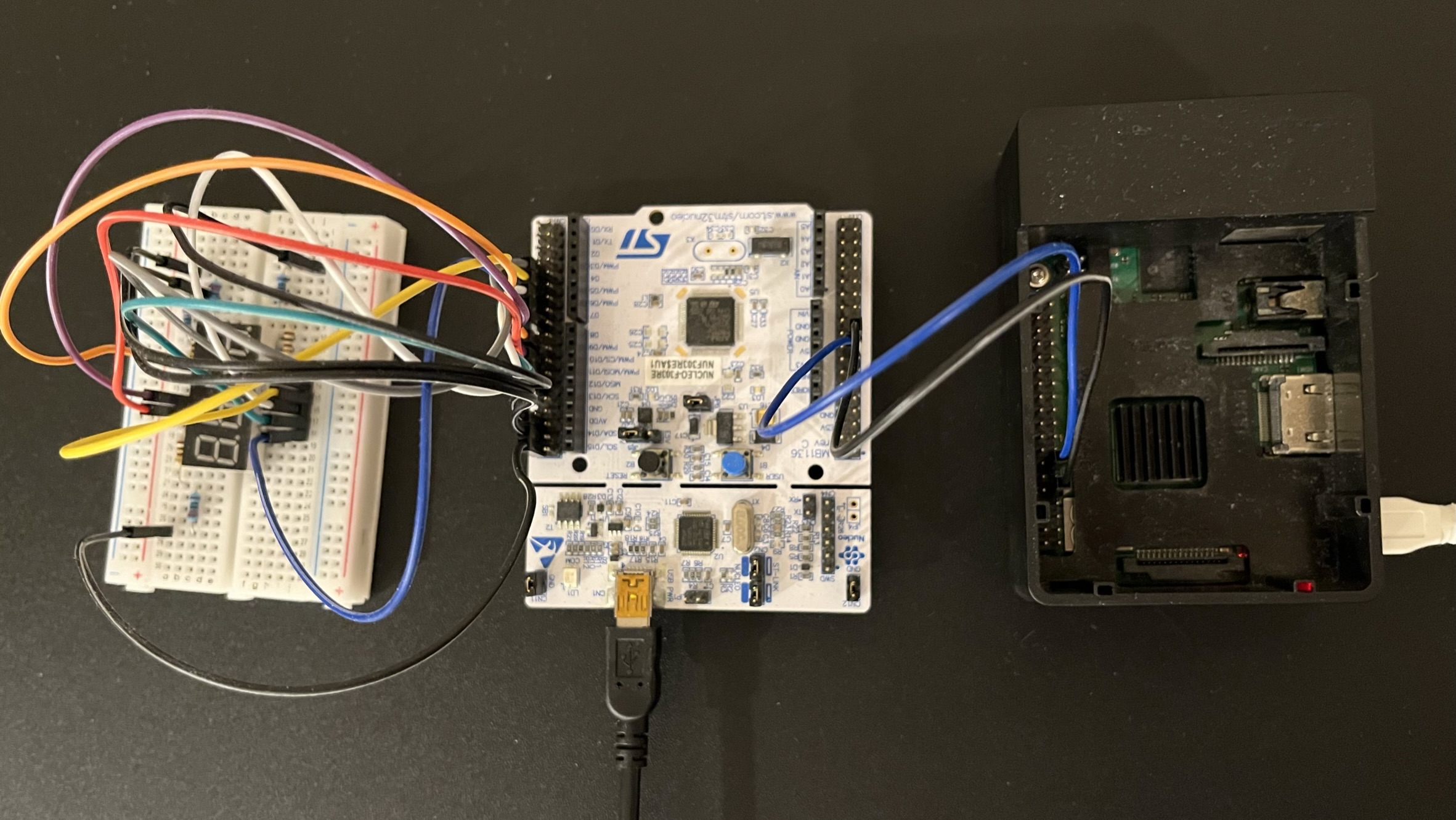
Numerical 7-segment display device driver for Linux. This repository only contains the code for the Raspberry Pi. The RPi only sends the digits and commands via serial to a microcontroller and the mcu just displays the bytes. Although the display can be directly connected to the RPi or use a latch or some shift registers, I just wanted to try bit-banging using kernel timers. The kernel module consists of the upper half which handles user I/O, and the lower half which handles bit transmission via hrtimer. A detailed overview is on my blog.
- kernel headers : the kernel headers are needed to compile a kernel module. The version to download will depend on your (target) kernel version.
- dtc : the RPi uses device tree for hardware enumeration. The
dtccommand will be used to compile the overlay and it should already be installed by default.
Clone the repository, run make to compile the device tree overlay and the kernel module.
This kernel module uses the GPIO pins specified in the fragments in the overlay n7d_overlay.dts.
Therefore, the overlay must be compiled, and put into the /boot/firmware/overlays/ directory for it to be accessible on boot.
To apply the overlay, it must be specified in /boot/config.txt.
For example,
# Compile the overlay
dtc -@ -I dts -O dtb -o $(DT_OVERLAY).dtbo $(DT_OVERLAY).dts
# Place the overlay in the overlays dir
cp $(DT_OVERLAY).dtbo /boot/firmware/overlays/.
# Edit config.txt to include the overlay (specify parameters if needed)
echo "dtoverlay=$(DT_OVERLAY)" >> /boot/config.txt
To install the kernel module, run :
insmod n7d.ko
sudo or some access may be needed due to permission.
modprobe may be used instead of insmod but there are no other dependencies for this module.
The baudrate (default 38400) for the serial communication can be specified during module installation:
insmod n7d.ko n7d_baudrate=19200
Run rmmod n7d to remove the module from the kernel.
GPL