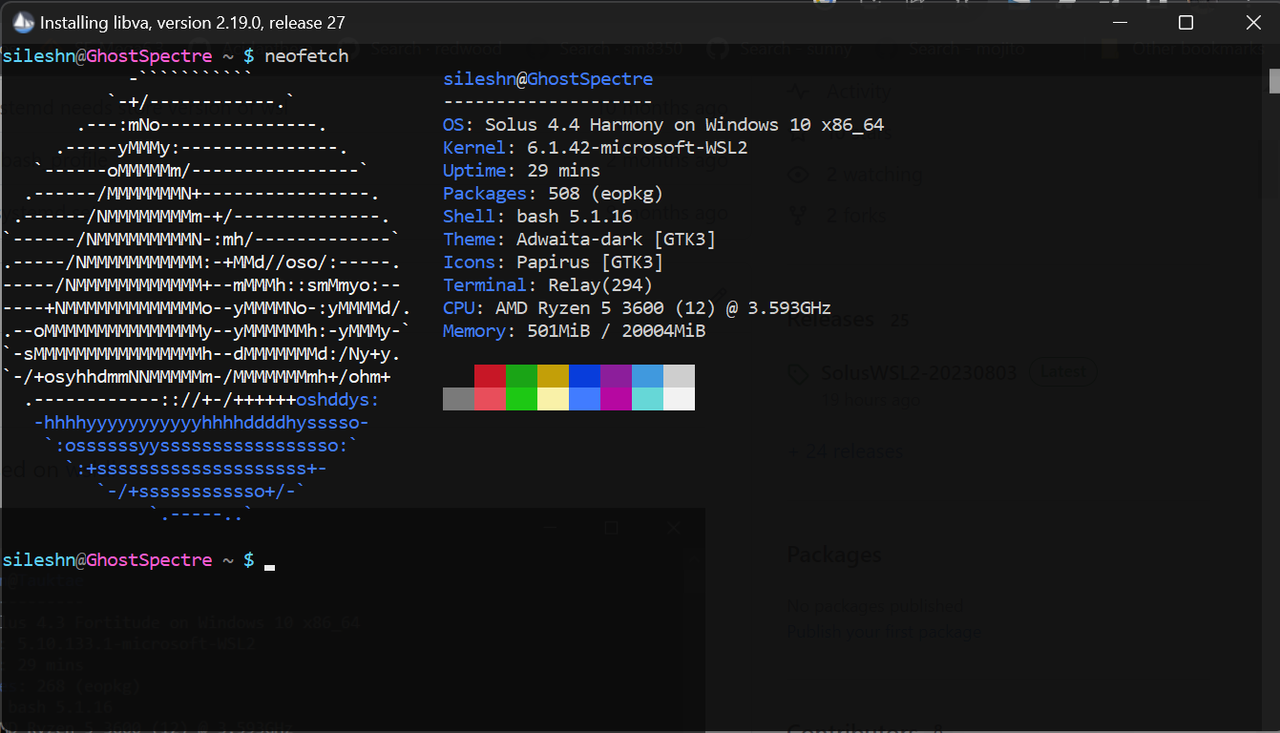
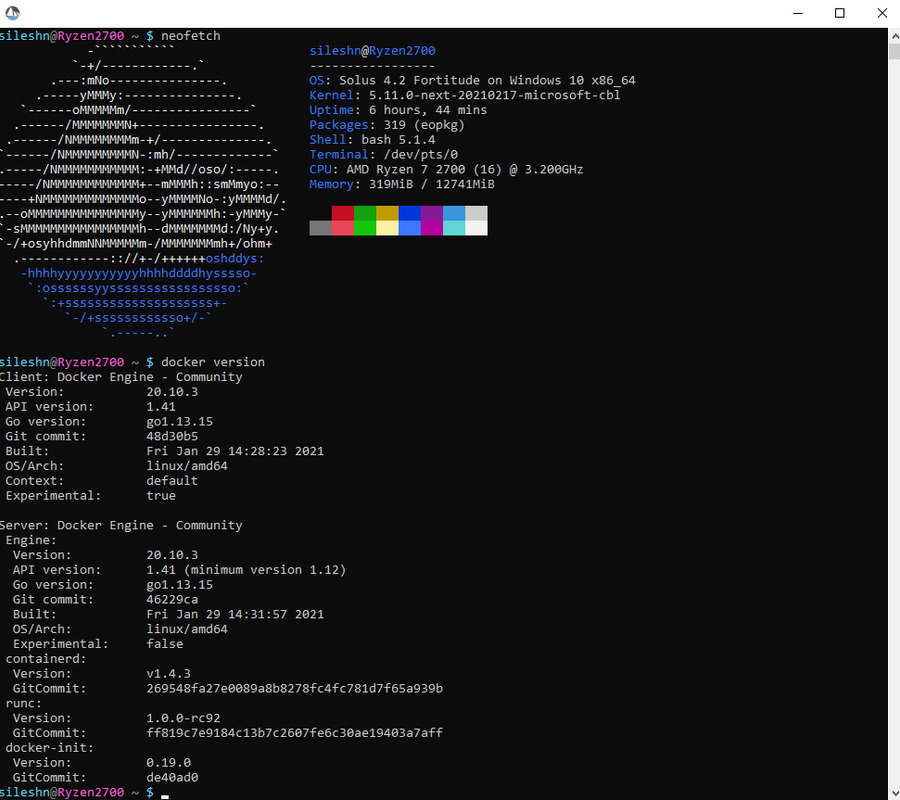
Solus on WSL2 (Windows 10 FCU or later) based on wsldl
SolusWSL2 may display errors while installing packages. This is due to usysconf running post installation triggers. It doesn't affect the normal functioning of SolusWSL2 afaik.
You need a kernel with apparmor support for proper functioning of SolusWSL2. The standard wsl kernel doesn't include apparmor. You can find more information on how to compile and load a custom kernel here.
SolusWSL2 has the following features during the installation stage.
- Increase virtual disk size from the default 256GB
- Create a new user and set the user as default
- Supports systemd natively if you are running wsl v0.67.6 (more details here) and above. You will need the store version of wsl for native systemd support. For previous versions of wsl, systemd is supported using diddledani's one-script-wsl2-systemd. This is done automatically during initial setup.
SolusWSL2 includes a wsl.conf file which only has section headers. Users can use this file to configure the distro to their liking. You can read more about wsl.conf and its configuration settings here.
- For x64 systems: Version 1903 or higher, with Build 18362 or higher.
- For ARM64 systems: Version 2004 or higher, with Build 19041 or higher.
- Builds lower than 18362 do not support WSL 2.
- If you are running Windows 10 version 2004 or higher, you can install all components required to run wsl2 with a single command. This will install ubuntu by default. More details are available here.
wsl.exe --install
- If you are running Windows 10 lower then version 2004, follow the steps below. For more details, check this microsoft document.
- Enable Windows Subsystem for Linux feature.
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
- Enable Virtual Machine feature
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
- Download and install the latest Linux kernel update package from here.
- Make sure all the steps mentioned under "Requirements" are completed.
- Download installer zip
- Extract all files in zip file to same directory
- Set version 2 as default. Note that this step is required only for manual installation.
wsl --set-default-version 2 - Run Solus.exe to extract rootfs and register to WSL
Note: Exe filename is using the instance name to register. If you rename it you can register with a diffrent name and have multiple installs.
Open Solus.exe and run the following commands.
passwd
sed -i 's#\# %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL#%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL#g' /etc/sudoers
useradd -m -G wheel -s /bin/bash <username>
passwd <username>
exit
Execute the command below in a windows cmd terminal from the directory where Solus.exe is installed.
>Solus.exe config --default-user <username>
Usage :
<no args>
- Open a new shell with your default settings.
run <command line>
- Run the given command line in that instance. Inherit current directory.
runp <command line (includes windows path)>
- Run the given command line in that instance after converting its path.
config [setting [value]]
- `--default-user <user>`: Set the default user of this instance to <user>.
- `--default-uid <uid>`: Set the default user uid of this instance to <uid>.
- `--append-path <true|false>`: Switch of Append Windows PATH to $PATH
- `--mount-drive <true|false>`: Switch of Mount drives
- `--default-term <default|wt|flute>`: Set default type of terminal window.
get [setting]
- `--default-uid`: Get the default user uid in this instance.
- `--append-path`: Get true/false status of Append Windows PATH to $PATH.
- `--mount-drive`: Get true/false status of Mount drives.
- `--wsl-version`: Get the version os the WSL (1/2) of this instance.
- `--default-term`: Get Default Terminal type of this instance launcher.
- `--lxguid`: Get WSL GUID key for this instance.
backup [contents]
- `--tar`: Output backup.tar to the current directory.
- `--reg`: Output settings registry file to the current directory.
- `--tgz`: Output backup.tar.tar to the current directory.
- `--vhdx`: Output backup.ext4.vhdx to the current directory.
- `--vhdxgz`: Output backup.ext4.vhdx.gz to the current directory.
clean
- Uninstall that instance.
help
- Print this usage message.
>{InstanceName}.exe
[root@PC-NAME user]#>{InstanceName}.exe run uname -r
4.4.0-43-Microsoft>{InstanceName}.exe runp echo C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe
/mnt/c/Windows/System32/cmd.exe>{InstanceName}.exe config --default-user user
>{InstanceName}.exe
[user@PC-NAME dir]$>{InstanceName}.exe config --default-term wt>Solus.exe clean
export to backup.tar.gz
>Solus.exe backup --tgzexport to backup.ext4.vhdx.gz
>Solus.exe backup --vhdxgzThere are 2 ways to do it.
Rename the backup to rootfs.tar.gz and run Solus.exe
(or)
.tar(.gz)
>Solus.exe install backup.tar.gz.ext4.vhdx(.gz)
>Solus.exe install backup.ext4.vhdx.gzYou may need to run the command below in some circumstances.
>Solus.exe --default-uid 1000Docker, tar, zip, unzip need to be installed.
If you want to build using solus unstable profile, checkout the unstable branch.
git clone git@gitlab.com:sileshn/SolusWSL2.git
cd SolusWSL2
make
Copy the Solus-main.zip file to a safe location and run the command below to clean.
make clean
Install docker binaries. Note that installing docker from solus repos doesn't work as the latest version in solus is 19.03.14. We need 20.10 versions and above.
sudo eopkg it -y wget
wget https://download.docker.com/linux/static/stable/x86_64/docker-20.10.6.tgz
tar xzvf docker-20.10.6.tgz
sudo cp docker/* /usr/bin/
You can now delete the downloaded files if needed.
rm -rf docker
rm docker-20.10.6.tgz
To manage docker as a non-root user, create and add user to docker group.
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Follow this blog post for further setup instructions.