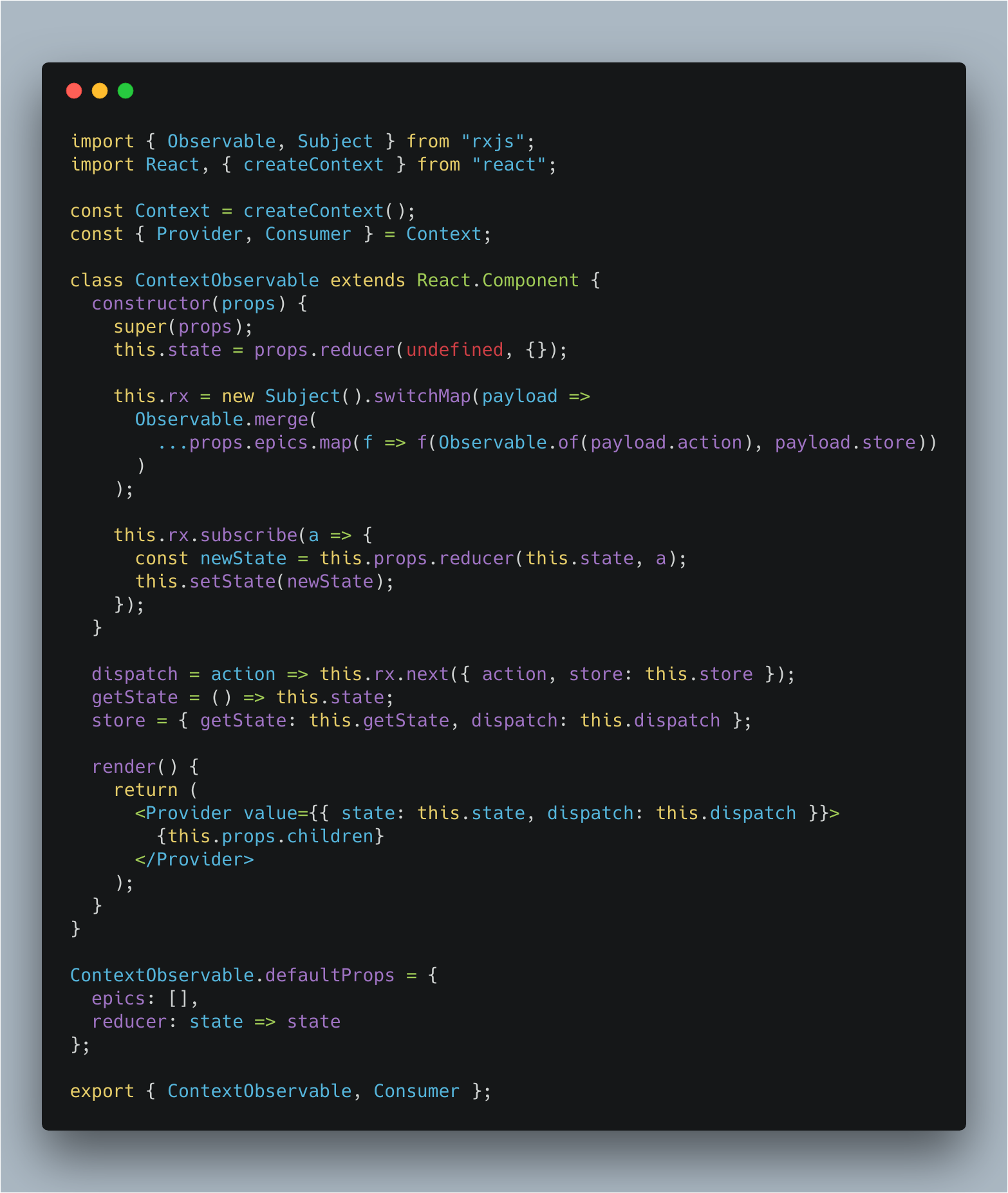
Context-Observable Component manages the state of your React App using new React Context Api following same interfaces of Redux (actions and reducers) and using the same idea behind redux-observable to avoid "side-effect".
- React v16.3 (https://reactjs.org/)
- Rxjs 5 (http://reactivex.io/rxjs)
Via npm
`npm install --save context-observable
Via UMD (to use as jsbin, etc..)
`https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stvkoch/context-observable/master/umd/context-observable.js
git clone git@github.com:stvkoch/context-observable.git
cd context-observable
npm start
As a redux, you will need create reducers and actions.
Context-Observable following same ideia behind redux-observable, so what you will need is create your epics the same way that you already do in redux-observable.
Then you import Context-Observable Component and pass your epics and reducers.
import { ContextObservable } from "context-observable";
import rootEpics as epics from "./epics";
import rootReducers as reducer from "./reducers";
const App = () => (
<ContextObservable {...{ epics, reducer }}>
<Product />
</ContextObservable>
);
import {Consumer} from 'context-observable';
// ... in your render method:
<Consumer>
{({ state, dispatch }) => (
<React.Fragment>
<ul>
{state &&
state.products.map(p => (
<li key={p.id}>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(addProduct(p))}>
{p.name}
</button>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</React.Fragment>
)}
</Consumer>