I have started from May 8th in this Challenge. And this repository contains my solutions to the challenge. Only the exact solution. If you want to improve the solutions, Please open a Issue first.
Check If It Is a Straight Line :
You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
Example :
Input: coordinates = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]]
Output: true
Input: coordinates = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]]
Output: false
Constraints :
2 <= coordinates.length <= 1000coordinates[i].length == 2-10^4 <= coordinates[i][0], coordinates[i][1] <= 10^4- coordinates contains no duplicate point.
Valid Perfect Square :
Given a positive integer num, write a function which returns True if num is a perfect square else False.
Note: Do not use any built-in library function such as
sqrt.
Example :
Input: 16
Output: true
Input: 14
Output: false
Find the Town Judge :
In a town, there are N people labelled from 1 to N. There is a rumor that one of these people is secretly the town judge.
If the town judge exists, then: 1.The town judge trusts nobody. 2.Everybody (except for the town judge) trusts the town judge. 3.There is exactly one person that satisfies properties 1 and 2. 4.You are given trust, an array of pairs trust[i] = [a, b] representing that the person labelled a trusts the person labelled b.
If the town judge exists and can be identified, return the label of the town judge. Otherwise, return -1.
Example :
Input: N = 2, trust = [[1,2]]
Output: 2
Input: N = 3, trust = [[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: 3
Input: N = 3, trust = [[1,3],[2,3],[3,1]]
Output: -1
Input: N = 3, trust = [[1,2],[2,3]]
Output: -1
Input: N = 4, trust = [[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[4,3]]
Output: 3
Constraints :
1 <= N <= 1000trust.length <= 10000trust[i]are all differenttrust[i][0] != trust[i][1]1 <= trust[i][0], trust[i][1] <= N
Flood Fill :
An
imageis represented by a 2-D array of integers, each integer representing the pixel value of the image (from 0 to 65535).
Given a coordinate
(sr, sc)representing the starting pixel (row and column) of the flood fill, and a pixel valuenewColor, "flood fill" the image.
To perform a "flood fill", consider the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to the starting pixel of the same color as the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to those pixels (also with the same color as the starting pixel), and so on. Replace the color of all of the aforementioned pixels with the newColor.
At the end, return the modified image.
Example :
Input:
image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]] sr = 1, sc = 1, newColor = 2
Output:
[[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]]
Explanation:
From the center of the image (with position (sr, sc) = (1, 1)), all pixels connected
by a path of the same color as the starting pixel are colored with the new color.
Note the bottom corner is not colored 2, because it is not 4-directionally connected
to the starting pixel.
Constraints :
- The length of
imageandimage[0]will be in the range[1, 50]. - The given starting pixel will satisfy
0 <= sr < image.length and 0 <= sc < image[0].length. - The value of each color in
image[i][j]andnewColorwill be an integer in[0, 65535].
Check If It Is a Straight Line :
You are given a sorted array consisting of only integers where every element appears exactly twice, except for one element which appears exactly once. Find this single element that appears only once.
Example :
Input: [1,1,2,3,3,4,4,8,8]
Output: 2
Input: [3,3,7,7,10,11,11]
Output: 10
Constraints :
- Your solution should run in
O(log n) timeandO(1) space.
Remove K smallest :
Given a non-negative integer num represented as a string, remove k digits from the number so that the new number is the smallest possible.
Example :
Input: num = "1432219", k = 3
Output: "1219"
Explanation: Remove the three digits 4, 3, and 2 to form the new number 1219 which is the smallest.
Input: num = "10200", k = 1
Output: "200"
Explanation: Remove the leading 1 and the number is 200. Note that the output must not contain leading zeroes.
Input: num = "10", k = 2
Output: "0"
Explanation: Remove all the digits from the number and it is left with nothing which is 0.
Constraints :
- The length of
num is less than 10002and will be≥ k. - The given num does not contain any leading zero.
Implement Trie (Prefix Tree) :
Implement a trie with
insert,search, andstartsWithmethods.
Example :
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // returns true
trie.search("app"); // returns false
trie.startsWith("app"); // returns true
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // returns true
Constraints :
- You may assume that all inputs are consist of lowercase letters
a-z. - All inputs are guaranteed to be non-empty strings.
Help : https://medium.com/@saurav.agg19/implement-trie-prefix-tree-692560ea448a
Maximum Sum Circular Subarray :
Given a circular array C of integers represented by
A, find the maximum possible sum of a non-empty subarray of C.
Here, a circular array means the end of the array connects to the beginning of the array. (Formally,
C[i] = A[i]when0 <= i < A.length, andC[i+A.length] = C[i]wheni >= 0.)
Also, a subarray may only include each element of the fixed buffer A at most once. (Formally, for a subarray
C[i], C[i+1], ..., C[j],there does not existi <= k1, k2 <= jwithk1 % A.length = k2 % A.length.)
Examples :
Input: [1,-2,3,-2]
Output: 3
Explanation: Subarray [3] has maximum sum 3
Input: [5,-3,5]
Output: 10
Explanation: Subarray [5,5] has maximum sum 5 + 5 = 10
Input: [-2,-3,-1]
Output: -1
Explanation: Subarray [-1] has maximum sum -1
Input: [3,-2,2,-3]
Output: 3
Explanation: Subarray [3] and [3,-2,2] both have maximum sum 3
Input: [3,-1,2,-1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Subarray [2,-1,3] has maximum sum 2 + (-1) + 3 = 4
Constraints :
-30000 <= A[i] <= 300001 <= A.length <= 30000
Odd Even Linked List :
Given a singly linked list, group all odd nodes together followed by the even nodes. Please note here we are talking about the node number and not the value in the nodes.
You should try to do it in place. The program should run in
O(1)space complexity andO(nodes)time complexity.
Example :
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
Input: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
Output: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
Constraints :
- The relative order inside both the even and odd groups should remain as it was in the input.
- The first node is considered odd, the second node even and so on.
Find All Anagrams in a String :
Given a string s and a non-empty string p, find all the start indices of p's anagrams in s.
Strings consists of lowercase English letters only and the length of both strings s and p will not be larger than 20,100.
The order of output does not matter.
Example :
Input: s: "cbaebabacd" p: "abc"
Output: [0, 6]
Explanation: The substring with start index = 0 is "cba", which is an anagram of "abc". The substring with start index = 6 is "bac", which is an anagram of "abc".
Input: s: "abab" p: "ab"
Output: [0, 1, 2]
Explanation: The substring with start index = 0 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab". The substring with start index = 1 is "ba", which is an anagram of "ab". The substring with start index = 2 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
Permutation in String :
Given two strings s1 and s2, write a function to return true if s2 contains the permutation of s1. In other words, one of the first string's permutations is the substring of the second string.
Example :
Input: s1 = "ab" s2 = "eidbaooo"
Output: True
Explanation: s2 contains one permutation of s1 ("ba").
Input:s1= "ab" s2 = "eidboaoo"
Output: False
Constraints :
- The input strings only contain lower case letters.
- The length of both given strings is in range [1, 10,000].
Online Stock Span :
Write a class
StockSpannerwhich collects daily price quotes for some stock, and returns the span of that stock's price for the current day.
The span of the stock's price today is defined as the maximum number of consecutive days (starting from today and going backwards) for which the price of the stock was less than or equal to today's price.
For example, if the price of a stock over the next 7 days were
[100, 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 85], then the stock spans would be[1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 6].
Example :
Input: ["StockSpanner","next","next","next","next","next","next","next"], [[],[100],[80],[60],[70],[60],[75],[85]]
Output: [null,1,1,1,2,1,4,6]
Explanation: First, S = StockSpanner() is initialized. Then: S.next(100) is called and returns 1, S.next(80) is called and returns 1, S.next(60) is called and returns 1, S.next(70) is called and returns 2, S.next(60) is called and returns 1, S.next(75) is called and returns 4, S.next(85) is called and returns 6.
Note that (for example) S.next(75) returned 4, because the last 4 prices (including today's price of 75) were less than or equal to today's price.
Constraints :
- Calls to
StockSpanner.next(int price)will have1 <= price <= 10^5. - There will be at most
10000calls to `StockSpanner.next per test case. - There will be at most
150000calls toStockSpanner.nextacross all test cases. - The total time limit for this problem has been reduced by 75% for C++, and 50% for all other languages.
Kth Smallest Element in a BST :
Given a binary search tree, write a function
kthSmallestto find the kth smallest element in it.
Example :
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
3
/ \
1 4
\
2
Output: 1
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
/
1
Output: 3
Constraints :
- The number of elements of the BST is between
1to10^4. You may assumekis always valid,1 ≤ k ≤ BST's total elements.
Count Square Submatrices with All Ones :
Given a
m * nmatrix of ones and zeros, return how many square submatrices have all ones.
Example :
Input: matrix =
[
[0,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1],
[0,1,1,1]
]
Output: 15
Explanation:
There are 10 squares of side 1.
There are 4 squares of side 2.
There is 1 square of side 3.
Total number of squares = 10 + 4 + 1 = 15.
Input: matrix =
[
[1,0,1],
[1,1,0],
[1,1,0]
]
Output: 7
Explanation:
There are 6 squares of side 1.
There is 1 square of side 2.
Total number of squares = 6 + 1 = 7.
Constraints :
1 <= arr.length <= 3001 <= arr[0].length <= 3000 <= arr[i][j] <= 1
Sort Characters By Frequency :
Given a string, sort it in decreasing order based on the frequency of characters.
Example :
Input:
"tree"
Output:
"eert"
Explanation:
'e' appears twice while 'r' and 't' both appear once.
So 'e' must appear before both 'r' and 't'. Therefore "eetr" is also a valid answer.
Input:
"cccaaa"
Output:
"cccaaa"
Explanation:
Both 'c' and 'a' appear three times, so "aaaccc" is also a valid answer.
Note that "cacaca" is incorrect, as the same characters must be together.
Input:
"Aabb"
Output:
"bbAa"
Explanation:
"bbaA" is also a valid answer, but "Aabb" is incorrect.
Note that 'A' and 'a' are treated as two different characters.
Interval List Intersections :
Given two lists of closed intervals, each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
(Formally, a closed interval
[a, b](witha <= b) denotes the set of real numbersxwitha <= x <= b. The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that is either empty, or can be represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].)
Example :
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Reminder: The inputs and the desired output are lists of Interval objects, and not arrays or lists.
Constraints :
0 <= A.length < 10000 <= B.length < 10000 <= A[i].start, A[i].end, B[i].start, B[i].end < 10^9
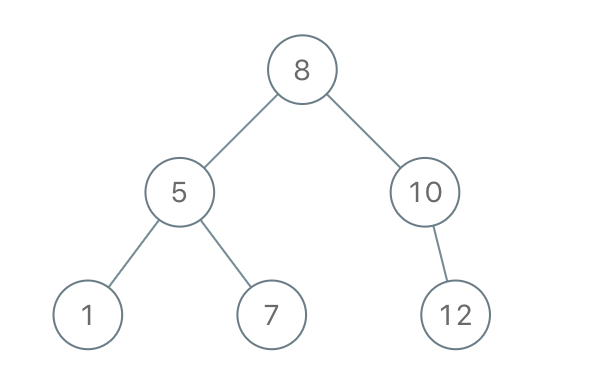
Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal :
Return the root node of a binary search tree that matches the given
preordertraversal.
(Recall that a binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of
node.lefthas a value<node.val, and any descendant ofnode.righthas a value>node.val. Also recall that a preorder traversal displays the value of thenodefirst, then traversesnode.left, then traversesnode.right.)
It's guaranteed that for the given test cases there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements.
Example :
Input: [8,5,1,7,10,12]
Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Constraints :
1 <= preorder.length <= 1001 <= preorder[i] <= 10^8- The values of
preorderare distinct.
Uncrossed Lines :
We write the integers of A and B (in the order they are given) on two separate horizontal lines.
Now, we may draw connecting lines: a straight line connecting two numbers A[i] and B[j] such that:
- A[i] == B[j];
- The line we draw does not intersect any other connecting (non-horizontal) line.
Note that a connecting lines cannot intersect even at the endpoints: each number can only belong to one connecting line.
Return the maximum number of connecting lines we can draw in this way.
Example :
Input: A = [1,4,2], B = [1,2,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: We can draw 2 uncrossed lines as in the diagram.
We cannot draw 3 uncrossed lines, because the line from A[1]=4 to B[2]=4 will intersect the line from A[2]=2 to B[1]=2.
Input: A = [2,5,1,2,5], B = [10,5,2,1,5,2]
Output: 3
Input: A = [1,3,7,1,7,5], B = [1,9,2,5,1]
Output: 2
Constraints :
1 <= A.length <= 5001 <= B.length <= 5001 <= A[i], B[i] <= 2000
Contiguous Array :
Given a binary array, find the maximum length of a contiguous subarray with equal number of 0 and 1.
Example :
Input: [0,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: [0, 1] is the longest contiguous subarray with equal number of 0 and 1.
Input: [0,1,0]
Output: 2
Explanation: [0, 1] (or [1, 0]) is a longest contiguous subarray with equal number of 0 and 1.
Constraints :
- The length of the given binary array will not exceed 50,000.
Possible Bipartition :
Given a set of
Npeople (numbered1, 2, ..., N), we would like to split everyone into two groups of any size.
Each person may dislike some other people, and they should not go into the same group.
Formally, if
dislikes[i] = [a, b], it means it is not allowed to put the people numbered a and b into the same group.
Return
trueif and only if it is possible to split everyone into two groups in this way.
Example :
Input: N = 4, dislikes = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,4]]
Output: true
Explanation: group1 [1,4], group2 [2,3]
Input: N = 3, dislikes = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: false
Input: N = 5, dislikes = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[1,5]]
Output: false
Constraints :
1 <= N <= 20000 <= dislikes.length <= 10000dislikes[i].length == 21 <= dislikes[i][j] <= Ndislikes[i][0] < dislikes[i][1]- There does not exist
i != jfor whichdislikes[i] == dislikes[j].
Counting Bits :
Given a non negative integer number
num. For every numbersiin the range0 ≤ i ≤ numcalculate the number of 1's in their binary representation and return them as an array.
Example :
Input: 2
Output: [0,1,1]
Input: 5
Output: [0,1,1,2,1,2]
Constraints :
- It is very easy to come up with a solution with run time O(n*sizeof(integer)). But can you do it in linear time O(n) /possibly in a single pass?
- Space complexity should be O(n).
- Can you do it like a boss? Do it without using any builtin function like __builtin_popcount in c++ or in any other language.
Course Schedule :
There are a total of
numCoursescourses you have to take, labeled from0tonumCourses-1.
Some courses may have prerequisites, for example to take course 0 you have to first take course 1, which is expressed as a pair:
[0,1]
Given the total number of courses and a list of prerequisite pairs, is it possible for you to finish all courses?
Example :
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]]
Output: true
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: false
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should
also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
Constraints :
- The input prerequisites is a graph represented by a list of edges, not adjacency matrices.
- You may assume that there are no duplicate edges in the input prerequisites.
1 <= numCourses <= 10^5
K Closest Points to Origin :
We have a list of
pointson the plane. Find theKclosest points to the origin(0, 0).
(Here, the distance between two points on a plane is the Euclidean distance.)
You may return the answer in any order. The answer is guaranteed to be unique (except for the order that it is in.)
Example :
Input: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], K = 1
Output: [[-2,2]]
Explanation:
The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10).
The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8).
Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin.
We only want the closest K = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]].
Input: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], K = 2
Output: [[3,3],[-2,4]]
(The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted.)
Constraints :
1 <= K <= points.length <= 10000-10000 < points[i][0] < 10000-10000 < points[i][1] < 10000
Edit Distance :
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
Example :
Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
Output: 3
Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
rose -> ros (remove 'e')
Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
Output: 5
Explanation:
intention -> inention (remove 't')
inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
exection -> execution (insert 'u')
If you found this project useful, then please consider giving it a ⭐ on Github and sharing it with your friends via social media.
Microsoft Student Partner, Student, Working for betterment of all, Competitive Coder, YouTuber
If you found this project helpful or you learned something from the source code and want to thank me, consider buying me a cup of ☕