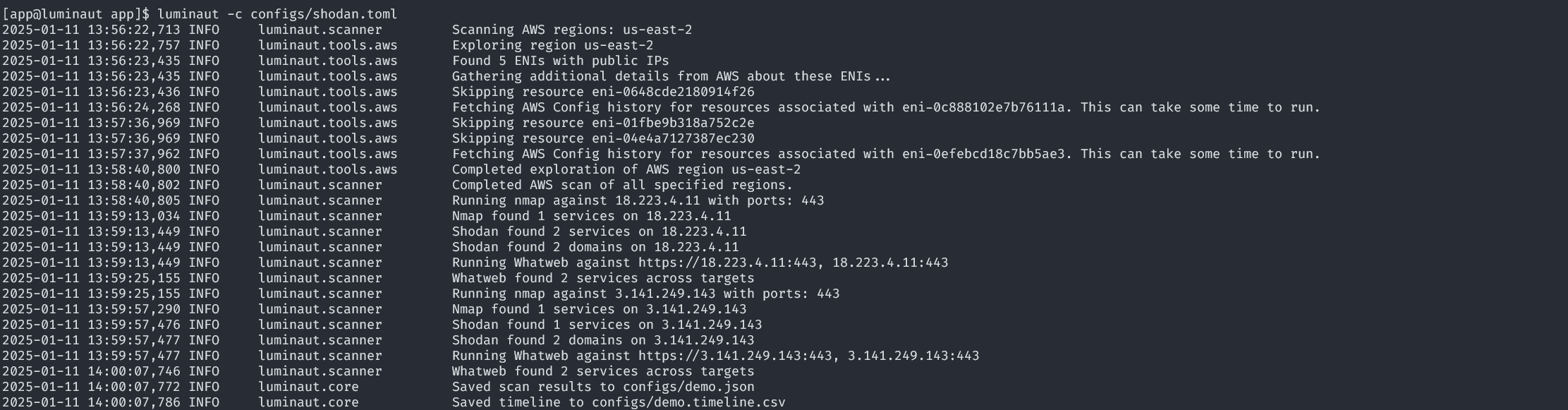
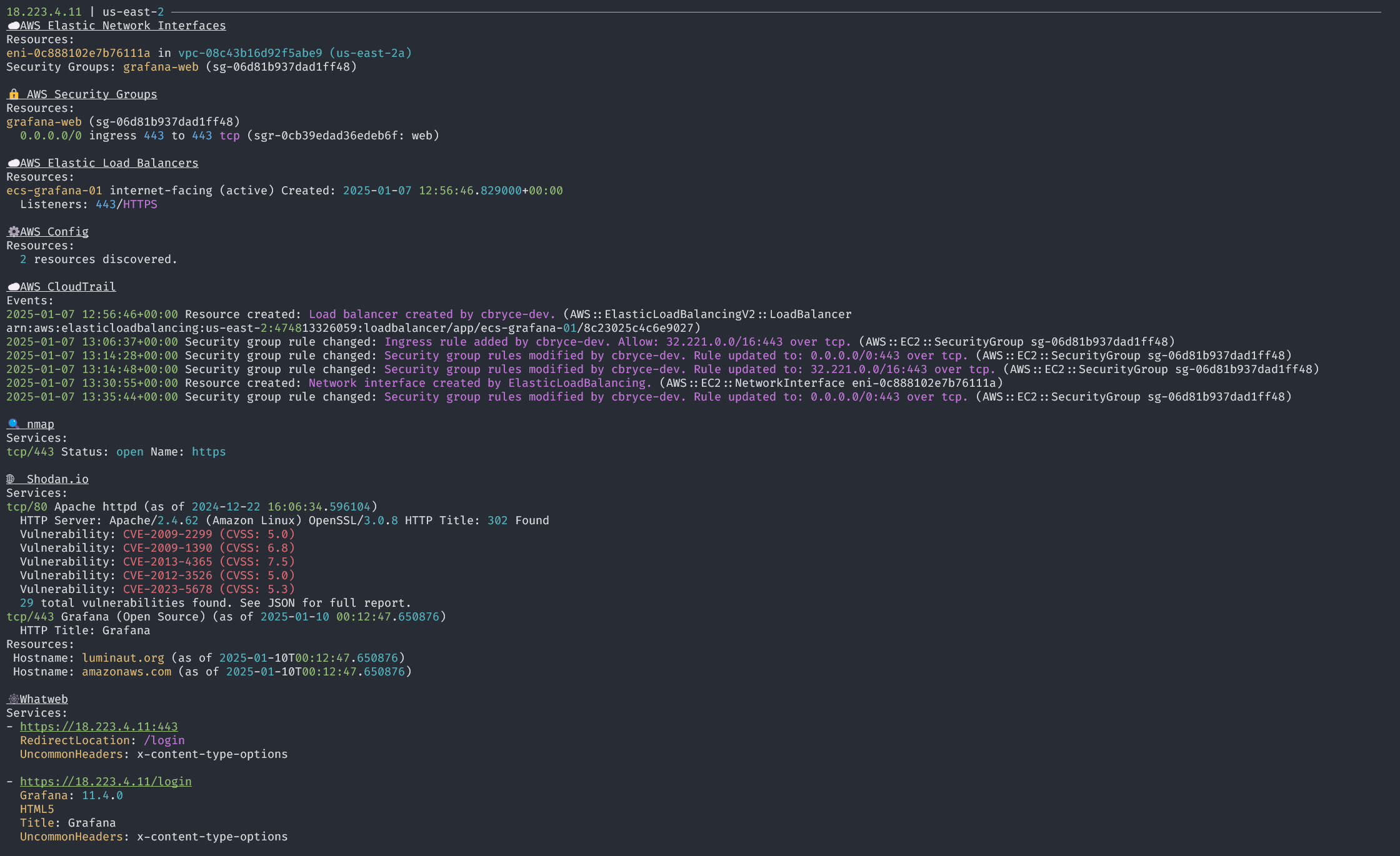
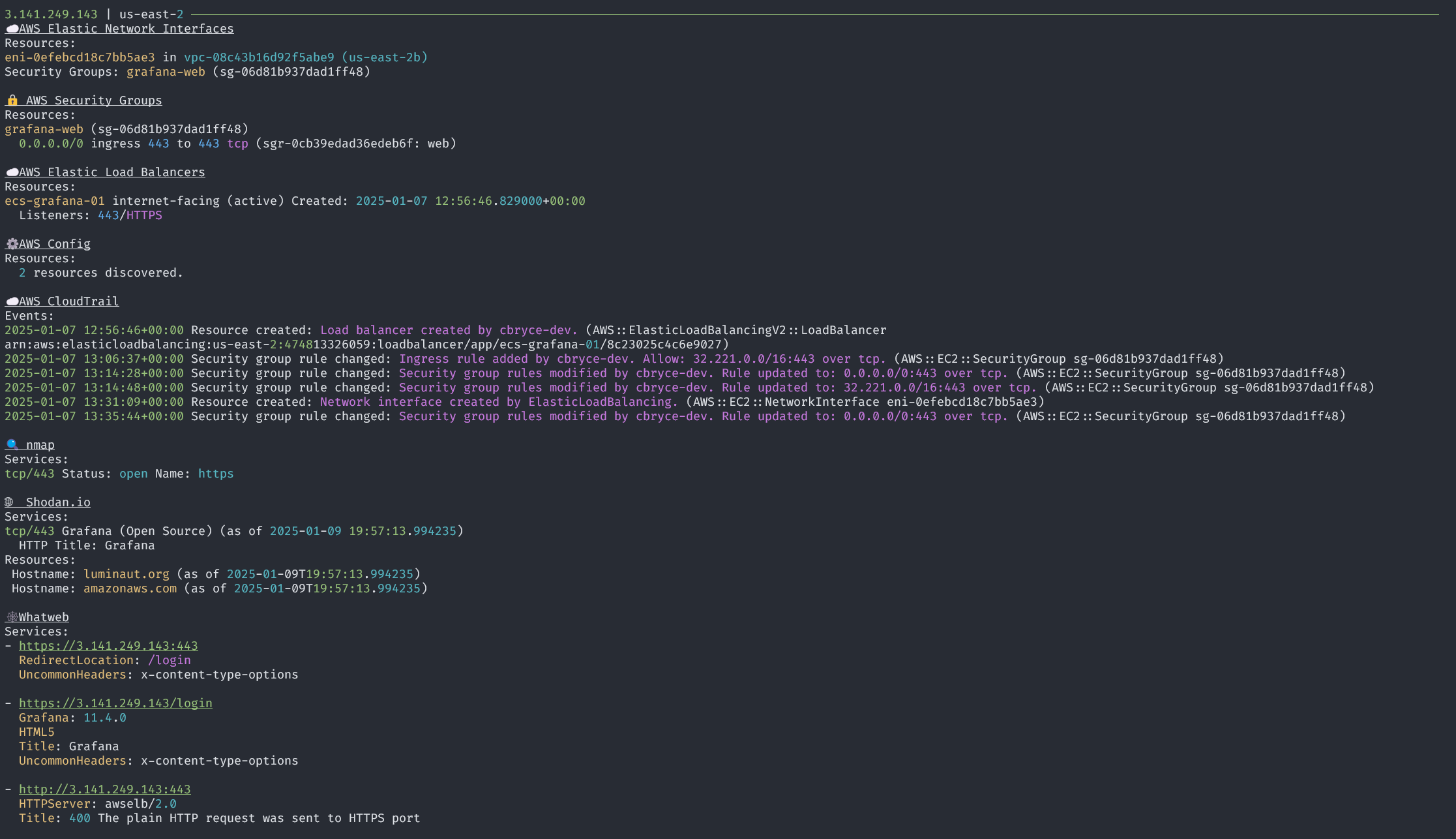
Starting from the public IP addresses of AWS Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs), Luminaut gathers information about the associated EC2 instances, load balancers, security groups, and related events. The framework also includes active scanning tools like nmap and whatweb, to identify services running on exposed ports, and passive sources like Shodan.
By combining cloud configuration data with external sources, Luminaut provides context to guide the next steps of an investigation.
While focused on AWS, Luminaut can be extended to support other cloud providers and services. The framework is designed to be modular, allowing for the addition of new tools and services as needed.
- Enumerate ENIs with public IPs.
- Gather information about associated EC2 instances and Elastic load balancers.
- Identify permissive rules for attached security groups.
- Scan CloudTrail history for related events to answer who, what, and when.
- Supports querying for activity related to discovered ENI, EC2, ELB, and Security Group resources.
- Optionally specify a time frame to limit the scan to a specific time period.
- Query AWS Config for resource configuration changes over time.
- Supports scanning AWS Config history for the discovered ENI and EC2 Instance associated with the ENI.
- Optionally specify a time frame to limit the scan to a specific time period.
- Skip scanning and reporting on resources based on the resource id or tag values
- Supports skipping based on the resource id of the ENI.
- nmap to scan common ports and services against identified IP addresses.
- nmap will only scan ports associated with permissive security group rules or a load balancer listener.
- whatweb to identify services running on ports associated with exposed security group ports.
- whatweb will only scan ports associated with permissive security group rules or a load balancer listener.
- shodan to gather information about exposed services and vulnerabilities.
- Console output with rich formatting, displaying key information.
- HTML capture of console output to preserve prior executions.
- CSV Timeline of events from CloudTrail and other sources.
- JSON lines output with full event information for parsing and integration with other tools.
Luminaut is available on PyPI and can be installed with pip:
pip install luminautYou can also download a release artifact from the GitHub releases page and install it with pip.
Once installed, you can run luminaut from the command line.
luminaut --helpNote: Luminaut requires Python 3.11 or later. If you would like to leverage nmap or whatweb, you will need to install these tools separately.
The docker image is available on GitHub, you can pull it locally by running:
docker pull ghcr.io/luminaut-org/luminautIf you would like to run it locally with just the name luminaut, you can then run:
docker tag ghcr.io/luminaut-org/luminaut luminaut:latestFor development, clone the repository and run docker build --tag luminaut:latest to build the container.
You can then run the container with:
docker run -it luminaut --helpLuminaut requires access to AWS. The commands in this documentation assumes that your shell is already configured with the necessary AWS credentials. You can confirm your credential configuration by running aws sts get-caller-identity. For additional information on configuring AWS credentials, see the AWS CLI documentation.
No arguments are required to run luminaut. The default is to look for a luminaut.toml file in the same directory
and run available tools to start detecting resources.
The default configuration options are shown in the Configuration section.
Luminaut help is available with the argument --help.
$ luminaut --help
usage: luminaut [-h] [--config CONFIG] [--log LOG] [--verbose]
Luminaut: Casting light on shadow cloud deployments.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--config CONFIG Configuration file. (default: luminaut.toml)
--log LOG Log file. (default: luminaut.log)
--verbose Verbose output in the log file. (default: False)By default, Luminaut will run all available tools. It requires your AWS profile to be configured with the necessary permissions, otherwise the first step of public IP detection on ENIs will fail.
luminautThe AWS Config scanner takes at least 50 seconds to run per resource type. If you would like to disable this, you can do so as shown in the provided configs/disable_aws_config.toml configuration file. You can provide this configuration with -c configs/disable_aws_config.toml.
luminaut -c configs/disable_aws_config.tomlSimilarly, if you'd like to enable Shodan, you will need to specify a configuration file that includes the Shodan API key. See the Configuration section for more information on the configuration file specification.
When running with docker, we need to supply a few arguments:
-itto run the container interactively and display the output in the terminal.-v ~/.aws:/home/app/.awsto mount the AWS credentials from your host machine to the container.-e AWS_PROFILE=profile-nameto set the AWS profile to use in the container. Replaceprofile-namewith the name of your AWS profile.-v $(pwd)/configs:/app/configsto mount the configuration file from your host machine to the container.luminautto select the luminaut container.--helpto display the help message, though replace this with your desired arguments (ie-c disable_aws_config.toml).
Note that saved files, such as the log file and JSON reports, will be saved within the container. You may want to mount another volume to save the report files.
Example commands for...
Bash, zsh, and similar terminals:
docker run -it -v ~/.aws:/home/app/.aws -e AWS_PROFILE=profile-name -v $(pwd)/configs:/app/configs luminaut --helpPowershell:
docker run -it -v $env:USERPROFILE\.aws:/home/app/.aws -e AWS_PROFILE=profile-name -v ${PWD}\configs:/app/configs luminaut --helpLuminaut uses a configuration file to define the tools and services to use. The default configuration will run with all tools enabled, though during runtime any tool not found will be skipped. The default reporting uses console output with JSON reporting disabled.
The configuration files are merged with the default configuration, meaning that you can omit any default values from your configuration file.
The configuration file is a TOML file with the following structure and defaults:
[report]
console = true # Rich STDOUT console output
html = false # Save the console output to an HTML file. Disabled by default.
html_file = "luminaut.html" # Path is required if html is true
json = false # JSON lines output, written to STDOUT. Disabled by default.
json_file = "luminaut.json" # JSON lines output, written to a file. If omitted will write to stdout
timeline = false # Timeline output, written to a CSV file. Disabled by default.
timeline_file = "luminaut_timeline.csv" # Path is required if timeline is true
[tool.aws]
enabled = true # Enable the AWS tool, requires the configuration of AWS credentials.
# aws_regions = ["us-east-1"] # The AWS regions to scan. Defaults to the region set in your AWS profile if none is supplied.
[tool.aws.config]
enabled = false # Enables the scanning of AWS config. This can take a long time to run, as it scans all resource history. Disabled by default.
# The below dates must be specified as offset aware timestamps in RFC-3339 format, per https://toml.io/en/v1.0.0#offset-date-time.
# You can specify either the start, end, both, or None to influence the time period of the scan as desired.
# start_time = 2025-01-01T00:00:00Z # The start time for the AWS Config scan. Defaults to no start time
# end_time = 2025-01-02T00:00:00Z # The end time for the AWS Config scan. Defaults to no end time
[tool.aws.cloudtrail]
enabled = true # Enables the collection of CloudTrail events related to discovered resources.
# The below dates must be specified as offset aware timestamps in RFC-3339 format, per https://toml.io/en/v1.0.0#offset-date-time
# You can specify either the start, end, both, or None to influence the time period of the scan as desired.
# start_time = 2025-01-01T00:00:00Z # The start time for the AWS Config scan. Defaults to no start time
# end_time = 2025-01-02T00:00:00Z # The end time for the AWS Config scan. Defaults to no end time
[[tool.aws.allowed_resources]]
# This configuration allows you to skip resources based on their type, ID, or tags.
# If an `id` is provided, the associated `type` is also required. Tags may be provided independently of the id and resource type.
# These settings only support skipping ENIs at the moment and applies across all scanned regions.
type = "AWS::EC2::NetworkInterface" # The resource type, as specified by AWS
id = "eni-1234567890abcdef0" # The resource ID
# Skip resources that match any of the specified tags. The key and value are case-sensitive.
# This is applied before, and separately from, the checks of a type and id. This is also applied across all scanned regions.
tags = { "luminaut" = "ignore", "reviewed" = "true" }
[tool.nmap]
enabled = true # Enable the nmap tool, requires the nmap utility installed and on the system path. Enabled by default but will not run if nmap is not found on the path.
[tool.shodan]
enabled = true # Enable the shodan tool, requires the shodan API key to be set in the configuration. Enabled by default, but will not run without an API key.
api_key = "" # Shodan API key. If this is populated, treat the configuration file as a secret.
[tool.whatweb]
enabled = true # Enable the whatweb tool, requires the whatweb utility installed and on the system path. Enabled by default, but will not run if whatweb is not found on the path.The source of truth for the luminaut configuration is located in luminaut.models.LuminautConfig.
Luminaut requires the following minimum permissions to run:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "LuminautReadResourcePermissions",
"Action": [
"cloudtrail:LookupEvents",
"config:GetResourceConfigHistory",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroupRules",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListeners",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}If you would like to contribute to Luminaut, please follow the guidelines in the CONTRIBUTING.md file.